Electrochemical Biosensors for Medical Diagnosis (Closed)
A topical collection in Chemosensors (ISSN 2227-9040). This collection belongs to the section "Electrochemical Devices and Sensors".
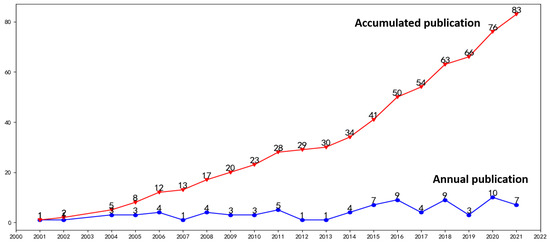
Viewed by 44889
Editor
Interests: amperometric biosensors based on enzyme immobilization; electrosynthesized conducting and insulating polymers; characterization of modified electrodes by electrochemical; gravimetric (QCM) and spectroscopic techniques (XPS and AFM); metal nanoparticles and electrochemical sensors
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The recent events we are experienced tragically highlight the need of establishing an accurate diagnosis at the early stage of severe diseases to preserve patient healing and, sometimes, even survival. Current methodologies for the detection of specific biomarkers that identify a particular clinical condition certainly assure reliable results but are limited by the expensive equipment, time consuming sample pre-treatment and need of skilled operators.
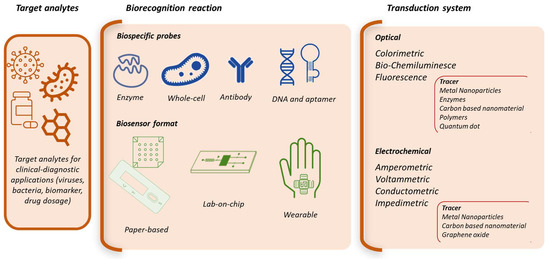
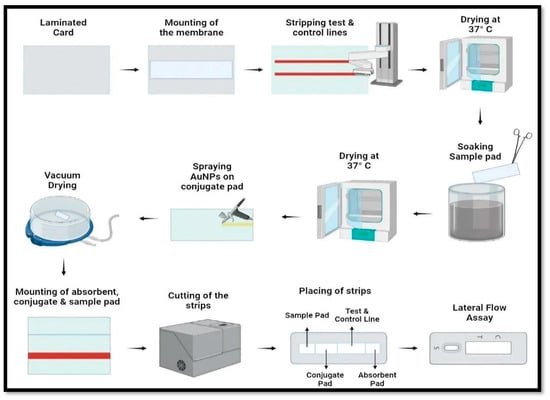
Among the new analytical methods capable of accomplishing effective clinical diagnostic tools, biosensors play a promising role providing ease of execution, specificity for the target analyte, fast response time and capability for continuous monitoring. Particularly, electrochemical biosensors exploit a detection mechanism based on electrochemical reactions that directly generate an electronic signal. This feature greatly simplifies signal transduction avoiding expensive equipment requirements.
Since the pioneering Clark’s enzyme electrode which was then implemented into blood-glucose self-testing device, a huge number of electrochemical biosensors with application in medical diagnostic has been realized. The success of these devices relies on the feasibility to combine the sensitivity of electrochemical methods with the selectivity of the biocomponent towards the target analyte.
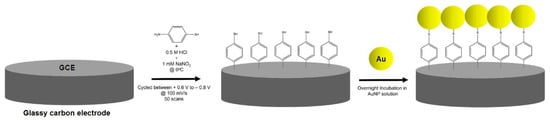
In order to get increasingly performing devices, in the last years many efforts have been devoted to the development of electrode modification approaches able to realize efficient platforms for bioreceptors immobilization along with detection schemes aimed to overcome the undesired effects of electrochemical detection, namely electrode fouling and faradic interference. As an example, novel polymeric films with improved built-in permselectivity and biocompatibility have been electrosynthesized. Particularly, the synergistic interaction of electrochemical detection with electrode modification strategies employing advanced nanostructures and nanomaterials revealed a key element to increase binding sites for anchoring biocomponents on the electrode surface and to enhance the electron transfer between the electrode and target molecules, thus improving the sensitivity of the electrochemical sensor.
The aim of this Special Issue is to focus on the most recent approaches to realize innovative and enhanced electrochemical biosensors for medical diagnosis.
Both review articles and research papers on the highlighted topics are welcome.
Dr. Rosanna CirielloCollection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Chemosensors is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Electrochemical biosensors
- Enzyme-based sensors
- Bioreceptors immobilization
- Amperometric detection
- Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
- Surface functionalization
- Modified electrodes
- Polymeric films
- Composite materials
- Nanostructures and Nanomaterials
- Medical diagnostics