New Trends in Optical Networks
A topical collection in Applied Sciences (ISSN 2076-3417). This collection belongs to the section "Optics and Lasers".
Viewed by 52139Editors
Interests: electronics and communication engineering; optics; telecommunications engineering
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: optical communications and networks; high capacity systems; quantum communications; photonic integrated circuits; optical networks field trials
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
A photonics-enhanced information and communication infrastructure will be the key enabler that the future digital society, industry, and economy will rely upon, shared by humans and machines. This infrastructure will be connected to a myriad of connected devices. It will require unprecedented capacity, energy, and cost efficiency and ultrafast responsivity for time-sensitive applications for humans and robots.
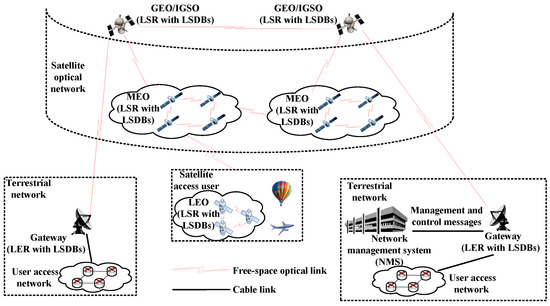
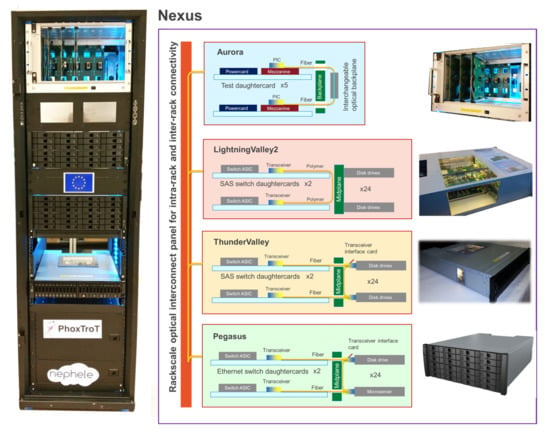
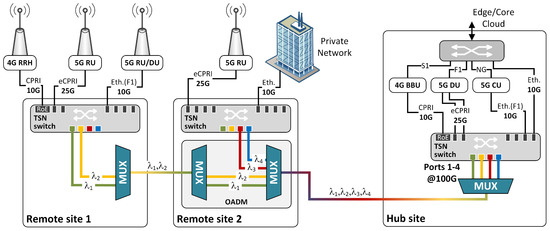
This Topical Collection covers recent advances and new trends in the research and standardization of optical networks with high impact on the future digitized society and economy, encompassing all network layers, from new optical components to smart network operations. Covered topics include, but are not limited to, the following: new materials, technologies, and production processes for integrated photonics devices, for example, graphene and CMOS photonics modulators, photodectors, and switches; ultra-high-speed optical transport networks, beyond terabit/s; broadband optical amplification; high bandwidth density and energy-efficient interconnection systems; co-packaged electrical and optical ICs; photonics applications for broadband radio systems; optical generation and detection of millimeter waves and THz; optical wireless communications; optical beamforming; new switching paradigms for flexible capacity scaling, low latency, and time-deterministic networking; new network architecture and control paradigms; self-configuring optical networks; virtualized highly flexible network control; integrated fixed-mobile architectures; convergence of mobile, optical, and cloud computing; evolution of NFV, SDN, and AI-based network control; multi-domain routing; secure optical networking; quantum secure networks. Survey papers and reviews are welcome.
Dr. Fabio CavaliereProf. Dr. Luca Potì
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- integrated photonics
- beyond terabit/s optical networks
- ultra-broadband optical amplifiers
- co-packaged ICs
- photonics applications for radio systems
- time-deterministic switching
- highly flexible and self-configurable optical networks
- convergence of mobile, optical, and cloud
- AI-based network control
- secure and quantum secure optical networks
Related Special Issue
- Photonic Technologies and Systems Enabling 6G in Applied Sciences (2 articles)