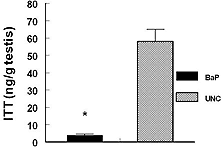
Correction: Archibong, A.E., et al. Effects of Benzo(a)pyrene on Intra-testicular Function in F-344 Rats

Reference
- Archibong, AE; Ramesh, A; Niaz, MS; Brooks, CM; Roberson, SI; Lunstra, DD. Effects of Benzo(a)pyrene on Intra-testicular Function in F-344 Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Archibong, A.E.; Ramesh, A.; Niaz, M.S.; Brooks, C.M.; Roberson, S.I.; Lunstra, D.D. Correction: Archibong, A.E., et al. Effects of Benzo(a)pyrene on Intra-testicular Function in F-344 Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1224-1225. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijerph7031224
Archibong AE, Ramesh A, Niaz MS, Brooks CM, Roberson SI, Lunstra DD. Correction: Archibong, A.E., et al. Effects of Benzo(a)pyrene on Intra-testicular Function in F-344 Rats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2010; 7(3):1224-1225. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijerph7031224
Chicago/Turabian StyleArchibong, Anthony E., Aramandla Ramesh, Mohammad S. Niaz, Cynthia M. Brooks, Shannon I. Roberson, and Donald D. Lunstra. 2010. "Correction: Archibong, A.E., et al. Effects of Benzo(a)pyrene on Intra-testicular Function in F-344 Rats" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 7, no. 3: 1224-1225. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijerph7031224