Digital Engineering for a Sustainable Built Environment
A special issue of Applied Sciences (ISSN 2076-3417). This special issue belongs to the section "Environmental Sciences".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (31 May 2022) | Viewed by 41937
Special Issue Editors
Interests: sustainable construction; green building information modelling; technology assessment, industry competition and market dynamics of sustainable construction technologies
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: construction and demolition waste recycling; green building; energy policy; stakeholder engagement; competitiveness; housing quality; smart construction
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Digital transition and sustainability transition are the two major trends happening in the architecture, construction, and engineering (AEC) industry worldwide. On one hand, the Industry 4.0 movement is revolutionizing the AEC industry, which is being digitalized rapidly at both the project and regional level. For instance, building information modeling (BIM) and the geographical information system (GIS) have been increasingly used by practitioners to better design, construct, and operate construction projects. On the other hand, environmental issues such as climate change and depletion of natural resources have put increasing pressure on the AEC industry to adopt more environmentally-friendly technologies and practices in delivering construction projects. The connections between these two transitions, however, have not been deeply investigated by academics. A fundamental question needs to be answered, namely, how can digital technologies such as BIM be used to facilitate a sustainable built environment?
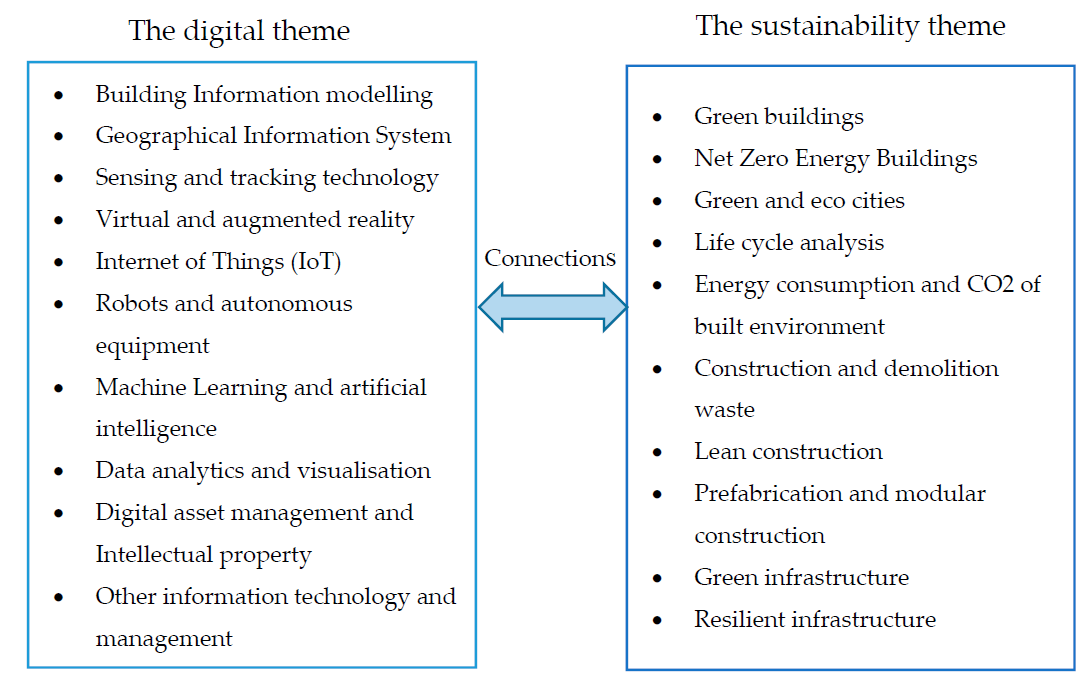
The aim of this Special Issue is to encourage academic thinking and investigation on the linkages between digital technologies and sustainable built environment. Theoretical, simulation, empirical, and experimental studies are all welcomed. Ideally, topics should link at least one area in the digital theme and one area in the sustainability theme to explore the connections between digital engineering and sustainable built environment. Papers that only focus on one area will also be considered if the contribution to body of knowledge is significant. The areas may include, but are not limited to, the following:
Dr. Ruidong Chang
Prof. Dr. Jian Zuo
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.






