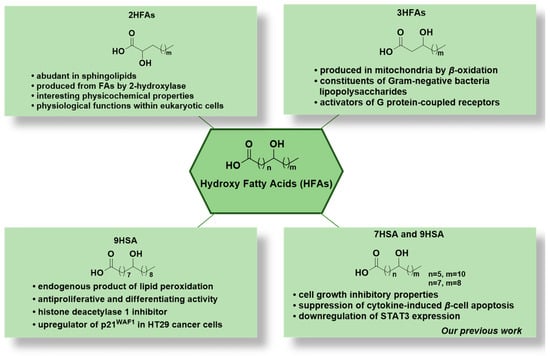
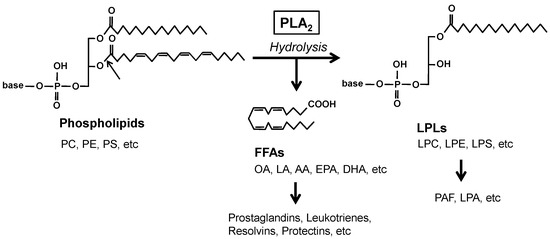
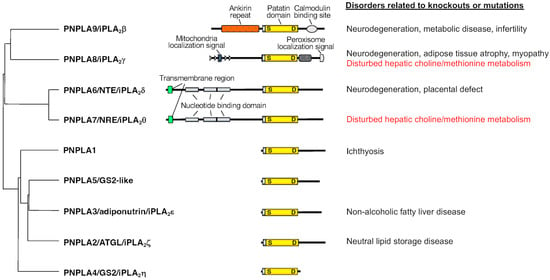
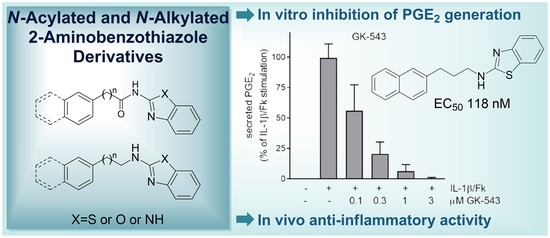
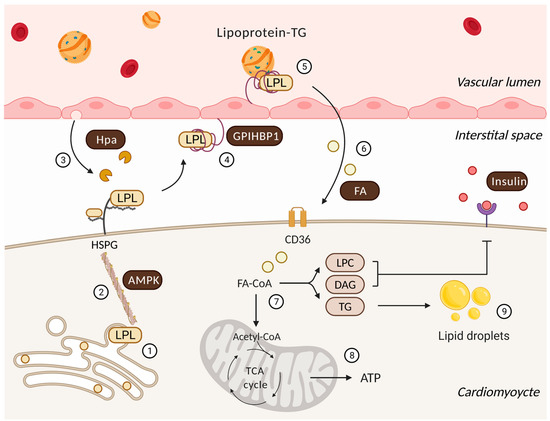
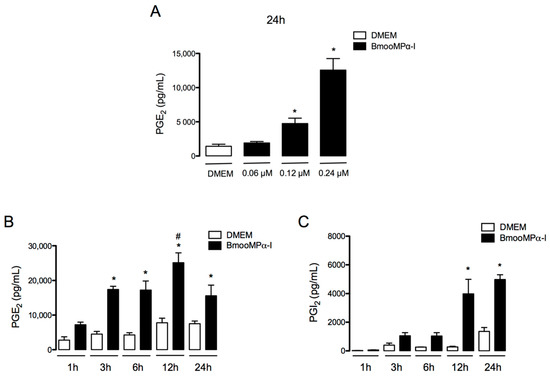
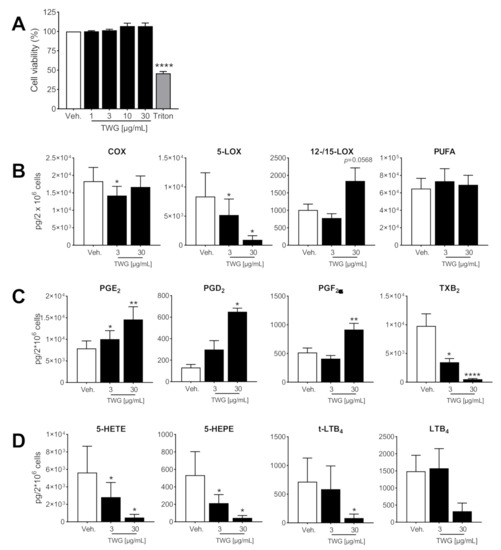
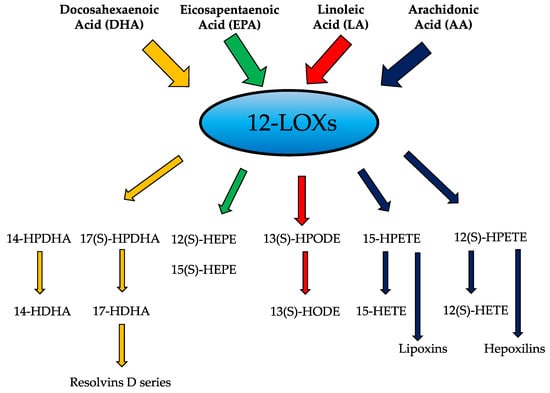
Bioactive Lipids in Inflammation, Diabetes and Cancer
A topical collection in Biomolecules (ISSN 2218-273X). This collection belongs to the section "Biological Factors".
Viewed by 55966Editors
Interests: design, synthesis and study of enzyme inhibitors; inhibitors of phospholipase A2; inhibitors of autotaxin; synthesis and study of bioactive lipids; synthesis of small molecules exhibiting anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activity; organocatalysis; biotransformations in organic synthesis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: pancreatic islet function; beta-cell death; lipid signaling; lipidomics; phospholipases A2; type 1 diabetes; autoimmunity; alternative splicing; bone formation
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
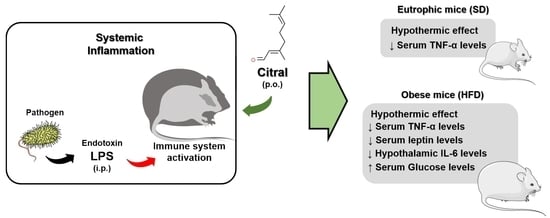
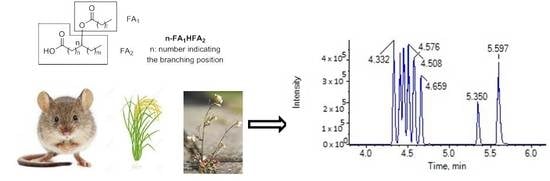
Lipids are essential components of the cell membrane shown to play many roles in mediating and controlling a wide array of cellular activities including membrane structure and organization, metabolic and gene regulation, protein structure and function, and signaling pathways. Various lipid molecules have been intimately linked to inflammatory and immune responses, cell proliferation and apoptosis and clearly shown to be major contributors to many pathologies, including diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. Lipid metabolizing enzymes and lipid receptors are excellent targets for the development of enzyme inhibitors and receptor modulators as novel therapeutic agents. The aim of this collection is to compile review articles and original research articles covering the recent advances in the biochemistry, chemistry, pharmacology, analysis, functional assessment, and clinical translational impact of bioactive lipids relating to their involvement in inflammation, diabetes and cancer.
Prof. Dr. George Kokotos
Prof. Sasanka Ramanadham
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Biomolecules is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- bioactive lipids
- lipidomics–lipid analysis
- lipid metabolizing enzymes
- enzyme inhibitors
- lipid signaling
- lipid receptors
- fatty acids
- eicosanoids
- sphingolipids
- specialized pro-resolving mediators
- therapeutic molecules
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Essential fatty acids and their metabolites in inflammation, fisbetes mellitus and cancer- based on our previous snd current work in these three areas.
Authors: Undurti N. Das; et al.
Affiliation: UND Life Sciences, 2221 NW 5th St, Battle Ground, WA 98604, USA