Anti-Proliferative and Genotoxic Activities of the Helichrysum petiolare Hilliard & B.L. Burtt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Plant Material and Extract Preparation
2.3. Cell Culture Conditions
2.4. Imaging and Analysis
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay and Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Genotoxicity (Micronucleus Assay)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
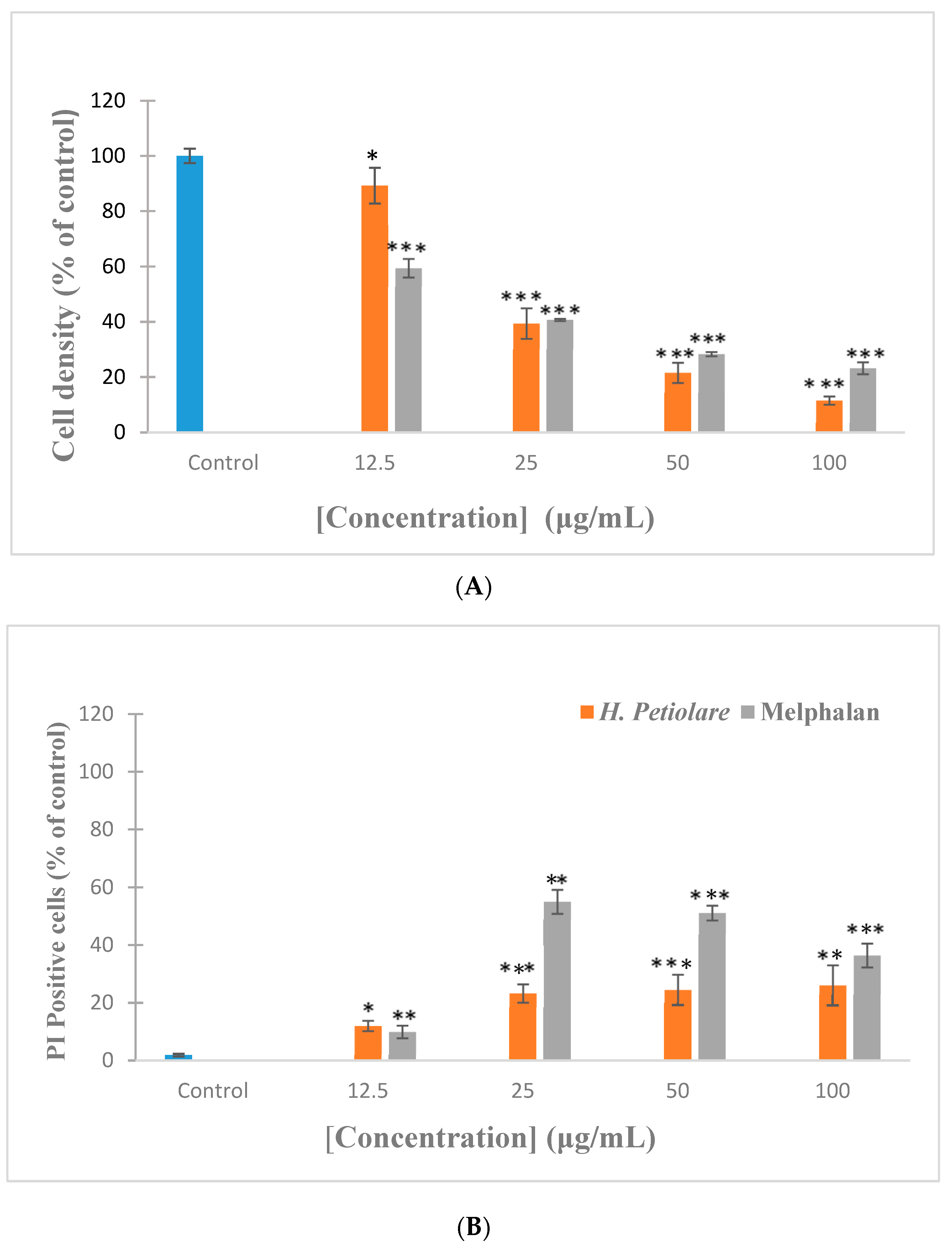
3.1. Cytotoxicity towards B16F10 Melanoma (Hoechst/Propidium Iodide)
3.2. Cytotoxicity towards MeWo Melanoma (Hoechst/PI)
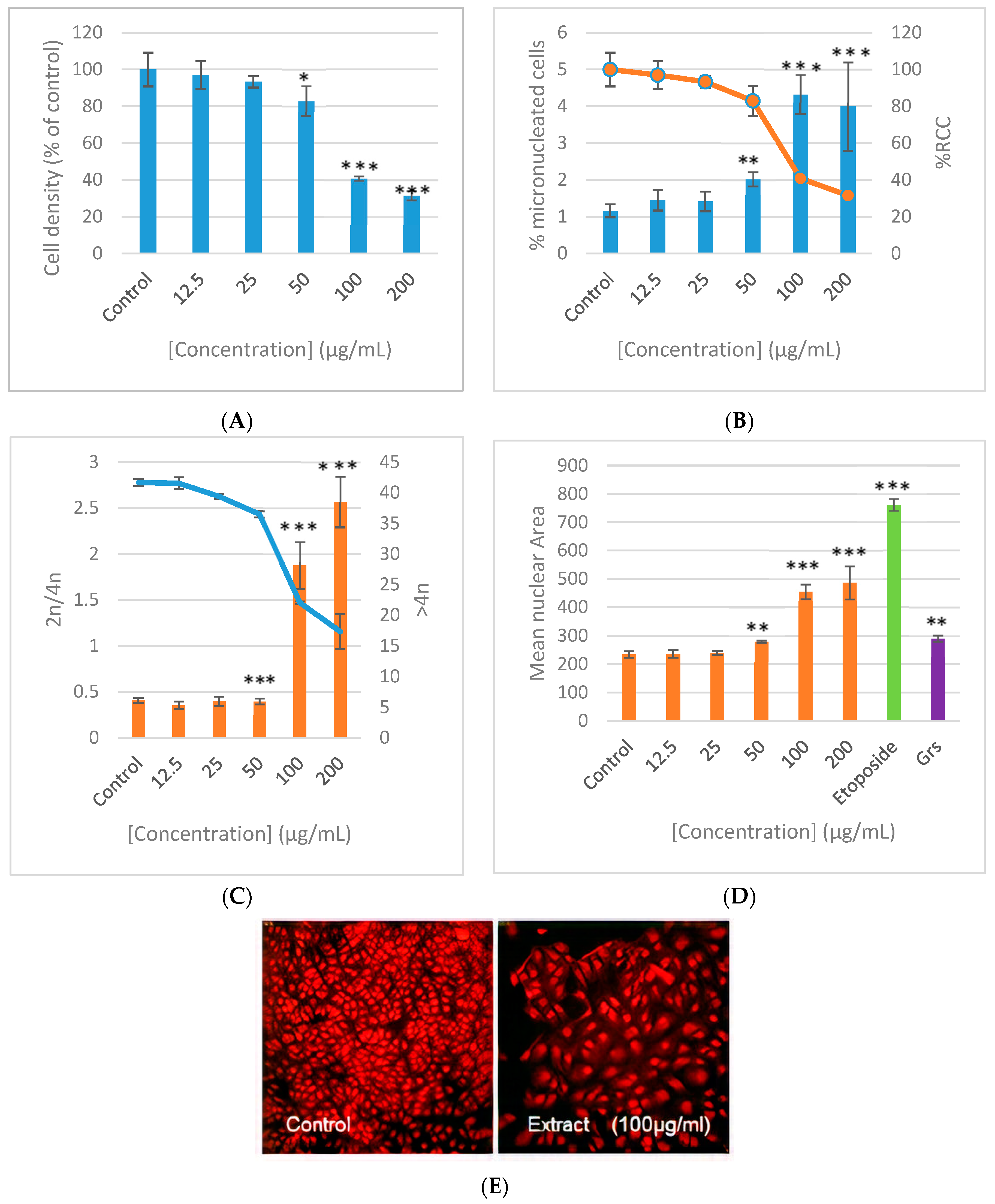
3.3. Cell Cycle Analysis in B16F10 Melanoma (Annexin V/Hoechst)
3.4. Cell Cycle Analysis in MeWo Melanoma (Annexin V/Hoechst)
3.5. Genotoxicity (Micronucleus Assay)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giri, B.; Gomes, A.; Debnath, A.; Saha, A.; Biswas, A.K.; Dasgupta, S.C. Antiproliferative, cytotoxic and apoptogenic activity of Indian toad (Bufo melanostictus, Schneider) skin extract on U937 and K562 cells. Toxicon 2006, 48, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbaveng, A.T.; Kuete, V.; Mapunya, B.M.; Beng, V.P.; Nkengfack, A.E.; Meyer, J.J.M.; Lall, N. Evaluation of four cameroonian medicinal plants for anticancer, antigonorrheal and antireverse transcriptase activities. Environ.Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 32, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, M.A.; Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Li, C.-Y. Cell death–stimulated cell proliferation: A tissue regeneration mechanism usurped by tumors during radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 23, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soura, E.; Chasapi, V.; Stratigos, A.J. Pharmacologic treatment options for advanced epithelial skin cancer. Expert Opin.Pharmacotherl. 2015, 16, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, E.W.; Thareja, S.; Cherpelis, B.B. Oral therapy for non melanoma skin cancer in patients with advanced disease and large tumor burden: A review of the literature with focus on a new generation of targeted therapies. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.F.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Lumbera, W.M.L.; Hwang, S.G. Viscum Album Var Hot Water Extract Mediates Anti-cancer Effects through G1 Phase Cell Cycle Arrest in SK-Hep1 Human Hepatocarcinoma cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 6417–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmaeilbeig, M.; Kouhpayeh, S.A.; Amirghofran, Z. An Investigation of the Growth Inhibitory Capacity of Several Medicinal Plants From Iran on Tumor Cell Lines. Iran. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 8, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijaybabu, K.; Punnagai, K. In-Vitro Anti-Proliferative Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Vanilla Planifolia Leaf Extract Against A431 Human Epidermoid Carcinoma Cells. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2019, 12, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, E.; De Martino, L.; Marandino, A.; Scognamiglio, M.R.; De Feo, V. Chemical Composition and Possible in Vitro Phytotoxic Activity of Helichrsyum italicum (Roth) Don ssp. italicum. Molecules 2011, 16, 7725–7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akaberia, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Azizid, N.; Emamiae, S.A. Everlasting flowers: Phytochemistry and pharmacology of the genus Helichrysum. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 138, 111471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroyi, A. Helicrysum Petiolare Hilland and B.L. Burtt: A review of its medicinal uses, phytochemistry, and biological activities. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2019, 12, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lourens, A.C.U.; Reddy, D.; Baser, K.H.C.; Viljoen, A.M.; Van Vuuren, S. In vitro biological activity and essential oil composition of four indigenous South African Helichrysum species. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 95, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otang-mbeng, W.; Sagbo, I.J. Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry Analysis of the Volatile Compounds from the Ethanol Extracts of Bulbine asphodeloides and Helichrysum petiolare. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2019, 11, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigovica, D.; Savikina, K.; Jankovica, T.; Menkovica, N.; Zdunica, G.; Tatjana, S.; Djuric, Z. Antiradical and Cytotoxic Activity of Different Helichrysum plicatum Flower Extracts. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 819–822. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, L.N.; Lima, T.C.; Amaral, R.G.; Pessoa, C.D.; Filho, M.O.M.; Soares, B.M.; Nascimento, L.G.; Carvalho, A.A.; De Sousa, D.P. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Structurally Correlatedp-Menthane Derivatives. Molecules 2015, 20, 13264–13280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afoulous, S.; Ferhout, H.; Raoelison, E.G.; Valentin, A.; Moukarzel, B.; Couderc, F.; Bouajila, J. Helichrysum gymnocephalum Essential Oil: Chemical Composition and Cytotoxic, Antimalarial and Antioxidant Activities, Attribution of the Activity Origin by Correlations. Molecules 2011, 16, 8273–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neergheen, V.S.; Bahorun, T.; Taylor, E.W.; Jen, L.S.; Aruoma, O.I. Targeting specific cell signaling transduction pathways by dietary and medicinal phytochemicals in cancer chemoprevention. Toxicology 2010, 278, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.R.; Kucuk, O.; Khuri, F.R.; Shin, D.M. Perspectives for cancer prevention with natural compounds. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2712–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alimbetov, D.; Askarova, S.; Umbayev, B.; Davis, T.; Kipling, D. Pharmacological Targeting of Cell Cycle, Apoptotic and Cell Adhesion Signaling Pathways Implicated in Chemoresistance of Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liao, W.; Fan, L.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, A.; Liu, F. Ethanol extract of Ophiorrhiza pumila suppresses liver cancer cell proliferation and migration. . Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Swanepoel, B.; Venables, L.; Olaru, O.T.; Nitulescu, G.M.; van de Venter, M. In Vitro Anti-proliferative Activity and Mechanism of Action of Anemone nemorosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, J.M.; Lopes-rodrigues, V.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Lima, M.J.; Lima, R.T.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Vasconcelos, M.H. An Aqueous Extract of Tuberaria lignosa Inhibits Cell Growth, Alters the Cell Cycle Profile and Induces Apoptosis of NCI-H460 Tumor Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khazaei, S.; Hamid, R.A.; Ramachandran, V.; Esa, N.M.; Pandurangan, A.K.; Danazadeh, F.; Ismail, P. Cytotoxicity and Proapoptotic Effects of Allium atroviolaceum Flower Extract by Modulating Cell Cycle Arrest and Caspase-Dependent and p53-Independent Pathway in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Evid. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, R. Natural flavonoids targeting deregulated cell cycle progression in cancer cells. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK inhibitors: Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busino, L.; Chiesa, M.; Draetta, G.F.; Donzelli, M. Cdc25A phosphatase: Combinatorial phosphorylation, ubiquitylation and proteolysis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konoshima, T.; Konishi, T.; Takasaki, M.; Yamazoe, K.; Tokuda, H. Anti-tumor-promoting activity of the diterpene from Excoecaria agallocha. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 1440–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.H.; Dai, J.; Chen, X.; Yuan, J.Q. Pentacyclic triterpenoids from leaves of Excoecaria agallocha. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, K.P.R.; Durairaj, P.; Thiruvanavukkarasu, P.; Hari, R. Effect of ethanolic extract of Excoecaria agallocha leaves on the cytotoxic activity and cell cycle arrest of human breast cancer cell lines—MCF-7. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2019, 15, 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Imreh, G.; Norberg, H.V.; Imreh, S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Chromosomal breaks during mitotic catastrophe trigger H2AX–ATM–p53-mediated apoptosis. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eroğlu1, E.H.; Hamzaoğlu1, E.; Aksoy, A.; Budak, U.; Özkul, Y. In Vitro Genotoxic Effects of Four Helichrysum Species in Human Lymphocytes Cultures. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sagbo, I.J.; Otang-Mbeng, W. Anti-Proliferative and Genotoxic Activities of the Helichrysum petiolare Hilliard & B.L. Burtt. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 49. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/scipharm88040049
Sagbo IJ, Otang-Mbeng W. Anti-Proliferative and Genotoxic Activities of the Helichrysum petiolare Hilliard & B.L. Burtt. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2020; 88(4):49. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/scipharm88040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleSagbo, Idowu Jonas, and Wilfred Otang-Mbeng. 2020. "Anti-Proliferative and Genotoxic Activities of the Helichrysum petiolare Hilliard & B.L. Burtt" Scientia Pharmaceutica 88, no. 4: 49. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/scipharm88040049




