Coatings: 10th Anniversary
(Closed)
A topical collection in Coatings (ISSN 2079-6412).
Viewed by 58666
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
 Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
E-Mail
Guest Editor
Istituto di Chimica dei Composti OrganoMetallici (ICCOM-CNR), Via Madonna del Piano 10, 50019 Sesto Fiorentino, Firenze, Italy
Interests: electrodeposition of materials for renewable energy production; surface engineering; corrosion and corrosion protection; thermal barriers coatings; electron microscopy (SEM, TEM); X-ray techniques for surface structure and composition (XPS, XRF, XRD); electroless deposition of metals and cermet’s; simulation and modelling of complex electrochemical systems
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In 2021, we are celebrating the 10th anniversary of the journal Coatings (ISSN 2079-6412). Since 2011, when the inaugural issue of Coatings was launched, we have already published more than 3,000 papers from more than 5,000 authors. More than 4,000 reviewers have submitted at least one review report. Our sincerest thanks go to our readers, innumerable authors, anonymous peer reviewers, editors, and all the people working in some way for the journal who have joined their efforts for years. These highlights would not have occurred without your participation.
To mark this significant milestone, a Special Issue entitled “Coatings: 10th Anniversary” is being launched. This Special Issue includes high-quality papers under the broad scope of Coatings. We would like to invite you to contribute an original research paper or a comprehensive review article on a trendy or hot topic for peer-review and possible publication.
Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Coatings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (21 papers)
Open AccessReview
Surface Modification of 6xxx Series Aluminum Alloys
by
Kuruveri Udaya Bhat, Devadas Bhat Panemangalore, Spandana Bhat Kuruveri, Merbin John and Pradeep L. Menezes
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 6053
Abstract
Due to their superior mechanical properties, formability, corrosion resistance, and lightweight nature, 6xxx series aluminum (Al) alloys are considered as a promising structural material. Nevertheless, the successful application of these materials depends on their response to the external environment. Recently, designers considered the
[...] Read more.
Due to their superior mechanical properties, formability, corrosion resistance, and lightweight nature, 6xxx series aluminum (Al) alloys are considered as a promising structural material. Nevertheless, the successful application of these materials depends on their response to the external environment. Recently, designers considered the surface properties an equally important aspect of the component design. Due to this concern, these alloys are subjected to varieties of surface modification methodologies. Many methodologies are explored to modify the 6xxx series Al alloys surfaces effectively. These methods are anodizing, plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO), cladding, friction stir processing, friction surfacing, melting, alloying, and resolidification using high energy beams, etc. This review work discusses some of these methods, recent research activities on them, important process variables, and their role on the final properties of the surfaces.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Trends in Chemical Wood Surface Improvements and Modifications: A Review of the Last Five Years
by
Pierre Blanchet and Simon Pepin
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 4667
Abstract
Increasing the use of wood in buildings is regarded by many as a key solution to tackle climate change. For this reason, a lot of research is carried out to develop new and innovative wood surface improvements and make wood more appealing through
[...] Read more.
Increasing the use of wood in buildings is regarded by many as a key solution to tackle climate change. For this reason, a lot of research is carried out to develop new and innovative wood surface improvements and make wood more appealing through features such as increased durability, fire-retardancy, superhydrophobicity, and self-healing. However, in order to have a positive impact on the society, these surface improvements must be applied in real buildings. In this review, the last five years of research in the domain of wood surface improvements and modifications is first presented by sorting the latest innovations into different trends. Afterward, these trends are correlated to specifications representing different normative, ecologic and economic factors which must be considered when expecting to introduce a wood treatment to the market. With this review, the authors hope to help researchers to take into consideration the different factors influencing whether new innovations can leave the research laboratory or not, and thereby facilitate the introduction of new wood surface treatments in the society.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Bio-Based Render for Insulating Agglomerated Cork Panels
by
Francesco Barreca, Natale Arcuri, Giuseppe Davide Cardinali and Salvatore Di Fazio
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2190
Abstract
Natural and bio-based thermal insulation materials play an important role in the lifecycle impact of buildings due to their influence on the amount of energy used in indoor temperature control and the environmental impact of building debris. Among bio-based materials, cork is widespread
[...] Read more.
Natural and bio-based thermal insulation materials play an important role in the lifecycle impact of buildings due to their influence on the amount of energy used in indoor temperature control and the environmental impact of building debris. Among bio-based materials, cork is widespread in the Mediterranean region and is one of the bio-based materials that is most frequently used as thermal insulation for buildings. A particular problem is the protection of the cork-agglomerated panels from external stress and adverse weather conditions; in fact, cork granulates are soft and, consequently, cork panels could be damaged by being hit or by excessive sun radiation. In this study, an innovative external coat for cork-agglomerated panels made of a blending composite of beeswax and rosin (colophony) is proposed. The performance of this composite, using different amounts of elements, was analysed to discover which mix led to the best performance. The mix of 50% beeswax and 50% rosin exhibited the best performance out of all the mixes. This blend demonstrated the best elongation and the lowest fracture density, characteristics that determine the durability of the coating. A performance comparison was carried out between cork panel samples coated with lime render and beeswax–rosin coating. The coating of beeswax and resin highlighted a detachment value about 3.5 times higher than the lime plaster applied on the side of the cork.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Thermal Shock Behavior and Particle Erosion Resistance of Toughened GZ Coatings Prepared by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying
by
Zining Yang, Weize Wang, Shujuan Deng, Huanjie Fang, Ting Yang and Lubin Wang
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 1809
Abstract
Gadolinium zirconate with excellent high-temperature phase stability and sintering resistance has become a very promising candidate material for a new generation of thermal barrier coatings (TBCs). However, the low fracture toughness of gadolinium zirconate greatly limits its application. In this study, gadolinium zirconate
[...] Read more.
Gadolinium zirconate with excellent high-temperature phase stability and sintering resistance has become a very promising candidate material for a new generation of thermal barrier coatings (TBCs). However, the low fracture toughness of gadolinium zirconate greatly limits its application. In this study, gadolinium zirconate (GZ) and two kinds of toughened gadolinium zirconate (GZ/YSZ prepared by mixed powder of Gd
2Zr
2O
7 and YSZ and GSZC prepared by (Gd
0.925Sc
0.075)
2(Zr
0.7Ce
0.3)
2O
7 powder) double-layered TBCs were prepared by atmospheric plasma spraying (APS). The fracture toughness of the GZ/YSZ coating and GSZC coating were 9 times and 3.5 times that of GZ coating, respectively. The results of thermal shock test showed that the three TBCs exhibit different failure mechanisms. During the thermal shock test, cracking occurred at the interfaces between the YSZ layer and the BC or GZ/YSZ layer, while GSZC TBC failed due to premature cracking inside the GSZC layer. The particle erosion rate of the GZ, GZ/YSZ, and GZSC coatings were 1.81, 0.48, and 1.01 mg/g, respectively, indicating that the erosion resistance of coatings is related to their fracture toughness. Furthermore, the superior erosion resistance of the GZ/YSZ and GSZC coatings can be attributed to the conversion of crack propagation path during the erosion test.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Nano-Micro-Structured 6%–8% YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings: A Comprehensive Review of Comparative Performance Analysis
by
Amarnath Kumar, Jenna Moledina, Yuan Liu, Kuiying Chen and Prakash C. Patnaik
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 4085
Abstract
Beneficial properties achieved by nanostructuring effects in materials have generated tremendous interests in applications in surface engineering, especially in thermal barrier coatings (TBC). Limitations in conventional TBC processing for gas turbines and aero-propulsion systems have been exposed during past decades when rapid progress
[...] Read more.
Beneficial properties achieved by nanostructuring effects in materials have generated tremendous interests in applications in surface engineering, especially in thermal barrier coatings (TBC). Limitations in conventional TBC processing for gas turbines and aero-propulsion systems have been exposed during past decades when rapid progress was made in nano-structuring coating research and developments. The present work is a comprehensive review of the current state of progress in nanostructured TBC (Ntbc) in reference to its microstructure, damage progression, failure mechanisms and a wide range of properties. The review aims to address the comparative performance analysis between the nanostructured and conventional (microstructured) 6–8 wt.% yttrium stabilized zirconia (YSZ) TBC systems. Oxidation resistance and sintering behavior in two TBCs are considered as the central focus of discussion. A few schematics are used to represent major microstructural features and failure progression. A performance analysis is performed for standard 2-layer, as well as functionally graded multilayer, TBC systems. A comparison of TBC characteristics processed by plasma spray and vapor deposition techniques is also made as reference. Compared to the sea of R&D efforts made for conventional TBC (Ctbc), limited experimental studies on Ntbc offers conflicting data, and prediction modeling and computational research are scarce.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
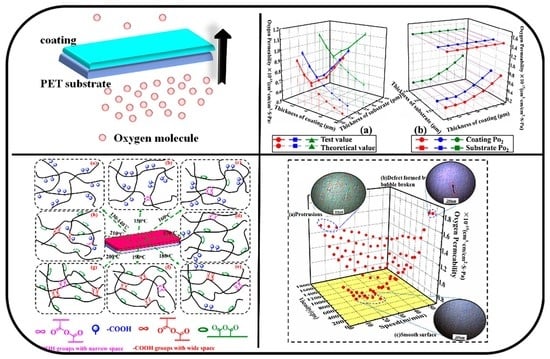
Polyacrylate Decorating Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Film Surface for Boosting Oxygen Barrier Property
by
Wen Zhong, Xiaobin Yang, Jikun Sun, Hongwei Gao, Yongping Bai and Lu Shao
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2720
Abstract
Polymeric barrier materials are critical in contemporary industries for food, medicine, and chemical packaging. However, these materials, such as PET films, are impeded by the optimization of barrier properties by virtue of molecular design. Herein, a new methyl methacrylate-methyl acrylate-diallyl maleate-maleic acid (MMA-MAc-DAM-MA)
[...] Read more.
Polymeric barrier materials are critical in contemporary industries for food, medicine, and chemical packaging. However, these materials, such as PET films, are impeded by the optimization of barrier properties by virtue of molecular design. Herein, a new methyl methacrylate-methyl acrylate-diallyl maleate-maleic acid (MMA-MAc-DAM-MA) was synthesized to tailor the surface properties of PET films for maximizing oxygen barrier properties. During the MMA-MAc-DAM-MA coating and curing process, the chemical structure evolutions of MMA-MAc-DAM-MA coatings were characterized, indicating that the cross-linking conversion and proportion of –COOH groups are critical for the oxygen barrier properties of coatings. The inherent –COOH groups are transformed into designed structures, including intramolecular anhydride, inter-chain anhydride and retained carboxylic acid. Therein, the inter-chain anhydride restraining the activity of coated polymer chain mainly contributes to enhanced barrier properties. The thermal properties of novel coatings were analyzed, revealing that the curing behavior is strongly dependent on the curing temperatures. The impacts of viscosity of the coating solution, coating velocity, and coating thickness on the oxygen permeability (
Po
2) of the coatings were investigated using a gas permeability tester to explore the optimum operating parameters during practical applications, which can reduce the
Po
2 of PET film by 47.8%. This work provides new insights on advanced coating materials for excellent barrier performance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
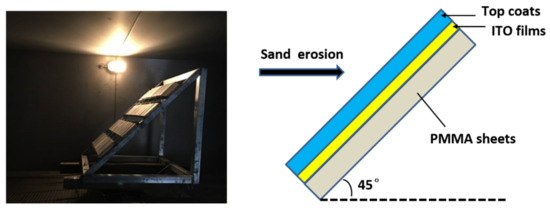
Synergetic Design of Transparent Topcoats on ITO-Coated Plastic Substrate to Boost Surface Erosion Performance
by
Xuan Zhang, Yuandong Chen, Wenqiao Zhang, Yanli Zhong, Pei Lei, Changshan Hao and Yue Yan
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1728
Abstract
Transparent conductive films (TCFs) have received much research attention in the area of aeronautical canopies. However, bad wear, corrosion resistance and weak erosion performance of TCFs dramatically limit their scalable application in the next-generation aeronautical and optoelectronic devices. To address these drawbacks, three
[...] Read more.
Transparent conductive films (TCFs) have received much research attention in the area of aeronautical canopies. However, bad wear, corrosion resistance and weak erosion performance of TCFs dramatically limit their scalable application in the next-generation aeronautical and optoelectronic devices. To address these drawbacks, three types of optically transparent coatings, including acrylic, silicone and polyurethane (PU) coatings were developed and comparatively investigated ex situ in terms of Taber abrasion, nanoindentation and sand erosion tests to improve the wear-resistance and sand erosion abilities of ITO-coated PMMA substrates. To elucidate the sand erosion failure of the coatings, the nanoindentation technique was employed for quantitative assessment of the shape recovery abilities under probe indentation. Results show that the PU topcoats can greatly enhance the sand erosion properties, which were superior to those of acrylic and silicone topcoats. This result can be attributed to the good toughness and self-healing properties of PU topcoats. Additionally, high hardness and good Taber abrasion properties of the ITO films and silicone topcoats did not have an obvious or affirmatory effect on the sand erosion abilities, based on their brittleness and irreparable properties under sand erosion.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
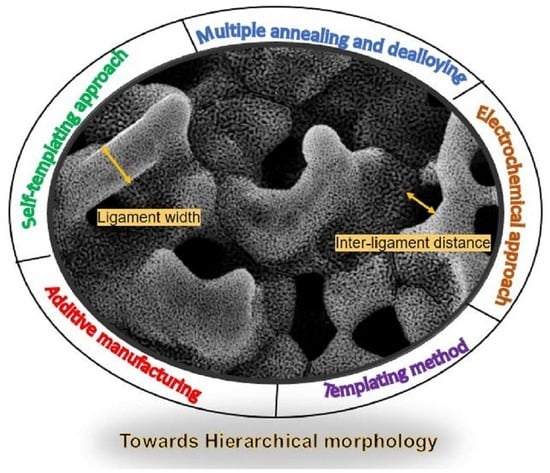
Methods to Generate Structurally Hierarchical Architectures in Nanoporous Coinage Metals
by
Palak Sondhi and Keith J. Stine
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 1818
Abstract
The fundamental essence of material design towards creating functional materials lies in bringing together the competing aspects of a large specific surface area and rapid transport pathways. The generation of structural hierarchy on distinct and well-defined length scales has successfully solved many problems
[...] Read more.
The fundamental essence of material design towards creating functional materials lies in bringing together the competing aspects of a large specific surface area and rapid transport pathways. The generation of structural hierarchy on distinct and well-defined length scales has successfully solved many problems in porous materials. Important applications of these hierarchical materials in the fields of catalysis and electrochemistry are briefly discussed. This review summarizes the recent advances in the strategies to create a hierarchical bicontinuous morphology in porous metals, focusing mainly on the hierarchical architectures in nanoporous gold. Starting from the traditional dealloying method and subsequently moving to other non-traditional top-down and bottom-up manufacturing processes including templating, 3D printing, and electrodeposition, this review will thoroughly examine the chemistry of creating hierarchical nanoporous gold and other coinage metals. Finally, we conclude with a discussion about the future opportunities for the advancement in the methodologies to create bimodal structures with enhanced sensitivity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Hot Salt-Water Corrosion Resistance of NiCoCrAlY-AlSiY Coating by Ion-Beam-Assisted Deposition
by
Guanming Xue, Zhiguo Wang, Enlei Wang, Yan Tang, Yanhui Zhao, Yihe Wang, Suying Hu, Lin Xiang and Zhiwen Xie
Viewed by 2017
Abstract
A promising ion-beam-assisted deposition (IBAD) method was developed to improve the salt-water corrosion resistance of NiCoCrAlY-AlSiY coating. During hot salt-water exposure, hydrochloric acid (HCl) was produced when chloride salt, water, and metal oxide reacted with each other, while HCl was also produced when
[...] Read more.
A promising ion-beam-assisted deposition (IBAD) method was developed to improve the salt-water corrosion resistance of NiCoCrAlY-AlSiY coating. During hot salt-water exposure, hydrochloric acid (HCl) was produced when chloride salt, water, and metal oxide reacted with each other, while HCl was also produced when chlorine reacted with water. The as-deposited AlSiY layer exhibited a loose texture accompanied by numerous pore defects, which triggered the multi-scale diffusion of HCl, resulting in the large-area corrosion degradation of the coating texture and the rapid diffusion of the NiCoCrAlY bonding layer. By contrast, the ion-beam-assisted AlSiY layer showed a dense texture that effectively inhibited the inner diffusion of HCl and suppressed the corrosion reactions as well as the diffusion of the NiCoCrAlY bonding layer. The current results confirmed the significant potential of IBAD in inhibiting corrosion damage and diffusion of thermal protective coatings.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
2-Phenylimidazole Corrosion Inhibitor on Copper: An XPS and ToF-SIMS Surface Analytical Study
by
Matjaž Finšgar
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2470
Abstract
This work presents a surface analytical study of the corrosion inhibitor 2-phenylimidazole (2PhI) adsorbed on a Cu surface from 3 wt.% NaCl solution. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) were used to investigate the surface phenomena. Various XPS
[...] Read more.
This work presents a surface analytical study of the corrosion inhibitor 2-phenylimidazole (2PhI) adsorbed on a Cu surface from 3 wt.% NaCl solution. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) were used to investigate the surface phenomena. Various XPS experiments were performed, i.e., survey- and angle-resolved high-resolution XPS spectra measurements, gas cluster ion beam sputtering in conjunction with XPS measurements, and XPS imaging in conjunction with principal component analysis. These measurements were used to detail the composition of the surface layer at depth. In addition, various ToF-SIMS experiments were performed, such as positive ion ToF-SIMS spectral measurements, ToF-SIMS imaging, and cooling/heating in conjunction with ToF-SIMS measurements. This study shows that organometallic complexes were formed between 2PhI molecules and Cu ions, that the surface layer contained entrapped NaCl, that the surface layer contained some Cu(II) species (but the majority of species were Cu(I)-containing species), that the surface was almost completely covered with a combination of 2PhI molecules and organometallic complex, and that the temperature stability of these species increases when 2PhI is included in the organometallic complex.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
On the Localized Surface Plasmonic Resonances of AgPd Alloy Nanoparticles by Experiment and Theory
by
Dimitrios Ntemogiannis, Maria Tsarmpopoulou, Alexandros G. Chronis, Dimitrios I. Anyfantis, Alexandros Barnasas, Spyridon Grammatikopoulos, Mihail Sigalas and Panagiotis Poulopoulos
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1887
Abstract
Ag/Pd multilayers and AgPd alloyed ultrathin films were deposited on Corning glass by magnetron sputtering. After being annealed in a furnace in air at 460 °C, self-assembled nanoparticles were formed. Localized surface plasmon resonances were observed only for the Ag-rich samples in the
[...] Read more.
Ag/Pd multilayers and AgPd alloyed ultrathin films were deposited on Corning glass by magnetron sputtering. After being annealed in a furnace in air at 460 °C, self-assembled nanoparticles were formed. Localized surface plasmon resonances were observed only for the Ag-rich samples in the full range of the visible light spectrum. The resonance position was found to depend on the initial film thickness. In order to gain further physical insight, rigorous theoretical calculations were carried out via the rigid coupled-wave analysis method for the entire compositional range between Ag and Pd. Theoretical calculations were proven to be in suitable agreement with the experimental results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
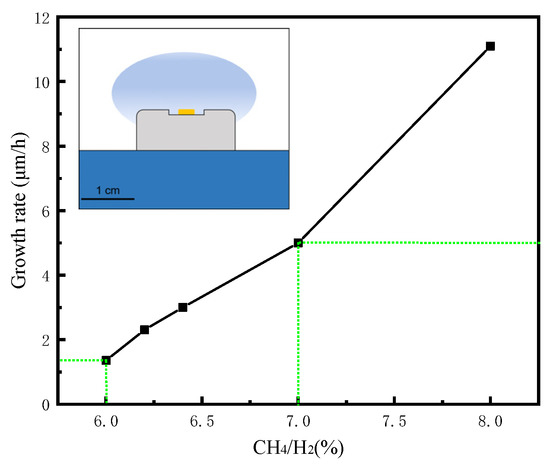
Evolution of High-Quality Homoepitaxial CVD Diamond Films Induced by Methane Concentration
by
Pengfei Zhang, Weidong Chen, Longhui Zhang, Shi He, Hongxing Wang, Shufang Yan, Wen Ma, Chunxia Guo and Yanfeng Wang
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2377
Abstract
In this paper, we successfully synthesized homoepitaxial diamond with high quality and atomically flat surface by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition. The sample presents a growth rate of 3 μm/h, the lowest RMS of 0.573 nm, and the narrowest XRD FWHM of 31.32
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we successfully synthesized homoepitaxial diamond with high quality and atomically flat surface by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition. The sample presents a growth rate of 3 μm/h, the lowest RMS of 0.573 nm, and the narrowest XRD FWHM of 31.32 arcsec. An effect analysis was also applied to discuss the influence of methane concentration on the diamond substrates.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Characterization of Electroless Nickel–Boron Deposit from Optimized Stabilizer-Free Bath
by
Muslum Yunacti, Alexandre Mégret, Mariana Henriette Staia, Alex Montagne and Véronique Vitry
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 2728
Abstract
Conventional electroless nickel–boron deposits are produced using solutions that contain lead or thallium, which must be eliminated due to their toxicity. In this research, electroless nickel–boron deposits were produced in a stabilizer-free bath that does not include any toxic heavy metal. During processing,
[...] Read more.
Conventional electroless nickel–boron deposits are produced using solutions that contain lead or thallium, which must be eliminated due to their toxicity. In this research, electroless nickel–boron deposits were produced in a stabilizer-free bath that does not include any toxic heavy metal. During processing, the plating rate increased from 10 to 14.5 µm/h by decreasing the concentration of the reducing agent, leading to increased bath stability. The thickness, composition, roughness, morphology, hardness, wear, and corrosion resistance of the deposits were characterized. The new deposit presents an excellent hardness of 933 ± 56 hv
50, 866 ± 30 hk
50, and 12 GPa from the instrumented indentation test (IIT), respectively, which are similar to that of hexavalent hard chromium coating. Moreover, by using both potentiodynamic polarization and salt spray tests it was shown that the coating presents higher corrosion resistance as compared to standard nickel-boron coatings. The new deposit exhibits properties close to those of the conventional electroless nickel–boron deposits. Therefore, it could replace them in any industrial applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Quaternary Oxidized Carbon Nanohorns—Based Nanohybrid as Sensing Coating for Room Temperature Resistive Humidity Monitoring
by
Bogdan-Catalin Serban, Cornel Cobianu, Octavian Buiu, Marius Bumbac, Niculae Dumbravescu, Viorel Avramescu, Cristina Mihaela Nicolescu, Mihai Brezeanu, Cristiana Radulescu, Gabriel Craciun, Cosmin Romanitan and Florin Comanescu
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2223
Abstract
We report the relative humidity (RH) sensing response of a resistive sensor, employing sensing layers, based on a quaternary organic–inorganic hybrid nanocomposite comprising oxidized carbon nanohorns (CNHox), graphene oxide (GO), tin dioxide, and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), at 1/1/1/1 and 0.75/0.75/1/1/1 mass ratios. The sensing
[...] Read more.
We report the relative humidity (RH) sensing response of a resistive sensor, employing sensing layers, based on a quaternary organic–inorganic hybrid nanocomposite comprising oxidized carbon nanohorns (CNHox), graphene oxide (GO), tin dioxide, and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), at 1/1/1/1 and 0.75/0.75/1/1/1 mass ratios. The sensing structure comprises a silicon substrate, a SiO
2 layer, and interdigitated transducer (IDT) electrodes. The sensing film was deposited via the drop-casting method on the sensing structure. The morphology and the composition of the sensing layers were investigated through Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and RAMAN spectroscopy. The organic–inorganic quaternary hybrid-based thin film’s resistance increased when the sensors were exposed to relative humidity ranging from 0 to 100%. The manufactured devices show a room temperature response comparable to that of a commercial capacitive humidity sensor and characterized by excellent linearity, rapid response and recovery times, and good sensitivity. While the sensor with CNHox/GO/SnO
2/PVP at 0.75/0.75/1/1 as the sensing layer has the best performance in terms of linearity and recovery time, the structures employing the CNHox/GO/SnO
2/PVP at 1/1/1/1 (mass ratio) have a better performance in terms of relative sensitivity. We explained each constituent of the quaternary hybrid nanocomposites’ sensing role based on their chemical and physical properties, and mutual interactions. Different alternative mechanisms were taken into consideration and discussed. Based on the sensing results, we presume that the effect of the
p-type semiconductor behavior of CNHox and GO, correlated with swelling of PVP, dominates and leads to the overall increasing resistance of the sensing layer. The hard–soft acid–base (HSAB) principle also supports this mechanism.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
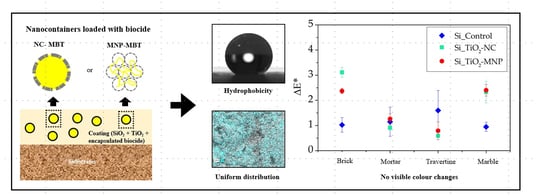
Effectiveness and Compatibility of Nanoparticle Based Multifunctional Coatings on Natural and Man-Made Stones
by
Martina Zuena, Ludovica Ruggiero, Giancarlo Della Ventura, Edoardo Bemporad, Maria Antonietta Ricci and Armida Sodo
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 1854
Abstract
The interaction of microorganisms with stone materials leads to biodeterioration processes, which may cause aesthetic damages and the loss of durability and strength of the substrates. Innovative solutions against this process are represented by nanotechnologies. In our previous works, 2-mercaptobenzothiazole was successfully encapsulated
[...] Read more.
The interaction of microorganisms with stone materials leads to biodeterioration processes, which may cause aesthetic damages and the loss of durability and strength of the substrates. Innovative solutions against this process are represented by nanotechnologies. In our previous works, 2-mercaptobenzothiazole was successfully encapsulated within two silica-based nanodevices: nanocapsules and mesoporous nanoparticles. Such loaded nanodevices have been dispersed in TEOS based coatings, characterized as far as their chemical–physical properties and in vitro biocide efficacy. Here, we adopt a multi-technic approach, to assess the coatings efficacy and compatibility with four types of stones of cultural heritage interest, namely, mortar, brick, travertine, and Carrara marble. In particular, we determine the protective function of the coatings, based on water transport properties (reduction up to a factor 10 of the water absorption for brick and mortar, without significantly influencing water vapor transmission rate), morphology of the surface (absence of coating cracks and color changes), and TiO
2 photocatalytic activity. Consequently, these coatings can be considered suitable for application on stone artifacts, without interfering with their artistic appearance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhancement of the Adhesion of Wire Arc Sprayed Coatings on Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Plastic by Surface Laser Structuring
by
Kevin Gustke, Jana Gebauer, Rico Drehmann, Andrés Fabián Lasagni and Thomas Lampke
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2738
Abstract
Due to their outstanding stiffness-to-weight ratio, fiber-reinforced plastics are established materials for weight reduction in the aerospace and automotive industries. To improve certain properties, such as their low thermal and electrical conductivity, metallic coatings can be applied to the polymer surface. One of
[...] Read more.
Due to their outstanding stiffness-to-weight ratio, fiber-reinforced plastics are established materials for weight reduction in the aerospace and automotive industries. To improve certain properties, such as their low thermal and electrical conductivity, metallic coatings can be applied to the polymer surface. One of the methods used for this purpose is thermal spraying. Studies have shown that the adhesion strength of metallic coatings on polymer surfaces is low. To improve the adhesion strength, the surface of the fiber-reinforced plastics was pretreated with pulsed laser-based methods. This study describes in detail the process chain, the resulting surface conditions and their effect on the adhesion strength of wire arc sprayed copper coatings in pull-off and shear tensile testing. The results show up to ~200% increase in adhesion strength for the laser-structured samples compared to the grit-blasted reference samples in the pull-off test.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
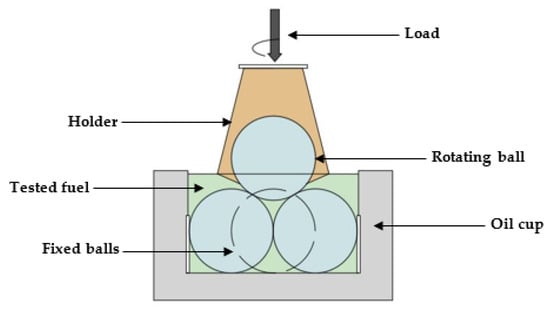
Tribological Behaviour and Lubricating Mechanism of Tire Pyrolysis Oil
by
Haseeb Yaqoob, Yew Heng Teoh, Farooq Sher, Muhammad Ahmad Jamil, Mirza Nuhanović, Omid Razmkhah and Begum Erten
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 2934
Abstract
The four-ball tester was used in this analysis to demonstrate the lubricity of tire pyrolysis oil (TPO). The tribological performance of the tire pyrolysis oil was compared with diesel fuel (DF) and their blends, DT10 (TPO 10%, Diesel 90%) and DT20 (TPO 20%,
[...] Read more.
The four-ball tester was used in this analysis to demonstrate the lubricity of tire pyrolysis oil (TPO). The tribological performance of the tire pyrolysis oil was compared with diesel fuel (DF) and their blends, DT10 (TPO 10%, Diesel 90%) and DT20 (TPO 20%, Diesel 80%). A scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to investigate the wear scar. In contrast to diesel fuel, TPO demonstrated better antiwear behaviour in terms of higher load-carrying capacity. DT10, DT20, and TPO’s wear scar diameter (WSD) was 22.35%, 16.01%, and 31.99% smaller than that of diesel at 80 kg load, respectively. The scanning electron microscope micrographs showed that the TPO and DT10 had less wear than their counterparts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Atomic Layer Deposition of Insulating AlF3/Polyimide Nanolaminate Films
by
Xinzhi Li, Marko Vehkamäki, Mikko Heikkilä, Miika Mattinen, Matti Putkonen, Markku Leskelä and Mikko Ritala
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2628
Abstract
This article describes the deposition of AlF
3/polyimide nanolaminate film by inorganic-organic atomic layer deposition (ALD) at 170 °C. AlCl
3 and TiF
4 were used as precursors for AlF
3. Polyimide layers were deposited from PMDA (pyromellitic dianhydride, 1,2,3,5-benzenetetracarboxylic anhydride)
[...] Read more.
This article describes the deposition of AlF
3/polyimide nanolaminate film by inorganic-organic atomic layer deposition (ALD) at 170 °C. AlCl
3 and TiF
4 were used as precursors for AlF
3. Polyimide layers were deposited from PMDA (pyromellitic dianhydride, 1,2,3,5-benzenetetracarboxylic anhydride) and DAH (1,6-diaminohexane). With field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and X-ray reflection (XRR) analysis, it was found that the topmost layer (nominally 10 nm in thickness) of the nanolaminate film (100 nm total thickness) changed when exposed to the atmosphere. After all, the effect on roughness was minimal. The length of a delay time between the AlF
3 and polyimide depositions was found to affect the sharpness of the nanolaminate structure. Electrical properties of AlF
3/polyimide nanolaminate films were measured, indicating an increase in dielectric constant compared to single AlF
3 and a decrease in leakage current compared to polyimide films, respectively.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
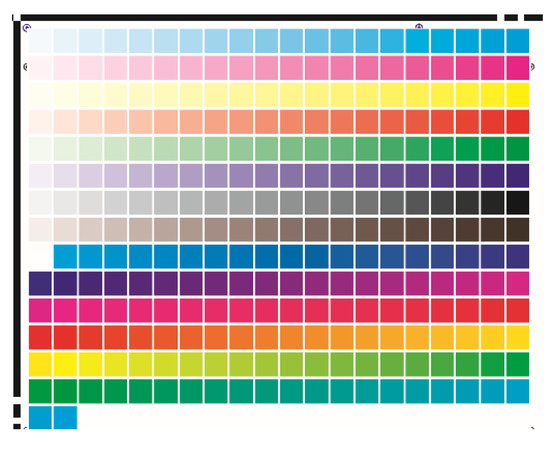
Investigation of Color Reproduction on Linen Fabrics when Printing with Mimaki TX400-1800D Inkjet with Pigment TP250 Dyes
by
Tim Tofan, Rimantas Stonkus and Raimondas Jasevičius
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2436
Abstract
The aim of this research is to investigate related effect of dyeability to linen textiles related to different printing parameters. The study investigated the change in color characteristics when printing on linen fabrics with an inkjet MIMAKI Tx400-1800D printer with pigmented TP 250
[...] Read more.
The aim of this research is to investigate related effect of dyeability to linen textiles related to different printing parameters. The study investigated the change in color characteristics when printing on linen fabrics with an inkjet MIMAKI Tx400-1800D printer with pigmented TP 250 inks. The dependence of color reproduction on linen fabrics on the number of print head passes, number of ink layers to be coated, linen fabric density, and different types of linen fabric was investigated. All this affects the quality of print and its mechanical properties. The change in color characteristics on different types of linen fabrics was determined experimentally. We determine at which print settings the most accurate color reproduction can be achieved on different linen fabrics. The difference between the highest and the lowest possible number of head passages was investigated. The possibilities of reproducing different linen fabric colors were determined.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
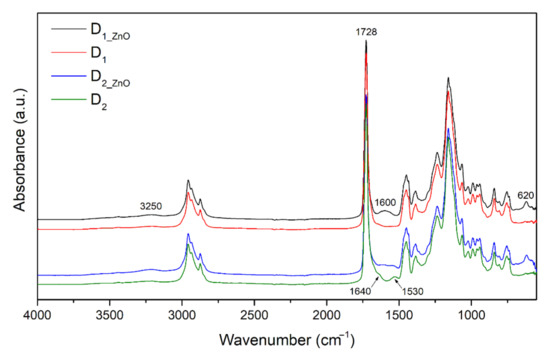
Water-Resistant Latex Coatings: Tuning of Properties by Polymerizable Surfactant, Covalent Crosslinking and Nanostructured ZnO Additive
by
Jana Machotová, Andréa Kalendová, Denisa Steinerová, Petra Mácová, Stanislav Šlang, Jaromír Šňupárek and Jan Vajdák
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 3809
Abstract
This paper deals with the development of acrylic latexes providing high-performance water-resistant coatings. For this purpose, mutual effects of anionic surfactant type (ordinary and polymerizable), covalent intra- and/or interparticle crosslinking (introduced by allyl methacrylate copolymerization and keto-hydrazide reaction, respectively) and ionic crosslinking (provided
[...] Read more.
This paper deals with the development of acrylic latexes providing high-performance water-resistant coatings. For this purpose, mutual effects of anionic surfactant type (ordinary and polymerizable), covalent intra- and/or interparticle crosslinking (introduced by allyl methacrylate copolymerization and keto-hydrazide reaction, respectively) and ionic crosslinking (provided by nanostructured ZnO additive) were investigated. The latexes were prepared by the standard emulsion polymerization of methyl methacrylate, butyl acrylate and methacrylic acid as the main monomers. The addition of surface-untreated powdered nanostructured ZnO was performed during latex synthesis, resulting in stable latexes comprising dispersed nanosized additive in the content of ca 0.9−1.0 wt.% (based on solids). The coating performance with emphasis on water resistance was evaluated. It was determined that the application of the polymerizable surfactant improved coating adhesion and water-resistance, but it wasn′t able to ensure high water-resistance of coatings. Highly water-resistant coatings were obtained provided that covalent intra- and interparticle crosslinking together with ionic crosslinking were employed in the coating composition, forming densely crosslinked latex films. Moreover, coatings comprising nanostructured ZnO additive displayed a significant antibacterial activity and improved solvent resistance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Interface Characterization of 2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole Corrosion Inhibitor on Brass
by
Matjaž Finšgar
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2043
Abstract
This work presents a detailed surface analytical study and surface characterization, with an emphasis on the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) analyses of 2‑mercapto‑1‑methylimidazole (MMI) as a corrosion inhibitor for brass. First, the electrochemical measurements demonstrated a
[...] Read more.
This work presents a detailed surface analytical study and surface characterization, with an emphasis on the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) analyses of 2‑mercapto‑1‑methylimidazole (MMI) as a corrosion inhibitor for brass. First, the electrochemical measurements demonstrated a corrosion inhibition effect of MMI in a 3 wt.% NaCl solution. Next, the formation of the MMI surface layer and its properties after 1 month of immersion was analyzed with attenuated total reflectance–Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, and contact angle analysis. Moreover, to gradually remove the organic surface layer, a gas cluster ion beam (GCIB) sputtering source at different accelerated voltages and cluster sizes was employed. After each sputtering cycle, a high-resolution XPS analysis was performed. Moreover, an angle‑resolved XPS analysis was carried out for the MMI-treated brass sample to analyze the heterogeneous layered structure (the interface of the MMI organic/inorganic brass substrate). The interface properties were also investigated in detail using ToF-SIMS for spectra measurements and 2D imaging. Special attention was devoted to the possible spectral interferences for MMI‑related species. The thermal stability of different MMI-related species using molecular-specific signals without possible spectral interferences was determined by performing a cooling/heating experiment associated with ToF-SIMS measurements. It was shown that these species desorbed from the brass surface in the temperature range of 310–370 °C.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures