-
 The Survival of Salmonella enterica Strains in Ready-to-Eat Fruit Purees under Different Storage Temperatures
The Survival of Salmonella enterica Strains in Ready-to-Eat Fruit Purees under Different Storage Temperatures -
 Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey
Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey -
 Understanding Sparkling Wine Consumers and Purchase Cues: A Wine Involvement Perspective
Understanding Sparkling Wine Consumers and Purchase Cues: A Wine Involvement Perspective
Journal Description
Beverages
Beverages
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on beverage research and development published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), FSTA, CAPlus / SciFinder, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Food Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.5 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.2 (2022)
Latest Articles
Fortification of White Wines with Antioxidants and Se: Impacts on Browning Development and Phenolic Content
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 31; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020031 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
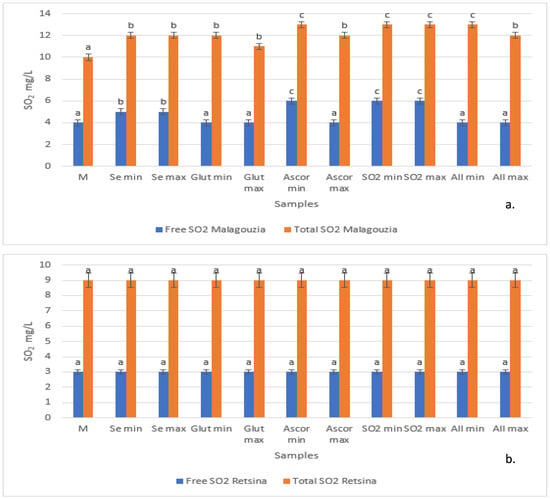
The present study explores the efficiency of selenomethionine (Semeth), an organic form of Se, as an antioxidant compared with commonly used antioxidants (ascorbic acid, glutathione, and potassium metabisulfite) in preventing oxidative browning in Greek white wines (Malagouzia and Retsina). The experimental procedure involved
[...] Read more.
The present study explores the efficiency of selenomethionine (Semeth), an organic form of Se, as an antioxidant compared with commonly used antioxidants (ascorbic acid, glutathione, and potassium metabisulfite) in preventing oxidative browning in Greek white wines (Malagouzia and Retsina). The experimental procedure involved an accelerated browning test conducted over 12 days at 55 °C, measurement of antioxidant activity values (using the Folin—Ciocalteau and the free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) methods), determination of free sulfhydryl groups using the Ellman’s method, and High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic analysis of selected phenolic compounds. Semeth consistently exhibited a preserving effect on total and free SO2 content and antioxidant activity values of Malagouzia wines. Semeth also showed a protecting effect on free sulfhydryl groups (-SH), even higher than that of SO2 suggesting that its role in maintaining wine color involves more mechanisms than just the prevention of SO2 reduction. Moreover, Semeth demonstrated promising effects in preserving individual phenolic content, in particular (+)-catechin and fertaric acid, compared to the other antioxidant additions. Both browning rate constants and percentage color change values of Retsina where higher than the corresponding values of Malagouzia wines indicating greater susceptibility to browning. Browning development was dependent on the particular antioxidant added, with ascorbic acid being the least effective. The results of this study suggest that Semeth could be an important candidate for enhancing the oxidative stability of white wines, offering at the same time valuable information for optimizing antioxidant strategies in winemaking practices.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wine and Spirits)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Ability of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC 36-9 Strain with Probiotic Potential to Ferment Coconut Milk and Produce a Yogurt-Type Beverage
by
Porntipha Vitheejongjaroen, Pooyanee Phettakhu, Wannicha Arsayot, Malai Taweechotipatr and Ulisa Pachekrepapol
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 30; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020030 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The efficacy of the Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC 36-9 strain with probiotic potential to ferment coconut milk and produce coconut milk yogurt-type beverages was examined. Tapioca starch was used as a stabilizer at concentrations of 0, 1.0, and 2.0% (w/w).
[...] Read more.
The efficacy of the Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC 36-9 strain with probiotic potential to ferment coconut milk and produce coconut milk yogurt-type beverages was examined. Tapioca starch was used as a stabilizer at concentrations of 0, 1.0, and 2.0% (w/w). The samples were stored at 4 °C for 21 days and analyzed for viability and resistance to in vitro gastrointestinal conditions of L. paracasei MSMC 36-9, pH changes, radical scavenging activity using the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay, and apparent viscosity. The viability of the strain with probiotic potential in the samples remained stable during storage and ranged between 12 and 13 log CFU/g by the end of the storage period. The strain L. paracasei MSMC 36-9 from all samples survived under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. The pH levels of all samples decreased during storage due to post-acidification. The radical scavenging activity of the products fermented with L. paracasei MSMC 36-9 was higher than that of the sample fermented with the commercial yogurt starter culture. The addition of tapioca starch to fermented coconut milk increased the viscosity of the samples. The results suggested that L. paracasei MSMC 36-9 can be used as a starter culture in the production of coconut milk yogurt-type beverages with antioxidant potential.
Full article
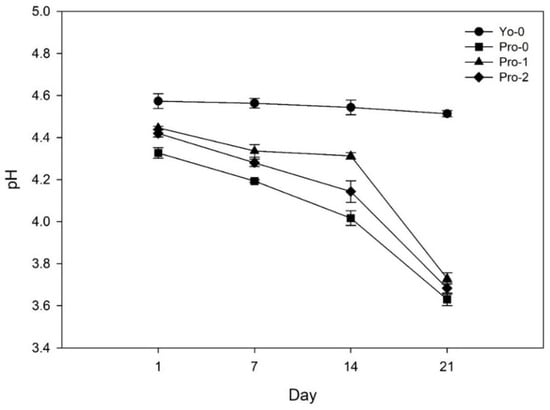
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of a New Kombucha from Grape Pomace: The Impact of Fermentation Conditions on Composition and Biological Activities
by
Nathalie Barakat, Jalloul Bouajila, Sandra Beaufort, Ziad Rizk, Patricia Taillandier and Youssef El Rayess
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 29; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020029 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Winemaking is one of the oldest biotechnology techniques in the world. The wine industry generates 20 million tons of by-products, such as wastewater, stalk, lees, pomace, and stems, each year. The objective of this research project is to valorize wine industry by-products by
[...] Read more.
Winemaking is one of the oldest biotechnology techniques in the world. The wine industry generates 20 million tons of by-products, such as wastewater, stalk, lees, pomace, and stems, each year. The objective of this research project is to valorize wine industry by-products by producing a functional beverage via the fermentation of grape pomace with the kombucha consortium. In this study, grape pomace kombucha was produced under different conditions, and the concentration of the added sucrose in addition to the fermentation duration and temperature were varied. Overall, fermentation was characterized by the consumption of sugars and the production of organic acids and ethanol. An improvement in the concentrations of the total polyphenols and anthocyanins was observed in the developed product (i.e., up to 100%). Moreover, an enhancement of the antioxidant potential by 100%, as well as increases of 50 to 75% in the anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic activities, was noted.
Full article
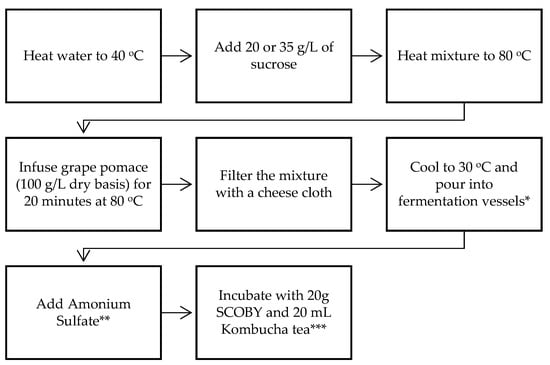
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Acetic Fermentation of Cagaita Pulp: Technological and Chemical Characteristics
by
Jeisa Farias De Sousa Santana, Guilherme Freitas de Lima Hercos, Josemar Gonçalves de Oliveira Filho, Daiane Costa dos Santos, Marilene Silva Oliveira, Bheatriz Silva Morais de Freitas, Fabiano Guimarães Silva and Mariana Buranelo Egea
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 28; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020028 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
The Brazilian Cerrado region has a rich plant diversity, with fruits that have peculiar and unique sensory characteristics. For these reasons, using these fruits for biotechnological production is a promising alternative, mainly to protect this biome from deforestation and degradation. The production of
[...] Read more.
The Brazilian Cerrado region has a rich plant diversity, with fruits that have peculiar and unique sensory characteristics. For these reasons, using these fruits for biotechnological production is a promising alternative, mainly to protect this biome from deforestation and degradation. The production of fermented acetic acid is an option to add value to native fruits and offer the market beverages with better nutritional quality and bioactive compounds. This work aimed to characterize fruits and to develop cagaita (Eugenia dysenterica DC.) acetic fermented beverage. The fruits were subjected to physical-chemical analyses in the first part. Subsequently, different treatments for fermentation were tested using two types of enzymes (amylase and pectinase), two subspecies of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast (UFLA CA11 and thermoresistant LNF Angel), and the chaptalization of the must with sucrose (16 °Brix). Alcoholic fermentation was carried out in an incubator with temperature control at 34 ± 1 °C. The pH, total soluble solids, titratable acidity, alcohol content, and density of the fermented products were monitored daily. The chaptalized must with amylase addition and thermoresistant yeast had the best performance during alcoholic fermentation, demonstrating that thermoresistant yeast is an economically advantageous and efficient alternative for the cagaita juice fermentation process. Subsequently, acetic fermentation was carried out using the slow method. Heat-resistant yeast without added enzymes was used to produce cagaita acetic fermented beverages within the parameters of the Brazilian legislation. Furthermore, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in the final product were observed. The work demonstrated the possibility of using cagaita fruits in biotechnological processes to produce new food products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Beverage Technology Fermentation and Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Leave the Milk for the Calf and Spread the Word: Exploring Factors Determining US Consumers’ Willingness to Try Plant-Based Milk Alternatives and Their Word-of-Mouth Sharing about Plant-Based Milk Alternatives
by
Meike Rombach, Lei Cong and David L. Dean
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 27; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020027 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Plant-based milk alternatives are important beverages in US consumer markets. Sustainability, consumer awareness, lifestyle changes, and other value-based reasons are why these beverages are increasing in popularity. The present study is focused on plant-based milk alternatives. It builds on an online consumer survey
[...] Read more.
Plant-based milk alternatives are important beverages in US consumer markets. Sustainability, consumer awareness, lifestyle changes, and other value-based reasons are why these beverages are increasing in popularity. The present study is focused on plant-based milk alternatives. It builds on an online consumer survey that explores the factors explaining US consumers’ willingness to try plant-based milk alternatives and their word-of-mouth sharing about these beverages. Animal welfare concerns, environmental concerns, health consciousness, and dairy preferences are the factors under investigation. Results show that animal welfare, dairy preference, environmental concerns, and plant-based milk enthusiasm are significant predictors for willingness to try plant-based milk alternatives. Dairy preferences, environmental concerns, and plant-based milk enthusiasm predict the word-of-mouth factors. Overall, plant-based milk enthusiasm is the strongest driver for both consumer behaviours. Best practice recommendations address marketers in the US food and beverage industry and provide suggestions on how to target different consumer groups based on nutritional preferences and needs and on value-based product characteristics.
Full article
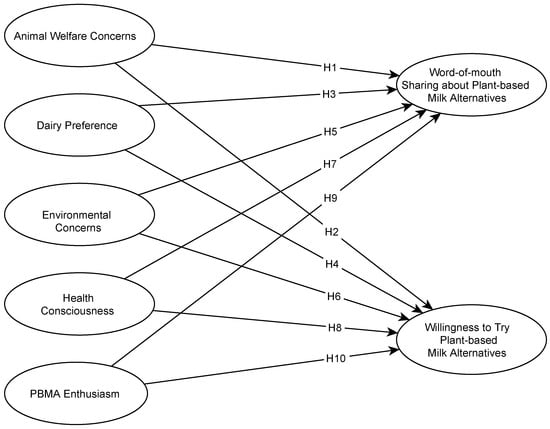
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Metschnikowia pulcherrima as a Co-Fermenter with Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Influence on Wine Aroma during Fermentation and Ageing
by
Lesly L. Torres-Díaz, Rebeca Murillo-Peña, Miquel Iribarren, Itziar Sáenz de Urturi, Sandra Marín-San Román, Miriam González-Lázaro, Eva P. Pérez-Álvarez and Teresa Garde-Cerdán
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020026 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Non-Saccharomyces yeasts, particularly Metschnikowia pulcherrima, are considered alternatives to SO2 in winemaking, combating specific microorganisms. The sensory profile of the wine is contingent upon the type of yeast, the fermentation conditions, and the concentration and mode of application with Saccharomyces
[...] Read more.
Non-Saccharomyces yeasts, particularly Metschnikowia pulcherrima, are considered alternatives to SO2 in winemaking, combating specific microorganisms. The sensory profile of the wine is contingent upon the type of yeast, the fermentation conditions, and the concentration and mode of application with Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains (whether pure or used in mixed/sequential co-fermentation). This study assessed the aroma in red wines produced with S. cerevisiae (Sc) and M. pulcherrima (Mp, non-Sc), incorporating variations in the method of addition and the inclusion or exclusion of SO2. The enological parameters of the wines were slightly affected. Volatile compounds were analysed in the wines through gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) at three moments: at the end of malolactic fermentation (MLF) and after 6 and 9 months of bottle ageing. Sequential fermentation of Sc and Mp reduced the concentration of most identified alcohols and acids, which is favourable, as these compounds can yield undesirable aromas at high concentrations. Regardless of the yeast mixture and Mp dose, a majority of the acetate esters and ethyl esters were quantified at concentrations above their perception thresholds, thus enhancing the sensory quality of the wines. Sensory analysis of wines showed generally positive evaluations. Using non-Saccharomyces as an alternative to SO2 improves the aromatic profile of wines.
Full article
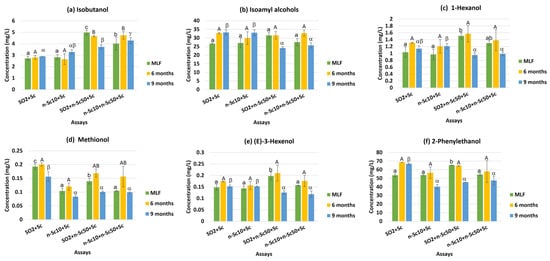
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Packaging Material Use Efficiency of Commercial PET and Glass Bottles for Mineral Water
by
Anna Gress, Kajetan Müller and Sven Sängerlaub
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 25; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020025 - 05 Apr 2024
Abstract
The influence of the bottle material (glass, PET), the reusability (reusable and disposable bottles), and the carbonization (still, medium, classic mineral water) on the filling ratio, packaging material use efficiency, cost, and shelf life were evaluated. Two hundred different bottles were purchased and
[...] Read more.
The influence of the bottle material (glass, PET), the reusability (reusable and disposable bottles), and the carbonization (still, medium, classic mineral water) on the filling ratio, packaging material use efficiency, cost, and shelf life were evaluated. Two hundred different bottles were purchased and characterized regarding their filling volume, the weight of the bottle, the weight of the closure, the weight of the label, and the maximum full-rim volume of the bottle. The packaging material use efficiency was calculated. The shelf life was evaluated by calculating the water vapor and carbon dioxide transmission rates. The ratio of filling volume to the packaging weight of disposable PET bottles was, on average, two times higher compared to returnable PET bottles and 20 times higher compared to glass bottles. Shelf life was, on average, higher than factor two for glass bottles compared to PET bottles. On average, but not in all cases, mineral water packaged in disposable PET bottles was cheaper compared to reusable PET and glass bottles. This paper provides a benchmark for the packaging community, especially when data for life cycle assessment are required, and the different advantages and disadvantages of different bottle materials for mineral water are shown.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Tea, Coffee, Water, and Other Non-Alcoholic Beverages)
►▼
Show Figures
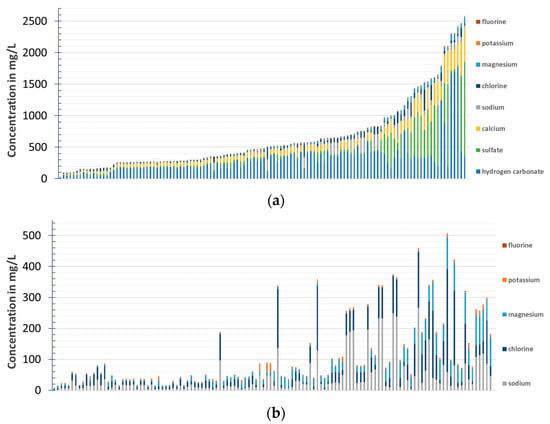
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Aromatic Characterization of Graševina Wines from Slavonia and Podunavlje Sub-Regions
by
Mitja Martelanc, Guillaume Antalick, Tatjana Radovanović Vukajlović, Branka Mozetič Vodopivec, Melita Sternad Lemut, Ahmad Hosseini, Valentina Obradović, Josip Mesić and Lorena Butinar
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 24; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020024 - 31 Mar 2024
Abstract
This study investigated the chemical aromatic profiles of 60 volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including 21 terpenes, 6 norisoprenoids, 6 volatile phenols, 4 C-6 alcohols, and 23 esters, in Graševina wines originating from Slavonia and Podunavlje sub-regions (Croatia). Headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography coupled
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the chemical aromatic profiles of 60 volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including 21 terpenes, 6 norisoprenoids, 6 volatile phenols, 4 C-6 alcohols, and 23 esters, in Graševina wines originating from Slavonia and Podunavlje sub-regions (Croatia). Headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometric detection (HS-SPME-GCMS) was used to assess 60 VOCs, and a novel HS-SPME-GCMS method for the determination of terpenes and norisoprenoids was developed and validated. Statistical analysis found no significant differences between VOCs present in Graševina wines and others wines (Chardonnay and Pinot gris); nonetheless, comparison of VOC fingerprints between different wines from the same producer showed that four terpenes (α-terpinene, γ-terpinene, 1,4-cineol, and 4-terpineol) were present in higher amounts in Graševina wines when compared to other wines. By exclusively examining VOCs within Graševina wines through the utilization of a heatmap and hierarchical clustering, a distinct visualization of samples and VOCs emerged, highlighting the vintage effect. Simultaneously, a partial least squares discriminant analysis model was developed with a confidence interval of 95%, demonstrating a noticeable distinction between samples originating from the western and eastern regions. Furthermore, by employing the heatmap using only VOCs from the terpene and norisoprenoidic groups, a clear separation of samples into two groups was observed based on geographical origin; namely, higher concentrations of norisoprenoids and terpenes were observed in the Slavonia sub-region. These results suggest that terpenes and norisoprenoids to a lower extent may be valuable aromatic markers for the regional typicality of Graševina wines.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Wine, Spirits and Oenological Products)
►▼
Show Figures
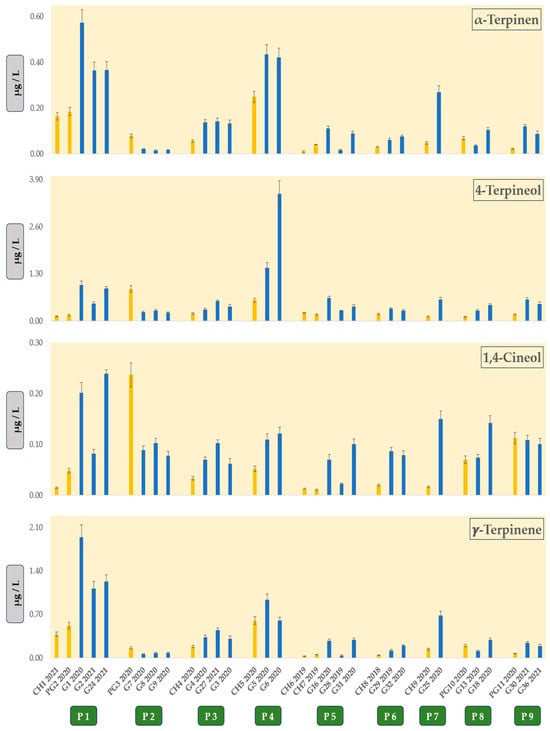
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Brewing Mainly from Stale Bread: A Pale Ale Case Study
by
Pedro Coelho, Catarina Prista and Isabel Sousa
Beverages 2024, 10(2), 23; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10020023 - 29 Mar 2024
Abstract
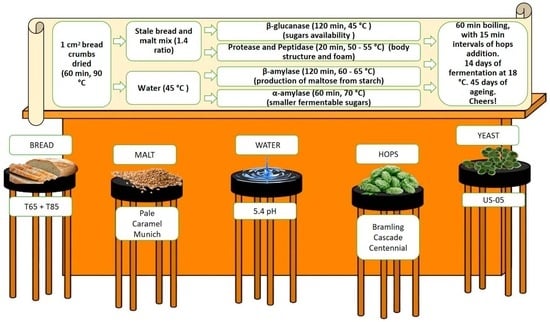
Contemporary environmental concerns have led to the prioritization of sustainable production and material circularity, no matter what the industrial field of activity. Bread waste is a major element of overall food waste since, worldwide, bread remains a widespread staple food. A considerable proportion
[...] Read more.
Contemporary environmental concerns have led to the prioritization of sustainable production and material circularity, no matter what the industrial field of activity. Bread waste is a major element of overall food waste since, worldwide, bread remains a widespread staple food. A considerable proportion of bread consumption is of fresh, baked bread, consumed daily, generating substantial amounts of stale bread. Therefore, efforts to reintroduce this waste into the food value chain can make a significant contribution to reaching zero food waste, which is a major target in European countries. Possible ways to produce new raw materials through starch enzymatic hydrolysis include brewing, which is an activity in which incorporating stale bread is of great interest. Mashing parameters in brewing processing are the main focus of this study, primarily the time and temperature required to acquire optimal enzymatic activity for starch-efficient hydrolysis. Extending the mashing time to 290 min, within a temperature range of 45–75 °C, allowed us to replace 50% of the required malt with stale bread, thus obtaining a successful pale ale beer. The incorporation of stale bread in a 50:50 ratio did not affect the overall character of the beer, although the alcohol levels stood around 2% below a standard beer’s average level. Depending on the brewer’s final goal, this lighter kind of beer may be well-aligned with new consumer trends supporting more sustainable and lower-alcohol beverages.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Malting, Brewing and Beer)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of Tea and Kombucha from Rhizophora mucronata Leaves
by
Yunita Eka Puspitasari, Emmy Tuenter, Annelies Breynaert, Kenn Foubert, Herawati Herawati, Anik Martinah Hariati, Aulanni’am Aulanni’am, Tess De Bruyne and Nina Hermans
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 22; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010022 - 15 Mar 2024
Abstract
A decoction of Rhizophora mucronata Lam. mangrove bark is used as an antidiabetic treatment in Asia. Kombucha tea is a fermented beverage, which is also claimed to be antidiabetic. In this work, the potency of R. mucronata leaves as α-glucosidase inhibitor was studied
[...] Read more.
A decoction of Rhizophora mucronata Lam. mangrove bark is used as an antidiabetic treatment in Asia. Kombucha tea is a fermented beverage, which is also claimed to be antidiabetic. In this work, the potency of R. mucronata leaves as α-glucosidase inhibitor was studied to assess whether it could be a suitable alternative to the use of R. mucronata bark. α-glucosidase inhibitory activities were determined for three extracts prepared from R. mucronata leaves, being the unfermented tea of R. mucronata leaves, the fermented kombucha tea and an 80% methanolic extract of the residual R. mucronata leaves. Flavonoid glycosides were identified in tea powder, kombucha tea and in the crude methanolic extract. Both the unfermented tea and the kombucha tea after 7 days of fermentation inhibited α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 0.12 ± 0.02 mg/mL and 0.09 ± 0.04 mg/mL, respectively. The methanolic extract showed a stronger α-glucosidase inhibitory activity compared to the kombucha tea and tea powder with an IC50 value of 0.0435 ± 0.0007 mg/mL. Acarbose, used as a positive control, inhibited α-glucosidase with an IC50 value of 2.4 ± 0.2 mg/mL. It was found that the three types of preparations of R. mucronata all were potent α-glucosidase inhibitors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Ways to Achieve Healthy and Sustainable Diets)
►▼
Show Figures
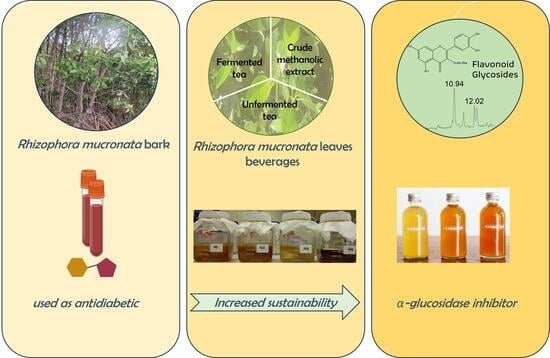
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
White Sparkling Wine Proteins and Glycoproteins and Their Behavior in Foam Expansion and Stability
by
Giovanna Lomolino, Simone Vincenzi, Stefania Zannoni, Mara Vegro and Alberto De Iseppi
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 21; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010021 - 07 Mar 2024
Abstract
The volume and stability of wine foams are influenced by many components of the matrix, especially proteins. However, the synergistic or inhibiting effects among these protein fractions, as well as their interactions with other wine components, are still under study. The present research
[...] Read more.
The volume and stability of wine foams are influenced by many components of the matrix, especially proteins. However, the synergistic or inhibiting effects among these protein fractions, as well as their interactions with other wine components, are still under study. The present research aims to understand the individual and cooperative effects of different wine proteins and glycoproteins on the volume and stability of foams. To address this objective, different protein fractions were purified from a Chardonnay white wine and tested in different model wine conditions (with/without ethanol), along with a commercial yeast-based oenological additive. Different fractions were considered, including total protein fraction (FT), Mannoproteins (MP), and non-mannosylated proteins (NMP), as well as a protein fraction soluble in ammonium sulfate (FSA). These protein fractions were characterized, and their foaming properties were evaluated using a modified Rudin apparatus. The results showed that FT exhibited higher foam expansion (FE%) compared to its subfractions (NMP and MP) that, when tested individually, did not guarantee optimal foam formation. This suggests that foaming properties are enhanced when both glycosylated and non-glycosylated proteins are present in the system. Additionally, the foaming behavior was influenced by the presence of ethanol in the model wine. The FSA fraction demonstrated high foam expansion and stability, with ethanol enhancing foam expansion but reducing stability. A commercial yeast-based oenological additive, mainly containing glycoproteins, was also tested and behaved similarly to MP. This study provides valuable insights for sparkling wine producers to optimize practices for enhancing product quality and confirm previous research regarding the role of the synergy between MP and NMP in wine foam formation and stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Quality, Nutrition, and Chemistry of Beverages)
►▼
Show Figures
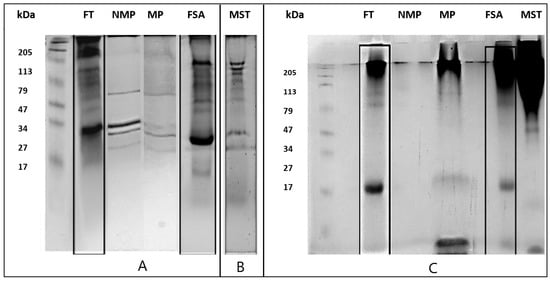
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Craft Brewery Wastewater Treatment in a Scalable Microbial Fuel Cell Stack
by
Olivia Zapata-Martínez, Denys Villa-Gomez, Raul Tapia-Tussell, Jorge Dominguez-Maldonado, Galdy Hernández-Zárate, Elda España-Gamboa, Rubí Valdez-Ojeda and Liliana Alzate-Gaviria
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 20; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010020 - 21 Feb 2024
Abstract
Craft breweries release wastewater into the environment, posing serious environmental concerns. Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are an attractive technology that has been used in industrial wastewater treatment. This study used a scalable system of nine MFCs (stacked) to treat 150 L of craft
[...] Read more.
Craft breweries release wastewater into the environment, posing serious environmental concerns. Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are an attractive technology that has been used in industrial wastewater treatment. This study used a scalable system of nine MFCs (stacked) to treat 150 L of craft brewery wastewater (CBW). The CBW had 1831 ± 85 mg COD (chemical oxygen demand) L−1. The hydraulic retention time was 5 days, with a COD removal percentage of 93 ± 1.8%. The total internal resistance of the stack was 204.8 ± 5.2 Ω at 26 ± 2 °C without the use of a metal catalyst; the reduction of oxygen was the limiting process. Finally, the sequence of treatments applied with this proposed system demonstrated its self-sustainability, which could be a viable option for the real-life conditions of this kind of wastewater. Further research is needed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Brewing Technology – Innovations in Raw Materials, Processing and Products)
►▼
Show Figures
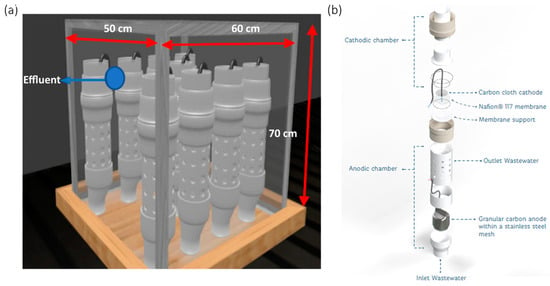
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Understanding Sparkling Wine Consumers and Purchase Cues: A Wine Involvement Perspective
by
Gary J. Pickering and Belinda Kemp
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 19; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010019 - 16 Feb 2024
Abstract
Research on sparkling wine (SW) consumers, their market segmentation, and how they use purchase cues is relatively sparse compared to that for table wine, despite the substantial growth in sparkling wine in recent years. We address these gaps and particularly how the importance
[...] Read more.
Research on sparkling wine (SW) consumers, their market segmentation, and how they use purchase cues is relatively sparse compared to that for table wine, despite the substantial growth in sparkling wine in recent years. We address these gaps and particularly how the importance of SW purchase cues varies with wine involvement in an online survey of SW consumers from Ontario, Canada (n = 1011). Thirty intrinsic and extrinsic purchase cues were rated for importance (n = 609), and wine involvement was determined using the shortened version of the wine involvement scale. Overall, consumers rated (in descending order) price, flavour, quality, country, and sweetness level as the most important purchase cues, whereas several extrinsic factors, including bottle colour and shape, awards won, and vintage were of low importance. Females were 1.4 times more likely than males to cite target end use as the most important purchase cue. We further show that SW consumers can be segmented into three wine involvement categories (low, medium, high) which vary across multiple demographic, consumption, knowledge, and preference measures (n = 1003). Notably, the importance of six purchase cue categories (manufacture, price, endorsements, parentage, prestige/reputation, and place) varied with wine involvement (n = 609). These findings provide timely guidance for marketers and retailers seeking to align their products and communications with the needs and perceptions of SW consumers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wine Economy and Consumption)
►▼
Show Figures
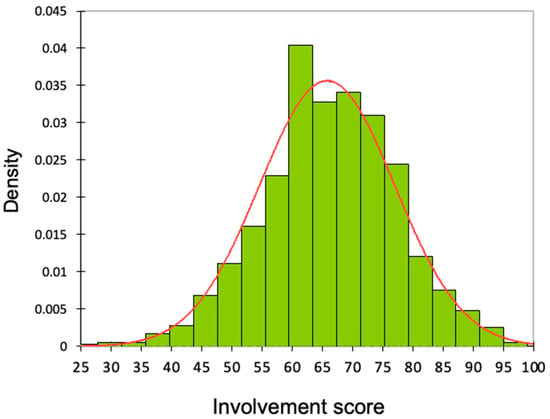
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey
by
Viral Shukla, Marcela Villarreal and Olga I. Padilla-Zakour
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 18; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010018 - 06 Feb 2024
Abstract
Drinkable yogurts are low-viscosity beverages often created by diluting yogurt with water or high-value-fluid milk. Yogurt acid whey, a typically discarded byproduct of the Greek yogurt industry, may serve as an upcycled ingredient for these types of products with minimal processing. In this
[...] Read more.
Drinkable yogurts are low-viscosity beverages often created by diluting yogurt with water or high-value-fluid milk. Yogurt acid whey, a typically discarded byproduct of the Greek yogurt industry, may serve as an upcycled ingredient for these types of products with minimal processing. In this study, differing concentrations of acid whey (35%, 40%, and 45% w/w) were added to a mango yogurt beverage with 0.2% and 0.4% w/w stabilizer and analyzed for physicochemical properties over a 40-day period. The analysis indicated that the percentage of acid whey was positively correlated with both viscosity and water-holding capacity. A hedonic sensory analysis of the beverages indicated positive consumer acceptance of such upcycled products, with enhanced acceptance at 25–35% addition. This study demonstrates the potential for consumer acceptance of yogurt beverages upcycled with native-acid whey, providing insights into sustainable practices within the food industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Tea, Coffee, Water, and Other Non-Alcoholic Beverages)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Survival of Salmonella enterica Strains in Ready-to-Eat Fruit Purees under Different Storage Temperatures
by
Maria Belén Bainotti, Pilar Colás-Medà, Inmaculada Viñas, Salvador Garza and Isabel Alegre
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 17; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010017 - 02 Feb 2024
Abstract
Salmonella enterica, known for its resilience to acidic environments, has been linked to foodborne outbreaks of illness from fruit derivatives. This study aimed to assess the survival of five serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica in various fruit purees subjected to different
[...] Read more.
Salmonella enterica, known for its resilience to acidic environments, has been linked to foodborne outbreaks of illness from fruit derivatives. This study aimed to assess the survival of five serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica in various fruit purees subjected to different storage temperatures. Among the studied serovars, S. enteritidis exhibited the most significant population decrease in all fruit purees. In contrast, S. Agona, S. Gaminara, S. Michigan, and S. Montevideo survived in peach puree at 4 °C for at least 3 days, and S. Agona, S. Gaminara, and S. Montevideo maintained their initial levels in pear puree under the same time/temperature conditions. However, none of the strains were detectable in plum and black currant purees after 2 days at 4, 15, or 25 °C. These findings highlight variations in the behaviour of S. enterica serovars within different fruit purees. Likewise, low-temperature conditions prolonged the survival of the tested strains in all fruit purees analysed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Beverage Technology Fermentation and Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
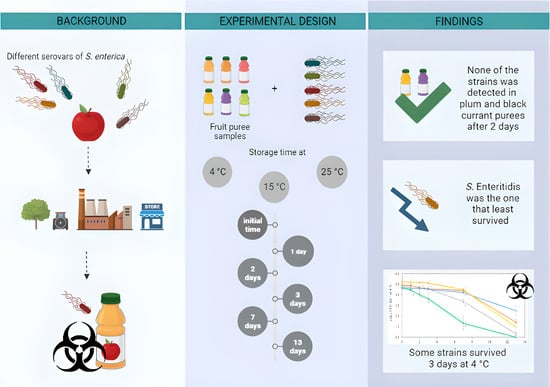
Graphical abstract
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Investigating the Malting Suitability and Brewing Quality of Different Rice Cultivars
by
Bernardo P. Guimaraes, Florian Schrickel, Nils Rettberg, Shannon R. M. Pinson, Anna M. McClung, Kaushik Luthra, Griffiths G. Atungulu, Xueyan Sha, Christian de Guzman and Scott Lafontaine
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 16; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010016 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
Nineteen globally diverse rice cultivars were analyzed for various chemical parameters important to malting, including germination energy, protein, apparent amylose content, and gelatinization temperatures (GT). The rice cultivars were then malted, and congress mashes were produced. Several parameters important to brewing were then
[...] Read more.
Nineteen globally diverse rice cultivars were analyzed for various chemical parameters important to malting, including germination energy, protein, apparent amylose content, and gelatinization temperatures (GT). The rice cultivars were then malted, and congress mashes were produced. Several parameters important to brewing were then assessed in the malts and worts (i.e., extract, soluble protein, free amino nitrogen (FAN), GT, etc.). The rice malts produced were saccharified to varying degrees, had high limit dextrinase activities, and contained sufficient FAN/protein concentrations. This suggests their potential to yield robust fermentations in beer styles with high adjunct inclusions without requiring additional nitrogen supplementation. Rice cultivars with purple-pigmented bran were found to yield unique wort colors and could serve as novel natural gluten-free colorants for future recipes. Overall, these findings suggest that malted rice could offer a more local and gluten-free source of starch for brewers and beverage/food producers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Featured Papers in Malting, Brewing and Beer Section—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
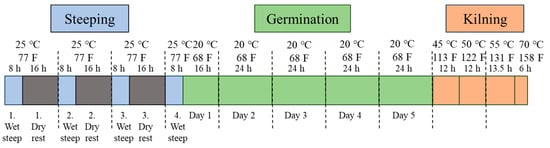
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Soft Drink Addiction Scale: Reliability and Validity Analysis in Young Mexican People
by
Cesar Campos-Ramírez, Nicolas Camacho-Calderon, Maria Elena Villagran-Herrera, Adriana Aguilar-Galarza, Miriam Aracely Anaya-Loyola and Jorge Palacios-Delgado
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 15; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010015 - 28 Jan 2024
Abstract
It has been proposed that the consumption of foods high in sugar or fat may cause addictive behavior. The aim of this study was to adapt and validate a soft drink addiction scale that can be used in future studies and to strengthen
[...] Read more.
It has been proposed that the consumption of foods high in sugar or fat may cause addictive behavior. The aim of this study was to adapt and validate a soft drink addiction scale that can be used in future studies and to strengthen the proposal of food addiction with the hypothesis that people with high consumption of soft drinks have similar characteristics to people who consume abuse drugs. A non-probabilistic convenience sample of 394 Mexican participants answered a soft drinks’ consumption frequency questionnaire, an addiction scale, and a self-efficacy scale for soft drinks’ consumption. Additionally, anthropometric measurements were taken. The addiction scale showed three factors with an adequate reliability (Cronbach’s alpha coefficient = 0.903), as well as construct validity and criterion validity with the self-efficacy scale and total body fat percentage on soft drinks, mainly those with substantial caloric content. Additionally, the results showed a predictive value for soft drink consumption, strengthening its validity. This scale is useful to identify and evaluate the characteristic patterns of a substance addiction. The total reliability indicates that the items as a whole are correlated with each other and that the scale is stable to be used over time. This is the first study that evaluates the addictive characteristics of soft drink consumption through a scale, and it represents an advance in the exploration of the behavioral sciences field and an important tool for the creation of public health policies, mainly in countries with a high consumption of these beverages.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Tea, Coffee, Water, and Other Non-Alcoholic Beverages)
Open AccessReview
Value Addition and Coconut-Based Beverages: Current Perspectives
by
Salvatore Parisi, Carmelo Parisi and Suni Mary Varghese
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 14; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010014 - 25 Jan 2024
Abstract
(1) Background: The definition of value addition is based on the process or processes which are used to transform, physically, the initial raw material into the final food or non-food article. Diversification can enhance the possibility of increased gains. The aim of this
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: The definition of value addition is based on the process or processes which are used to transform, physically, the initial raw material into the final food or non-food article. Diversification can enhance the possibility of increased gains. The aim of this work is to give a reliable description of value addition when speaking of coconut-based beverages among all possible derivatives. (2) Methods: A systematic review in which the main papers on the argument have been critically examined and discussed. (3) Results: Processing degree is a consequence of consumers’ requests. Three different drivers for value addition have been considered: packaging, durability, and size options; sensorial features; and sustainability. The results of this investigation have highlighted the added value of several products because of recyclable packaging materials, intermediate- or long-durability expectations, different available sizes, and good or excellent sensorial performances. (4) Conclusions: There are different value-added coconut-based beverages with interesting perspectives. On the other hand, sustainability and eco-friendly policies may be a problem for those products that are produced similarly to non-coconut-based beverages. The opportunity presented by certified organic and/or fair-trade products could help the coconuts industry in the near future. More research is still needed on this topic.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Tea, Coffee, Water, and Other Non-Alcoholic Beverages)
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of Xinomavro Red Wine Aging with Various Wood Chips Using Pulsed Electric Field
by
Artemis K. Toulaki, Vassilis Athanasiadis, Theodoros Chatzimitakos, Dimitrios Kalompatsios, Eleni Bozinou, Kosmas Roufas, George I. Mantanis, Vassilis G. Dourtoglou and Stavros I. Lalas
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 13; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010013 - 24 Jan 2024
Abstract
This study explored the potential of pulsed electric field (PEF) as an alternative wine-aging method in four Xinomavro red wines with the implementation of several wood chips (apricot, peach, apple, cherry, acacia, and oak trees). The evolution of total polyphenol content (TPC) and
[...] Read more.
This study explored the potential of pulsed electric field (PEF) as an alternative wine-aging method in four Xinomavro red wines with the implementation of several wood chips (apricot, peach, apple, cherry, acacia, and oak trees). The evolution of total polyphenol content (TPC) and sensory properties of the wines were investigated. Sensory evaluation revealed that PEF treatment increased volatile compound extraction from each wood chip, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the wines. The utilization of acacia tree wood chips in Goumenissa wine led to a notable increase of 10.84% in TPC from the control sample, reaching 2334.74 mg gallic acid equivalents/L. A notable outcome was that PEF decreased TPC, a trend that was also verified through correlation analyses. The highest positive impact of PEF was observed in peach tree wood chips in Goumenissa wine, with a significant increase of 11.05% in TPC. The results from the volatile compound analysis revealed an increase in alcohols and esters from 0.24% to 23.82%, with the highest proportion found in 2-phenylethanol (16.92 mg/L) when utilizing peach tree wood chips in the production of Amyndeo wine. This study could provide a benchmark for rapid, efficient, and cost-effective wine aging through the implementation of the PEF process.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Wine, Spirits and Oenological Products)
►▼
Show Figures
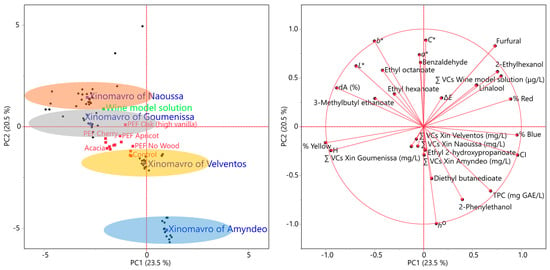
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Validation of N-Methylpyridinium as a Feasible Biomarker for Roasted Coffee Intake
by
Beate Brandl, Coline Czech, Susanne I. Wudy, Anja Beusch, Hans Hauner, Thomas Skurk and Roman Lang
Beverages 2024, 10(1), 12; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/beverages10010012 - 23 Jan 2024
Abstract
Health-related nutritional human studies rely on the validity of dietary data provided by study participants. Reliable biomarkers for food intake help objectify data collected by food frequency questionnaires. They facilitate the monitoring of compliance with the study requirements, e.g., abstinence from food, help
[...] Read more.
Health-related nutritional human studies rely on the validity of dietary data provided by study participants. Reliable biomarkers for food intake help objectify data collected by food frequency questionnaires. They facilitate the monitoring of compliance with the study requirements, e.g., abstinence from food, help clean biased data, and remove non-compliant individuals. Biomarker candidates are often revealed by sophisticated metabolomics analyses of body fluids, e.g., urine or plasma, collected from case and control study populations. However, validation for using a biomarker candidate in real-life scenarios is seldomly executed. Coffee is a food item of high interest because of the abundance of bioactive compounds and the regularity of life-time consumption by a large part of the population. Coffee has been found to positively impact cardiovascular risk, type 2 diabetes, and cognitive decline. Coffee and its health implications, therefore, are of high interest. A suitable dietary biomarker for coffee consumption is desirable for the clear classification of study participants as coffee drinkers or non-coffee drinkers to enable correlation of physiological response to dietary habits, e.g., coffee consumption. Here, we propose the roast coffee compound N-methylpyridinium (NMP) as a promising biomarker of pragmatic use to distinguish a coffee drinker from a non-coffee drinker. NMP is an easily accessible analytical target from the plasma and urine matrix that can help determine precedent exposure to roasted coffee products. We review the published information on the coffee compound N-methylpyridinium in foods, coffee, and plasma/urine after coffee consumption, and evaluate the data in the context of the proposed food biomarker criteria “plausibility”, “time- and dose–response”, “robustness”, “reliability”, “stability”, “analytical performance”, and “reproducibility”. An additional data set is acquired to fill the gaps in the literature. In summary, we conclude that the abundance of NMP can serve as a reliable analytical tool to verify recent consumption of roasted coffee. The use of NMP appears limited to being qualitative, as NMP abundance in coffee and human biosamples is affected by several parameters, e.g., the roasting conditions and the volume and time of coffee consumed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Tea, Coffee, Water, and Other Non-Alcoholic Beverages)
►▼
Show Figures
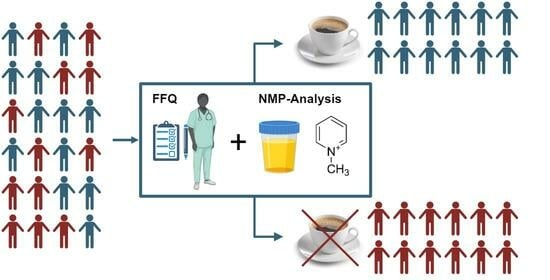
Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Beverages Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Beverages, Fermentation, Foods, Molecules, Separations
Advances in Analysis of Flavors and Fragrances: Chemistry, Properties and Applications in Food Quality Improvement
Topic Editors: Ana Leahu, Marìa Soledad Prats Moya, Cristina GhineaDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Agronomy, Beverages, Fermentation, Horticulturae, Plants
Grapevine Facing Climate Change: From Land, through Plants to Grapes and Wine
Topic Editors: Othmane Merah, Ana Fernandes De Oliveira, Daniela Satta, Mario Cunha, Jesus Yuste, Jalloul BouajilaDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Beverages, Dairy, Foods, IJERPH, Nutrients
Ways to Achieve Healthy and Sustainable Diets
Topic Editors: Verônica Cortez Ginani, Renata Puppin ZandonadiDeadline: 16 October 2024
Topic in
Beverages, Foods, Molecules, Nutrients, Separations
Advances in Analysis of Food and Beverages
Topic Editors: Anna M. Kaczmarek, Constantinos G. TsiafoulisDeadline: 31 January 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Beverages
Featured Papers in Malting, Brewing and Beer Section—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Luis F. Guido, Pavel DostálekDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Beverages
Sensory Analysis as a Tool for the Improvement of the Quality of Beverages
Guest Editors: Enrique Durán-Guerrero, M. Carmen Rodríguez-DoderoDeadline: 15 June 2024
Special Issue in
Beverages
Traditional, Functional and Novel Fruit Beverages: Cultivation, Processing and Consumption
Guest Editors: Nicola Francesca, Vita Di Stefano, Vittorio FarinaDeadline: 5 August 2024
Special Issue in
Beverages
Developments in Brewing Processing and Analytical Techniques for the Evaluation of Beer Quality
Guest Editor: Antonietta BaianoDeadline: 5 September 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Beverages
Wine and Beverage: Fermentation and Conservation Technologies
Collection Editors: Antonio Morata, António Manuel Jordão, Fernanda Cosme, Ileana Vigentini