Feature Paper Collection in Thin Films
A topical collection in Coatings (ISSN 2079-6412). This collection belongs to the section "Thin Films".
Viewed by 31042Editors
Interests: Li-ion batteries; Li-S batteries; all-solid-state batteries; pseudocapacitors; thin films; materials science; mesoporous materials; self-assembled nanostructures; structure-property relationships
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: high-entropy ceramics; printed electronics; batteries; electrochemistry; semiconductors; thin films; materials science; structure-property relationships
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
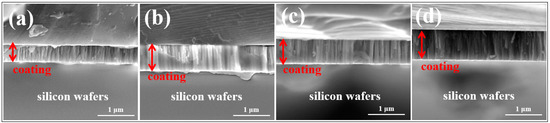
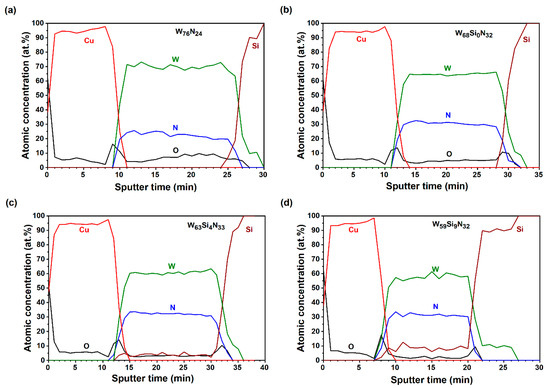
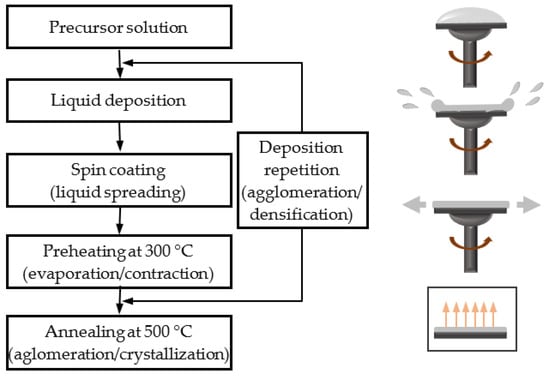
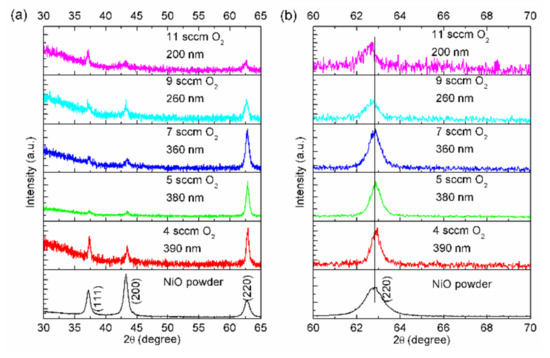
Oxides and non-oxides in thin-film form are technologically important materials with a variety of applications in energy storage and conversion, sensing, electronics, mechanics, optics and biomedicine, resulting from unique combinations of properties. Inorganic, organic, and hybrid inorganic-organic materials can be produced with a range of structures, compositions, and thicknesses by physical and chemical deposition methods (e.g., atomic layer deposition, pulsed laser deposition, chemical vapor deposition, chemical solution deposition, etc.), with low-cost solution processing routes being usually more flexible in terms of chemistry. Apart from interfacial engineering and compositional design, nanoscale structuring at different length scales—through “top-down” and “bottom-up” approaches—has been shown to be effective in tailoring the properties of thin-film materials. However, the characterization becomes increasingly difficult with decreasing film thickness, and often the lack of structure-property relationship understanding is an impediment to applications. This “Feature Paper Collection” is dedicated to advanced thin film structures and devices, with special emphasis placed on their preparation, characterization, and application in the energy field.
Potential topics include (but are not limited to):
- Novel oxide and non-oxide materials in thin-film form
- Preparation by chemical and physical methods
- Micro- and nanostructuring
- Surface and interface engineering
- Advanced characterization techniques
- Structure–composition–property relationships
- Application in electrochemical energy storage devices (e.g., as protective surface coating on anode/cathode materials for bulk-type batteries or as active component in thin-film batteries), catalysis, solar cells, sensors, data storage, etc.
Dr. Torsten Brezesinski
Dr. Ben Breitung
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Coatings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.