Journal Description
ChemEngineering
ChemEngineering
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science and technology of chemical engineering, published bimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (General Engineering)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.5 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2022)
Latest Articles
An Experimental Study of Heat Transfer in Pool Boiling to Investigate the Effect of Surface Roughness on Critical Heat Flux
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 44; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020044 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Utilizing pool boiling as a cooling method holds significant importance within power plant industries due to its ability to effectively manage temperature differentials amidst high heat flux conditions. This study delves into the impact of surface modifications on the pool boiling process by
[...] Read more.
Utilizing pool boiling as a cooling method holds significant importance within power plant industries due to its ability to effectively manage temperature differentials amidst high heat flux conditions. This study delves into the impact of surface modifications on the pool boiling process by conducting experiments on four distinct boiling surfaces under various conditions. An experimental setup tailored for this investigation is meticulously designed and implemented. The primary objective is to discern the optimal surface configuration capable of efficiently absorbing maximum heat flux while minimizing temperature differentials. In addition, this study scrutinizes bubble dynamics, pivotal in nucleation processes. Notably, surfaces polished unidirectionally (ROD), exhibiting lower roughness, demonstrate superior performance in critical heat flux (CHF) compared to surfaces with circular roughness (RCD). Moreover, the integration of bubble liquid separation methodology along with the introduction of a bubble micro-layer yields a microchannel surface. Remarkably, this modification results in a noteworthy enhancement of 131% in CHF and a substantial 211% increase in the heat transfer coefficient (HTC) without resorting to particle incorporation onto the surface. This indicates promising avenues for enhancing cooling efficiency through surface engineering without additional additives.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
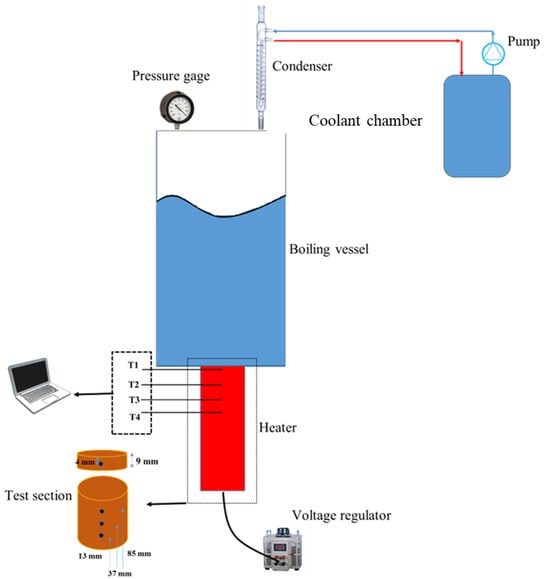
Evaluation of the Effect of Particle Size and Biomass-to-Water Ratio on the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sugarcane Bagasse
by
Leidy Natalia Moreno-Chocontá, Alejandra Sophia Lozano-Pérez and Carlos Alberto Guerrero-Fajardo
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 43; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020043 - 08 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The generation of platform chemicals and hydrochar is of great interest because they reduce dependence on fossil resources and contribute to climate change mitigation by reducing carbon emissions. The main objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of biomass particle size
[...] Read more.
The generation of platform chemicals and hydrochar is of great interest because they reduce dependence on fossil resources and contribute to climate change mitigation by reducing carbon emissions. The main objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of biomass particle size and biomass-to-water ratio in a hydrothermal conversion system for the generation of value-added products obtained from sugarcane bagasse. Biomass characterization was performed using proximal, elemental, and structural analysis; hydrothermal carbonization was carried out at 220 and 260 °C for one hour; and conversion was monitored using pH, conductivity, and IR spectroscopy. Platform chemicals were quantified using HPLC-IR. Hydrochars were characterized by using scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy. Optimizing biomass particle size and water ratio is crucial for maximizing the yield of platform chemicals and hydrochar. The study’s outcomes revealed that specific combinations, such as a biomass-to-water ratio of 1:50 and a particle size of 212 μm at 220 °C, resulted in a substantial 31.07% yield of platform chemicals on a dry basis. This highlights the critical role these parameters play in influencing the production efficiency of valuable chemicals. Furthermore, variations in biomass particle size and water ratio also affect the characteristics of hydrochar. For instance, utilizing a biomass-to-water ratio of 1:50 and a larger particle size of 600 μm at 260 °C led to the production of hydrochar with higher carbon content and increased porosity. These findings underscore how adjustments in these factors can impact not only chemical yields, but also the properties and quality of the resulting hydrochar.
Full article
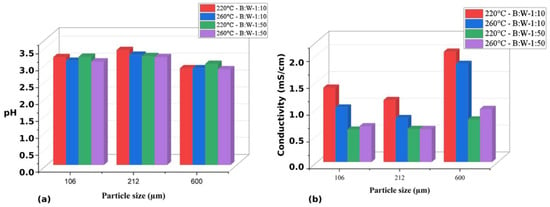
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Application of Machine Learning Models in Coaxial Bioreactors: Classification and Torque Prediction
by
Ali Rahimzadeh, Samira Ranjbarrad, Farhad Ein-Mozaffari and Ali Lohi
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 42; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020042 - 06 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Coaxial bioreactors are known for effectively dispersing gas inside non-Newtonian fluids. However, due to their design complexity, many aspects of their design and function, including the relationship between hydrodynamics and bioreactor efficiency, remain unexplored. Nowadays, various numerical models, such as computational fluid dynamics
[...] Read more.
Coaxial bioreactors are known for effectively dispersing gas inside non-Newtonian fluids. However, due to their design complexity, many aspects of their design and function, including the relationship between hydrodynamics and bioreactor efficiency, remain unexplored. Nowadays, various numerical models, such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and artificial intelligence models, provide exceptional opportunities to investigate the performance of coaxial bioreactors. For the first time, this study applied various machine learning models, both classifiers and regressors, to predict the torque generated by a coaxial bioreactor. In this regard, 500 CFD simulations at different aeration rates, central impeller speeds, anchor impeller speeds, and rotating modes were conducted. The results obtained from the CFD simulations were used to train and test the machine learning models. Careful feature scaling and k-fold cross-validation were performed to enhance all models’ performance and prevent overfitting. A key finding of the study was the importance of selecting the right features for the model. It turns out that just by knowing the speed of the central impeller and the torque generated by the coaxial bioreactor, the rotating mode can be labelled with perfect accuracy using k-nearest neighbors (kNN) or support vector machine models. Moreover, regression models, including multi-layer perceptron, kNN, and random forest, were examined to predict the torque of the coaxial impellers. The results showed that the random forest model outperformed all other models. Finally, the feature importance analysis indicated that the rotating mode was the most significant parameter in determining the torque value.
Full article
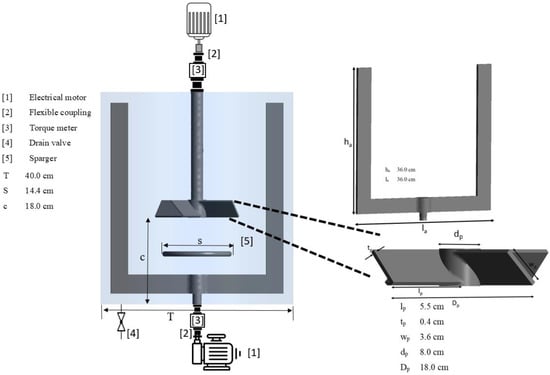
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Experimental Study on the Reaction of Magnesium in Carbon Dioxide and Nitrogen Atmosphere
by
Ioan Barabulica, Marius Sebastian Secula, Adriana Mariana Asoltanei, Eugenia Teodora Iacob-Tudose, Gabriela Lisa and Ioan Mamaliga
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 41; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020041 - 06 Apr 2024
Abstract
This manuscript presents an experimental study focusing on the combustion of magnesium in an atmosphere depleted of oxygen. The study explores various mixtures of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, examining their impact on the combustion performance. The experimental design involved evaluating how the carbon
[...] Read more.
This manuscript presents an experimental study focusing on the combustion of magnesium in an atmosphere depleted of oxygen. The study explores various mixtures of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, examining their impact on the combustion performance. The experimental design involved evaluating how the carbon content influences combustion parameters. Temperature profiles were analyzed to elucidate different stages of the combustion process. Furthermore, the effects of pressure (2 and 3 ata) and the composition of CO2-N2 mixtures (10%, 19.5%, 35%, 48%, 72%, and 80% CO2 content) on magnesium combustion, including ignition time, maximum temperature, and post-combustion temperatures, were investigated. The results revealed a substantial impact on the ignition delay and combustion time, with the ignition delay decreasing with higher chamber pressure. The combustion process, especially with regard to the ignition time and heat of combustion, was notably affected by CO2 concentration. The morphology of the combustion residue from the magnesium microparticles was characterized using scanning electron microscopy combined with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX). The reaction of Mg with CO2 represents a promising energy source, quickly releasing a substantial amount of heat with a very low quantity of Mg. The estimated value of the heat of combustion for magnesium in N2-CO2 atmosphere is 78.4 kJ mol−1.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fueling the Future: Chemical Engineering Approaches in Ceramic Materials for Energy Storage)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Simultaneous Environmental Waste Management through Deep Dewatering of Alum Sludge Using Waste-Derived Cellulose
by
Manasik M. Nour and Maha A. Tony
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 40; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020040 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
To simultaneously solve problems in an eco-friendly manner, introducing a waste residual as a sustainable conditioner to aid alum sludge dewatering is suggested as a cradle-to-cradle form of waste management. In this regard, the superiority of deep dewatering alum sludge with a powdered
[...] Read more.
To simultaneously solve problems in an eco-friendly manner, introducing a waste residual as a sustainable conditioner to aid alum sludge dewatering is suggested as a cradle-to-cradle form of waste management. In this regard, the superiority of deep dewatering alum sludge with a powdered wood chip composite residual as a novel conditioner was explored, whereby traditional conventional conditioners, i.e., polyelectrolytes and lime, were substituted with powdered wood chips. Initially, Fe3O4 was prepared at the nanoscale using a simple co-precipitation route. Next, wooden waste was chemically and thermally treated to attain cellulosic fine powder. Subsequently, the resultant wood powder and Fe3O4 nanoparticles were mixed at 50 wt % to attain a wood powder augmented with iron, and this conditioner was labeled nano-iron-cellulose (nIC-Conditioner). This material (nIC-Conditioner) was mixed with hydrogen peroxide to represent a dual oxidation and skeleton builder conditioning substance. Characterization of the resultant conditioner was carried out using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) transmittance spectrum analysis. The feasibility of the experimental results revealed that the moisture content in the sludge cake was lower after conditioning, and the capillary suction time (CST) was reduced to 78% compared to that of raw alum sludge after 5 min of dewatering time. Moreover, the optimal system parameters, including nIC-Conditioner and H2O2 concentrations, as well as the working pH, were optimized, and optimal values were recorded at 1 g/L and 200 mg/L for nIC-Conditioner and H2O2, respectively, with a pH of 6.5. Additionally, scanning electron microscope (SEM) analyses of the sludge prior to and after conditioning were conducted to verify the change in sludge molecules due to this conditioning technique. The results of this study confirm the sustainability of an alum sludge and waste management facility.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Catalytic Reactions and Development of (Bio)Chemical Processes for Synthesizing Value Added Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures
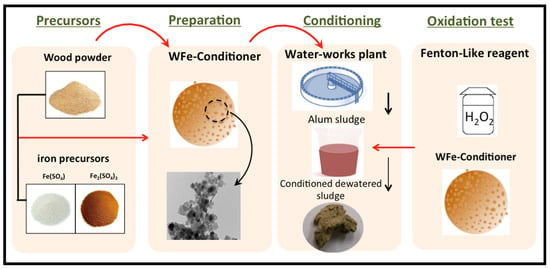
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of Donnan Steric Partitioning Pore Model and Dielectric Exclusion Applied to the Fractionation of Aqueous Saline Solutions through Nanofiltration
by
Aldo Saavedra, Hugo Valdés, Juan Velásquez and Sebastián Hernández
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 39; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020039 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
The aim of this study was to analyze, both theoretically and experimentally, the material transport mechanisms governing the separation of ionic species in aqueous solutions using nanofiltration membranes. To interpret the experimental results, the Donnan Steric Partitioning Model (DSPM) and the Dielectric Exclusion
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to analyze, both theoretically and experimentally, the material transport mechanisms governing the separation of ionic species in aqueous solutions using nanofiltration membranes. To interpret the experimental results, the Donnan Steric Partitioning Model (DSPM) and the Dielectric Exclusion Model (DSPM-DE) were applied and computationally simulated in Matlab. Experimental tests were conducted using a pilot-scale system with commercial NF90 membranes. The results indicate that the DSPM better describes the rejection of monovalent ions (sodium and chloride), while the DSPM-DE is more suitable for divalent ions (sulfate and magnesium). Additionally, both models were sensitized to explore the impact of hindrance factors on the rejection of different ionic species. For neutral molecules present in the solution, it was observed that the DSPM and DSPM-DE do not adequately interpret selectivity, suggesting that under such conditions, the electrostatic exclusion mechanism loses significance, with the steric mechanism prevailing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue State-of-the-Art Membrane Technologies in Chemical Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
New Approach for Sulfidation Process in Packed Bed with Hi-Fuel A310 Sorbent—Thermodynamical Studies
by
Clarisse Lorreyte, Barbara Malinowska, Vincent Butin, Nathalie Ruscassier, Joel Casalinho and Patrick Perré
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 38; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020038 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents tests related to the reactivity of commercial Hi-Fuel sorbent toward H2S (H2S/N2 mixture) in a packed bed at 300 °C. The sorbent used for breakthrough test was characterized before and after test by ESEM-EDX, FTIR-ATR,
[...] Read more.
This paper presents tests related to the reactivity of commercial Hi-Fuel sorbent toward H2S (H2S/N2 mixture) in a packed bed at 300 °C. The sorbent used for breakthrough test was characterized before and after test by ESEM-EDX, FTIR-ATR, Raman, and elemental analyses. Testing reveals that the commercial sorbent contains two compounds reacting with H2S: ZnO and ZnCO3. According to thermodynamical studies, the reactivity of ZnCO3 at 300 °C is privileged (KR = 9.5 × 108) than ZnO (KR = 6.6× 106). In addition, the reaction of H2S with ZnCO3 induces a volume decrease, which promotes the movement of gas through the newly formed layer. The properties of this sorbent thus hold a good potential for the desulfurization process of gases polluted with H2S. We observed that the maximum sulfidation rate was reached on the surface of the sorbent and showed a maximum conversion of 27%.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevention and Control of the Spread of Pathogens in a University of Naples Engineering Classroom through CFD Simulations
by
Maria Portarapillo, Salvatore Simioli and Almerinda Di Benedetto
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 37; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020037 - 01 Apr 2024
Abstract
The design of ventilation and air conditioning systems in university classrooms is paramount to ensure students’ correct number of air changes per hour and an optimal thermal profile for their comfort. With the spread of the COVID-19 virus, these systems will inevitably need
[...] Read more.
The design of ventilation and air conditioning systems in university classrooms is paramount to ensure students’ correct number of air changes per hour and an optimal thermal profile for their comfort. With the spread of the COVID-19 virus, these systems will inevitably need to evolve to cope with the current virus and any new airborne pathogens. The aim of this study is to analyze the quality of the ventilation system and the importance of the use of PPE in Lecture Hall C of the University of Naples Federico II compared to the premises in Piazzale Tecchio. After dimensioning the lecture theatre with the Autodesk software AutoCAD 2021, CFD simulations were carried out with the Computational Fluid Dynamics program Ansys 2021 R2. To study the trajectory of virus droplets released by a potentially infected student in the center of the classroom, the multispecies model was used, with carbon dioxide serving as the tracer gas for the virus cloud. After determining the CO2 contour zones at fifteen-minute intervals for a total duration of two hours, the probability of infection was calculated using the Wells–Riley equation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Applications of Computational Fluid Dynamics in Transport Phenomena)
►▼
Show Figures
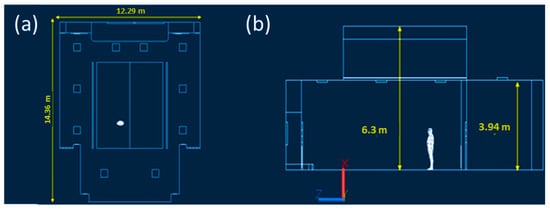
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Introduction and Advancements in Room-Temperature Ferromagnetic Metal Oxide Semiconductors for Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance
by
Ganeshraja Ayyakannu Sundaram, Govinda raj Muniyandi, Jayashree Ethiraj, Vairavel Parimelazhagan and Alagarsamy Santhana Krishna Kumar
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 36; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020036 - 01 Apr 2024
Abstract
Recent advancements in the field of room-temperature ferromagnetic metal oxide semiconductors (RTFMOS) have revealed their promising potential for enhancing photocatalytic performance. This review delves into the combined investigation of the photocatalytic and ferromagnetic properties at room temperature, with a particular focus on metal
[...] Read more.
Recent advancements in the field of room-temperature ferromagnetic metal oxide semiconductors (RTFMOS) have revealed their promising potential for enhancing photocatalytic performance. This review delves into the combined investigation of the photocatalytic and ferromagnetic properties at room temperature, with a particular focus on metal oxides like TiO2, which have emerged as pivotal materials in the fields of magnetism and environmental remediation. Despite extensive research efforts, the precise mechanism governing the interplay between ferromagnetism and photocatalysis in these materials remains only partially understood. Several crucial factors contributing to magnetism, such as oxygen vacancies and various metal dopants, have been identified. Numerous studies have highlighted the significant role of these factors in driving room-temperature ferromagnetism and photocatalytic activity in wide-bandgap metal oxides. However, establishing a direct correlation between magnetism, oxygen vacancies, dopant concentration, and photocatalysis has posed significant challenges. These RTFMOS hold immense potential to significantly boost photocatalytic efficiency, offering promising solutions for diverse environmental- and energy-related applications, including water purification, air pollution control, and solar energy conversion. This review aims to offer a comprehensive overview of recent advancements in understanding the magnetism and photocatalytic behavior of metal oxides. By synthesizing the latest findings, this study sheds light on the considerable promise of RTFMOS as effective photocatalysts, thus contributing to advancements in environmental remediation and related fields.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Novel Photocatalytic Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Profile of the Effectiveness Factor under Optimal Operating Conditions for the Conversion of Ortho-Xylene to Phthalic Anhydride in a Fixed-Bed Tubular Reactor
by
Luis Américo Carrasco-Venegas, Elsa Vásquez-Alvarez, José Vulfrano González-Fernández, Luz Genara Castañeda-Pérez, Juan Taumaturgo Medina-Collana, Guido Palomino-Hernández, Daril Giovanni Martínez-Hilario and Salvador Apolinar Trujillo-Pérez
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 35; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020035 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
The objective of this research is to find the effectiveness factor of the catalyst particles for the most favorable conditions of the phthalic anhydride production in a fixed bed reactor, with the aim of achieving the highest rate of phthalic anhydride production compared
[...] Read more.
The objective of this research is to find the effectiveness factor of the catalyst particles for the most favorable conditions of the phthalic anhydride production in a fixed bed reactor, with the aim of achieving the highest rate of phthalic anhydride production compared to other secondary products and analyzing the areas of lower effectiveness for the modification of the reactor design. Initially, the material and the energy balances in the catalytic bed are solved to obtain the concentration and temperature profiles based on the radius and length of the reactor, using polymath software(Polymath® v6.2 Software Minitab 19 Matlab 2019) with the data from literature. Once the profiles reproducibility was verified using the initial data (inlet temperature, pressure in the reactor, reactor wall temperature, reactor radius and mass flow rate) the experimental design 35 carry out, which generates 243 “experiments”, whose response variable (phthalic anhydride concentration) was obtained using Matlab. Subsequently, the variables were analyzed using the Minitab 18® that, through the response surface analysis method, allowed us to obtain the optimal values of the tested variables. Then, Subsequently, material and energy balances coupled with Fourier and Fick’s laws, along with the effectiveness factor equation, were applied, resulting in the generation of 9 coupled differential equations. Upon implementing the finite difference method, this yielded 90 nonlinear algebraic equations, which were solved using the Polymath software. A total of 78 particles were preselected based on their radial and axial positions to determine the effectiveness factor profile, with values ranging from 0.83 to near unity. The lower values correspond to the points with higher temperature, as evidenced by the calculations performed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Catalytic Kinetics)
►▼
Show Figures
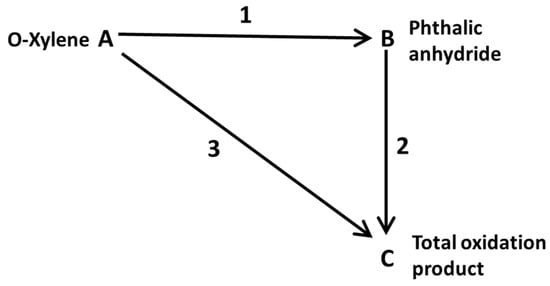
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Formulation and Characterization of Double Emulsions W/O/W Stabilized by Two Natural Polymers with Two Manufacturing Processes (Comparative Study)
by
Meriem Boudoukhani, Madiha Melha Yahoum, Kaouther Ezzroug, Selma Toumi, Sonia Lefnaoui, Nadji Moulai-Mostefa, Asma Nour El Houda Sid, Hichem Tahraoui, Mohammed Kebir, Abdeltif Amrane, Bassem Jaouadi and Jie Zhang
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 34; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020034 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
Four distinct types of multiple emulsions were synthesized using xanthan gum and pectin through two distinct manufacturing processes. The assessment encompassed the examination of morphology, stability, and rheological properties for the resulting water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsions. Formulations were meticulously crafted with emulsifiers that
[...] Read more.
Four distinct types of multiple emulsions were synthesized using xanthan gum and pectin through two distinct manufacturing processes. The assessment encompassed the examination of morphology, stability, and rheological properties for the resulting water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsions. Formulations were meticulously crafted with emulsifiers that were compatible with varying compositions. Remarkably stable multiple emulsions were achieved with a 0.5 wt% xanthan concentration, demonstrating resilience for nearly two months across diverse storage temperatures. In contrast, multiple emulsions formulated with a higher pectin concentration (2.75 wt%) exhibited instability within a mere three days. All multiple emulsions displayed shear-thinning behavior, characterized by a decline in apparent viscosity with escalating shear rates. Comparatively, multiple emulsions incorporating xanthan gum showcased elevated viscosity at low shear rates in contrast to those formulated with pectin. These results underscore the pivotal role of the stepwise process over the direct approach and emphasize the direct correlation between biopolymer concentration and emulsion stability. This present investigation demonstrated the potential use of pectin and xanthan gum as stabilizers of multiple emulsions with potential application in the pharmaceutical industry for the formulation of topical dosage forms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Process Intensification for Chemical Engineering and Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
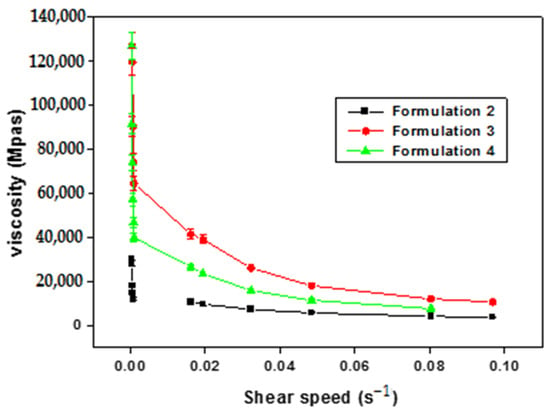
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Industrial Control System for Cement Sulfates Content Using a Feedforward and Feedback Mechanism
by
Dimitris Tsamatsoulis
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 33; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020033 - 07 Mar 2024
Abstract
This study examines the design and long-term implementation of a feedforward and feedback (FF–FB) mechanism in a control system for cement sulfates applied to all types of cement produced in two mills at a production facility. We compared the results with those of
[...] Read more.
This study examines the design and long-term implementation of a feedforward and feedback (FF–FB) mechanism in a control system for cement sulfates applied to all types of cement produced in two mills at a production facility. We compared the results with those of a previous controller (SC) that operated in the same unit. The Shewhart charts of the annual SO3 mean values and the nonparametric Mann–Whitney test demonstrate that, for the FF–FB controller, the mean values more effectively approach the SO3 target than the older controller in two out of the three cement types. The s-charts for the annual standard deviation of all cement types and mills indicate that the ratio of the central lines of FF–FB to SC ranges from 0.39 to 0.59, representing a significant improvement. The application of the error propagation technique validates and explains these improvements. The effectiveness of the installed system is due to two main factors. The feedforward (FF) component tracks the set point of SO3 when the mill begins grinding a different type of cement, while the feedback (FB) component effectively attenuates the fluctuations in the sulfates of the raw materials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Chemical Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
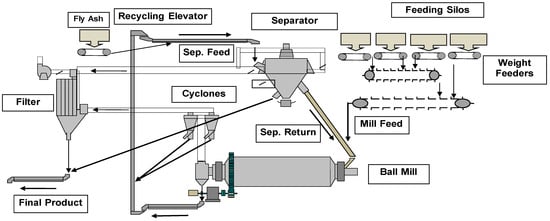
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation on UV Degradation and Mechanism of 6:2 Fluorotelomer Sulfonamide Alkyl Betaine, Based on Model Compound Perfluorooctanoic Acid
by
Naveed Ahmed, Marion Martienssen, Isaac Mbir Bryant, Davide Vione, Maria Concetta Bruzzoniti and Ramona Riedel
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 32; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020032 - 06 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The UV treatment of 6:2 FTAB involves the mitigation of this persistent chemical by the impact of ultraviolet radiation, which is known for its resistance to environmental breakdown. UV treatment of PFOA and/or 6:2 FTAB, and the role of responsible species and their
[...] Read more.
The UV treatment of 6:2 FTAB involves the mitigation of this persistent chemical by the impact of ultraviolet radiation, which is known for its resistance to environmental breakdown. UV treatment of PFOA and/or 6:2 FTAB, and the role of responsible species and their mechanism have been presented. Our investigation focused on the degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonamide alkyl betaine (6:2 FTAB, Capstone B), using UV photolysis under various pH conditions. Initially, we used PFOA as a reference, finding a 90% decomposition after 360 min at the original (unadjusted) pH 5.6, with a decomposition rate constant of (1.08 ± 0.30) × 10−4 sec−1 and a half-life of 107 ± 2 min. At pH 4 and 7, degradation averaged 85% and 80%, respectively, while at pH 10, it reduced to 57%. For 6:2 FTAB at its natural pH 6.5, almost complete decomposition occurred. The primary UV transformation product was identified as 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonic acid (6:2 FTSA), occasionally accompanied by shorter-chain perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) including PFHpA, PFHxA, and PFPeA. Interestingly, the overall decomposition percentages were unaffected by pH for 6:2 FTAB, though pH influenced rate constants and half-lives. In PFOA degradation, direct photolysis and reaction with hydrated electrons were presumed mechanisms, excluding the involvement of hydroxyl radicals. The role of superoxide radicals remains uncertain. For 6:2 FTAB, both direct and indirect photolysis were observed, with potential involvement of hydroxyl, superoxide radicals, and/or other reactive oxygen species (ROS). Clarification is needed regarding the role of
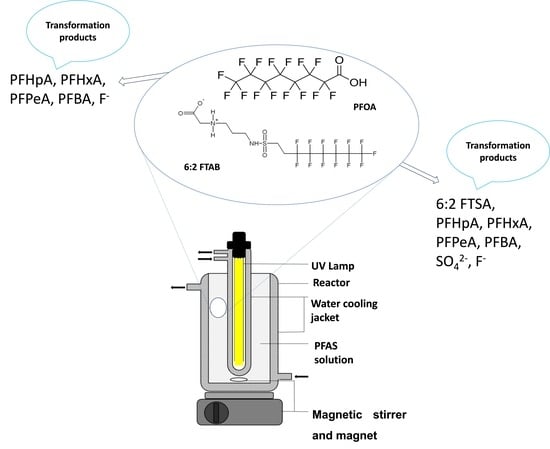
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comprehensive Modeling of Vacuum Systems Using Process Simulation Software
by
Eduard Vladislavovich Osipov, Daniel Bugembe, Sergey Ivanovich Ponikarov and Artem Sergeevich Ponikarov
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 31; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020031 - 06 Mar 2024
Abstract
Traditional vacuum system designs often rely on a 100% reserve, lacking precision for accurate petrochemical computations under vacuum. This study addresses this gap by proposing an innovative modeling methodology through the deconstruction of a typical vacuum-enabled process. Emphasizing non-prescriptive pressure assignment, the approach
[...] Read more.
Traditional vacuum system designs often rely on a 100% reserve, lacking precision for accurate petrochemical computations under vacuum. This study addresses this gap by proposing an innovative modeling methodology through the deconstruction of a typical vacuum-enabled process. Emphasizing non-prescriptive pressure assignment, the approach ensures optimal alignment within the vacuum system. Utilizing process simulation software, each component was systematically evaluated following a proposed algorithm. The methodology was applied to simulate vacuum-driven separation in phenol and acetone production. Quantifying the vacuum system’s load involved constructing mathematical models in Unisim Design R451 to determine the mixture’s volume flow rate entering the vacuum pump. A standard-sized vacuum pump was then selected with a 40% performance margin. Post-reconstruction, the outcomes revealed a 22.5 mm Hg suction pressure within the liquid-ring vacuum pump, validating the efficacy of the devised design at a designated residual pressure of 40 mm Hg. This study enhances precision in vacuum system design, offering insights that are applicable to diverse petrochemical processes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Chemical and Biochemical Processes for Energy Sources)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Raw Materials and Technological Factors on the Sorption Properties of Blast-Fuel Coke
by
Denis Miroshnichenko, Kateryna Shmeltser, Maryna Kormer, Daryna Sahalai, Serhiy Pyshyev, Oleg Kukhar, Bohdan Korchak and Taras Chervinskyy
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 30; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020030 - 05 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The influence of raw material factors (component composition of batches, petrographic characteristics, indicators of proximate and plastometric analyses, granulometric composition) and technological factors (coking period, process temperature) on the sorption properties of the carbonized product (coke) was studied. Based on the research results,
[...] Read more.
The influence of raw material factors (component composition of batches, petrographic characteristics, indicators of proximate and plastometric analyses, granulometric composition) and technological factors (coking period, process temperature) on the sorption properties of the carbonized product (coke) was studied. Based on the research results, it is shown that such characteristics of coke as low humidity and ash, minimal yield of volatile matters, developed pore system and low cost make its use as a sorbent promising and economically justified. The obtained equations for predicting the sorption capacity by alkali and acid and adsorption activity by iodine, taking into account the content of vitrinite and the yield of volatile matters coal batch. They are characterized by high approximation coefficients r (0.912 and 0.927 and 0.937, respectively), so they can be recommended for predicting the indicated indicators.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Continuous Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Mexican Sargassum Seaweed—An Analysis of Hydrocarbon Fractions and Elemental Composition
by
Michael J. Allen and Matthew Pearce
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 29; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020029 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) is often mooted as a promising and sustainable processing methodology for converting biomass into usable products, including bio-oils, which can potentially alleviate humanity’s reliance on fossil fuels. To date, most HTL development work with novel biomasses has been undertaken at
[...] Read more.
Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) is often mooted as a promising and sustainable processing methodology for converting biomass into usable products, including bio-oils, which can potentially alleviate humanity’s reliance on fossil fuels. To date, most HTL development work with novel biomasses has been undertaken at the laboratory scale in batch processes, and the results have been extrapolated to the theoretical continuous flow processes required for industrial uptake. Here, we assess the use of a novel continuous flow HTL system, applying it to Sargassum (seaweed) material and generating a bio-oil, which is assessed against typical crude oil fractions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Hydrotreating Catalyst Synthesis for Fuel and Chemical Production Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
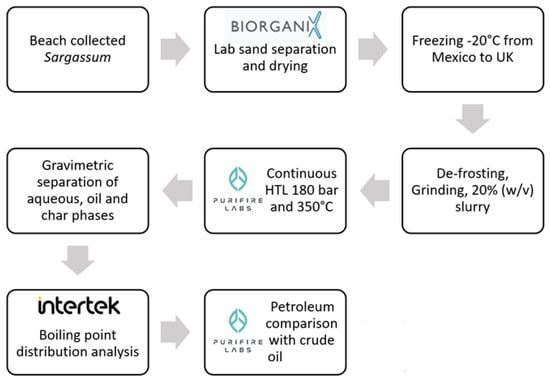
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Facile Synthesis Method of Zeolite NaY and Zeolite NaY-Supported Ni Catalyst with High Catalytic Activity for the Conversion of CO2 to CH4
by
Somkiat Krachuamram, Pinit Kidkhunthod, Yingyot Poo-arporn and Kingkaew Chayakul Chanapattharapol
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 28; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020028 - 01 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this work, the facile reflux method was used as a crystallization procedure for zeolite NaY synthesis. The zeolite mixture was aged for 7 days and then refluxed for crystallization at 100 °C for 12 h. The synthesized zeolite NaY was impregnated with
[...] Read more.
In this work, the facile reflux method was used as a crystallization procedure for zeolite NaY synthesis. The zeolite mixture was aged for 7 days and then refluxed for crystallization at 100 °C for 12 h. The synthesized zeolite NaY was impregnated with 10, 20 and 30 wt%Ni solution to use as a catalyst for CO2 methanation. The 30 wt% of Ni on the zeolite NaY catalyst showed the highest CO2 methanation catalytic activity, with almost 100% CH4 selectivity. This can be explained by an appropriate H2 and CO2 adsorption amount on a catalyst surface being able to facilitate the surface reaction between them and further react to form products. The oxidation state of Ni and the stability of the catalyst were monitored by time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The oxidation state of Ni2+ was reduced during the catalyst reduction prior to the CO2 methanation and it was completely reduced to Ni° at 600 °C. During CO2 methanation, Ni° remained unchanged. In addition, the stability test of the catalyst was conducted by exposing the catalyst to a fluctuating condition (CO2 + H2 and only CO2). The oxidation state of Ni° remained unchanged under the fluctuating condition. This indicated that the Ni/zeolite catalyst has high stability, which can be attributed to an appropriate binding strength between Ni and the zeolite support.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Use of Lignite Processing Products as Additives to Road Petroleum Bitumen
by
Serhiy Pyshyev, Denis Miroshnichenko, Taras Chipko, Myroslava Donchenko, Olena Bogoyavlenska, Liudmyla Lysenko, Mykhailo Miroshnychenko and Yuriy Prysiazhnyi
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 27; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020027 - 01 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
It is known that there are significant deposits of lignite (brown coal) in Ukraine, particularly in categories A + B + C1. At the same time, certain technical and legal obstacles limit its use as an energy carrier. Therefore, new methods of using
[...] Read more.
It is known that there are significant deposits of lignite (brown coal) in Ukraine, particularly in categories A + B + C1. At the same time, certain technical and legal obstacles limit its use as an energy carrier. Therefore, new methods of using lignite and processing its products are necessary. The latter includes humic acids. It was suggested that these acids could be used to stop road bitumens from breaking down. This is because they are antioxidants that contain functional phenolic and carboxyl groups. In particular, this article analyses the nature of the influence of humic acids on the physical and mechanical properties of road petroleum bitumen and its resistance to technological aging. It was found that at a modification temperature of 120 °C (duration-60 min., consumption of humic acids-2.0 wt.%), this additive has a slight negative effect (changes are within permissible limits) on the plastic properties of bitumen and slightly improves its elasticity. The main reason for adding humic acids to road bitumen under the specified conditions is to improve its resistance to technological aging compared to the original binder.
Full article
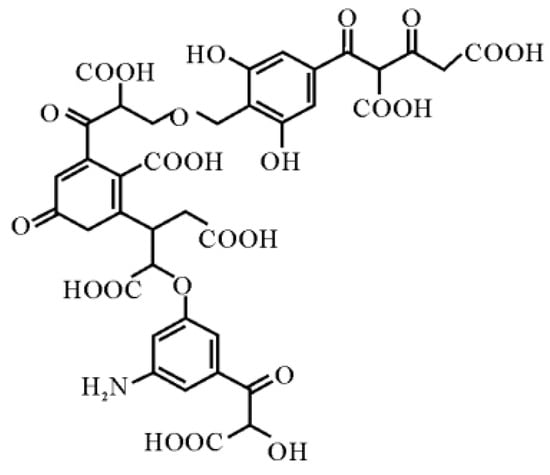
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing Extract Preparation from Laurel (Laurus nobilis L.) Leaves Using a Pulsed Electric Field
by
Theodoros Chatzimitakos, Vassilis Athanasiadis, Dimitrios Kalompatsios, Konstantina Kotsou, Martha Mantiniotou, Eleni Bozinou and Stavros I. Lalas
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(2), 26; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8020026 - 01 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study explores the bioactive compound extraction from laurel (Laurus nobilis L.) leaves using a pulsed electric field (PEF) as a standalone extraction technique. The primary parameters impacting the extraction process were optimized through response surface methodology. Specifically, solvent composition (ethanol and
[...] Read more.
This study explores the bioactive compound extraction from laurel (Laurus nobilis L.) leaves using a pulsed electric field (PEF) as a standalone extraction technique. The primary parameters impacting the extraction process were optimized through response surface methodology. Specifically, solvent composition (ethanol and water mixtures) and liquid-to-solid ratio, along with other key PEF conditions (i.e., electric field intensity, pulse period, and pulse length) were examined. The antioxidant capacity was evaluated through DPPH and FRAP assays, whereas total polyphenol content was also measured. A comparison was also made between the extracts produced with and without PEF. The results showed that after 30 min of extraction, the best parameters were a pulse period of 355 μs, a pulse duration of 55 μs, and an electric field intensity of 0.6 kV/cm. A liquid-to-solid ratio of 10 mL/g was chosen, whereas the best solvent was determined to be 25% (v/v) ethanol/water mixture. The PEF-treated extract contained 77% more polyphenols compared to the untreated sample. In addition, PEF-treated samples had a rise of up to 288% for certain individual polyphenols. Correlation analyses also revealed interesting trends among bioactive compounds and the antioxidant capacity of the extracts. The effect of the investigated parameters on polyphenol recovery was demonstrated, indicating that comparable investigations should consider these parameters to optimize polyphenol extraction yield. Regarding green and non-thermal standalone techniques, PEF outshines other extraction techniques as it could also be used as a sustainable way to swiftly generate health-promoting extracts from medicinal plants.
Full article
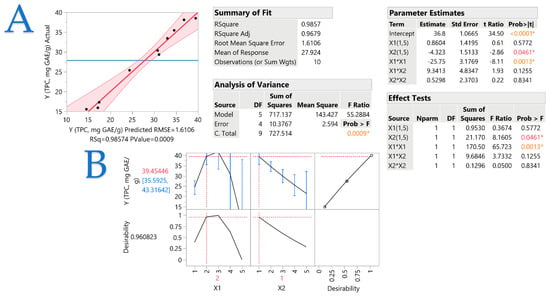
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Synthesis of ZnS/Al2O3/TaSe2 Core/Shell Nanowires Using Thin Ta Metal Film Precursor
by
Boris Polyakov, Kevon Kadiwala, Edgars Butanovs, Luize Dipane, Annamarija Trausa, Dmitry Bocharov and Sergei Vlassov
ChemEngineering 2024, 8(1), 25; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/chemengineering8010025 - 19 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study introduces a novel approach for fabricating ZnS/Al2O3/TaSe2 heterostructured core/shell nanowires (NWs) through the selenization of a metallic Ta thin film precursor. The synthesis process involves a meticulously designed four-step protocol: (1) generating ZnS NWs on an
[...] Read more.
This study introduces a novel approach for fabricating ZnS/Al2O3/TaSe2 heterostructured core/shell nanowires (NWs) through the selenization of a metallic Ta thin film precursor. The synthesis process involves a meticulously designed four-step protocol: (1) generating ZnS NWs on an oxidized silicon substrate, (2) encapsulating these NWs with a precisely controlled thin Al2O3 layer via atomic layer deposition (ALD), (3) applying a Ta precursor layer by magnetron sputtering, and (4) annealing in a Se-rich environment in a vacuum-sealed quartz ampoule to transform the Ta layer into TaSe2, resulting in the final core/shell structure. The characterization of the newly produced NWs using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was validated using the integrity and composition of the heterostructures. Our method not only establishes a new pathway for the synthesis of TaSe2-based core/shell NWs but also extends the potential for creating a variety of core/shell NW systems with chalcogenide shells by adapting the thin film metal precursor approach. This versatility opens the way for future advancements in nanoscale material applications, particularly in electronics and optoelectronics where core/shell geometries are increasingly important.
Full article
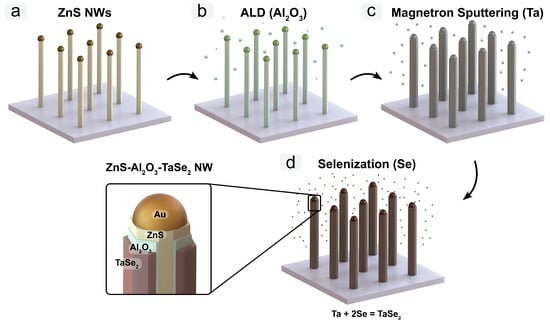
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
AppliedChem, ChemEngineering, Energies, Membranes, Processes, Recycling, Separations, Water
Capacitive Deionization Technology for Water Treatment
Topic Editors: Shenxu Bao, Xin ZhangDeadline: 30 September 2024
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Processes, ChemEngineering, Chemistry
Chemical and Biochemical Processes for Energy Sources, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Venko N. Beschkov, Konstantin PetrovDeadline: 30 September 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
ChemEngineering
Emerging Technologies for Remediation of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Contaminated Water
Guest Editors: Sirshendu De, Debarati Mukherjee, Biswajit BeraDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
ChemEngineering
Advanced Chemical Engineering in Nanoparticles
Guest Editors: Bei Liu, Xiaoming ZhangDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
ChemEngineering
Supramolecular Synthesis in Chemical Engineering
Guest Editor: Pathik SahooDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
ChemEngineering
Advances in Hydrotreating Catalyst Synthesis for Fuel and Chemical Production Processes
Guest Editors: Kirtika Kohli, Ravindra PrajapatiDeadline: 26 July 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
ChemEngineering
Green and Environmentally Sustainable Chemical Processes
Collection Editors: Consuelo Mugoni, Grazia Maria Cappucci, Roberto Rosa, Anna Ferrari