Development of Convenient System for Detecting Yeast Cell Stress, Including That of Amyloid Beta
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
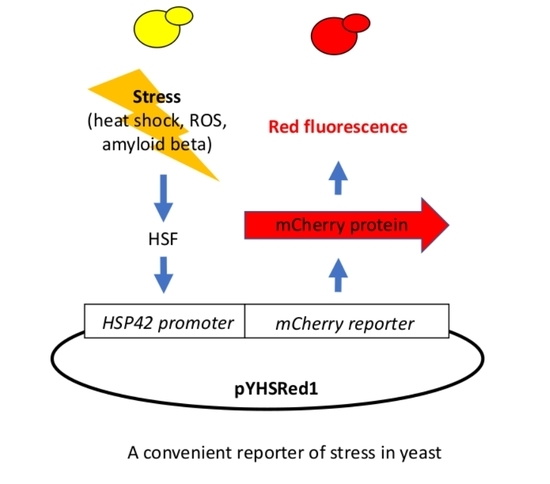
2.1. Construction of the pYHSRed1 Plasmid
2.2. Transformation of Yeast with pYHSRed1 and Basal Expression of mCherry
2.3. Increased mCherry Fluorescence in Cells Exposed to Heat Shock and Copper Sulphate
2.4. Stress Induced by Oligomeric and Fibrillar Aβ42 Measured by mCherry Fluorescence
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. pYHSRed1, Yeast Strain and Transformation
4.2. Yeast Culture Protocol
4.3. Preparation of Aβ42
4.4. Exposure of Yeast Cells to Heat Shock
4.5. Exposure of Yeast Cells to Copper Ions
4.6. Effect of Exposure to Oligomeric and Fibrillar Aβ on Yeast Cells
4.7. Spectrophotometry
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Aβ | Beta-amyloid |
| HSE | Heat shock element |
| HSF | Heat shock factor |
| HSP | Heat shock protein |
| HSR | Heat shock response |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Lindquist, S. The heat-shock proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1988, 22, 631–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, A.L. Chaperone-mediated protein folding. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 425–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.G.; Wisen, S.; Gestwicki, J.E. Heat shock proteins 70 and 90 inhibit early stages of amyloid β-(1-42) aggregation in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33182–33191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, J.S.; Hu, Z.; Thiele, D.J.; Iyer, V.R. Genome-wide analysis of the biology of stress responses through heat shock transcription factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5249–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.R.; Tan, M.S.; Xie, A.M.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Heat shock protein 90 in Alzheimer’s disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisamedtinov, I.; Lindsey, G.G.; Karreman, R.; Orumets, K.; Koplimaa, M.; Kevvai, K.; Paalme, T. The response of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to sudden vs. gradual changes in environmental stress monitored by expression of the stress response protein hsp12p. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, Y.; Lindquist, S. Hsp104 required for induced thermotolerance. Science 1990, 248, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.K.; Bharadwaj, P.R.; Varghese, J.N.; Macreadie, I.G. Alzheimer’s amyloid-β rescues yeast from hydroxide toxicity. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2009, 18, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmar, B.; Greensmith, L. Induction of heat shock proteins for protection against oxidative stress. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Liu, P.C.; Santoro, N.; Thiele, D.J. Conservation of a stress response: Human heat shock transcription factors functionally substitute for yeast hsf. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6466–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C. Heat shock transcription factors: Structure and regulation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995, 11, 441–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumalai, D.; Reddy, G.; Straub, J.E. Role of water in protein aggregation and amyloid polymorphism. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, D.M.; Walsh, D.M.; Ye, C.P.; Diehl, T.; Vasquez, S.; Vassilev, P.M.; Teplow, D.B.; Selkoe, D.J. Protofibrillar intermediates of amyloid β-protein induce acute electrophysiological changes and progressive neurotoxicity in cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8876–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakimura, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Takata, K.; Umeki, M.; Suzuki, S.; Shibagaki, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Nomura, Y.; Smith, M.A.; Gebicke-Haerter, P.J.; et al. Microglial activation and amyloid-β clearance induced by exogenous heat-shock proteins. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.C.; Rosen, K.M.; Pola, R.; Magrane, J. Stress proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Hyperther. 2005, 21, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caine, J.; Sankovich, S.; Antony, H.; Waddington, L.; Macreadie, P.; Varghese, J.; Macreadie, I. Alzheimer’s Aβ fused to green fluorescent protein induces growth stress and a heat shock response. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007, 7, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslbeck, M.; Braun, N.; Stromer, T.; Richter, B.; Model, N.; Weinkauf, S.; Buchner, J. Hsp42 is the general small heat shock protein in the cytosol of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porzoor, A.; Caine, J.M.; Macreadie, I.G. Pretreatment of chemically-synthesized Aβ42 affects its biological activity in yeast. Prion 2014, 8, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, B.K.; Pelham, H.R. Constitutive binding of yeast heat shock factor to DNA in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 5040–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mager, W.H.; De Kruijff, A.J. Stress-induced transcriptional activation. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 506–531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ananthan, J.; Goldberg, A.L.; Voellmy, R. Abnormal proteins serve as eukaryotic stress signals and trigger the activation of heat shock genes. Science 1986, 232, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, S.V.; Howlett, N.G.; Radice, S. Copper toxicity towards Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Dependence on plasma membrane fatty acid composition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3960–3966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, P.; Waddington, L.; Varghese, J.; Macreadie, I.G. A new method to measure cellular toxicity of non-fibrillar and fibrillar Alzheimer’s Aβ using yeast. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 13, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, K.N.; Manelli, A.M.; Stine, W.B., Jr.; Baker, L.K.; Krafft, G.A.; LaDu, M.J. Oligomeric and fibrillar species of amyloid-ß peptides differentially affect neuronal viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32046–32053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, M. Biochemical and biophysical features of both oligomer/fibril and cell membrane in amyloid cytotoxicity. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 4602–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Carson, K.; Rice-Ficht, A.; Good, T. Small heat shock proteins differentially affect Aβ aggregation and toxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, V.; Chauhan, A. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Pathophysiology 2006, 13, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadarajan, S.; Yatin, S.; Aksenova, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide-associated free radical oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 130, 184–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladiwala, A.R.; Litt, J.; Kane, R.S.; Aucoin, D.S.; Smith, S.O.; Ranjan, S.; Davis, J.; Van Nostrand, W.E.; Tessier, P.M. Conformational differences between two amyloid β oligomers of similar size and dissimilar toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24765–24773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porzoor, A.; Macreadie, I. Yeast as a model for studies on abeta aggregation toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease, autophagic responses, and drug screening. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1303, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luu, Y.N.; Macreadie, I. Development of Convenient System for Detecting Yeast Cell Stress, Including That of Amyloid Beta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2136. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijms19072136
Luu YN, Macreadie I. Development of Convenient System for Detecting Yeast Cell Stress, Including That of Amyloid Beta. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2136. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijms19072136
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuu, Yen Nhi, and Ian Macreadie. 2018. "Development of Convenient System for Detecting Yeast Cell Stress, Including That of Amyloid Beta" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2136. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijms19072136