Light and Laser Dentistry
A topical collection in Dentistry Journal (ISSN 2304-6767). This collection belongs to the section "Lasers in Dentistry".
Viewed by 35971Editors
Interests: oral surgery; laser dentistry; fluoride; dentinal adhesives; dentinal hypersensitivity; peri-implantitis; periodontitis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: photobiomodulation; laser dentistry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
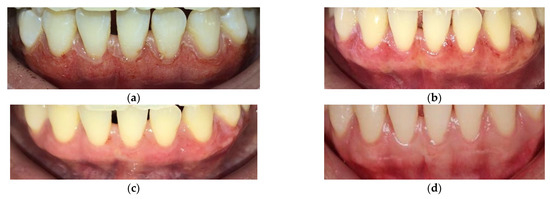
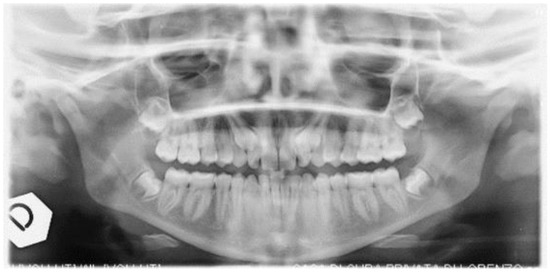
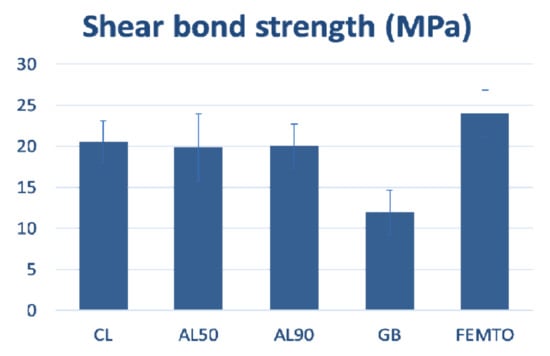
We invite you to submit your studies, letters, case reports and any overviews related to the keywords of our sub-editorial board. Several studies are currently focusing on the materials and lights used daily in practices. Their interactions with oral tissues can induce, produce or provoke biological effects that can be appreciated or unwished. Knowledge of their process of interaction is necessary to improve the quality of treatments or products and to avoid side effects. Furthermore, several lights have been proposed for oral treatments in different fields. The understanding of their effects on biological material can improve or prohibit their applications (e.g., bio-activation, bio-modulation, magnetic properties, mechanical properties, chemical properties, tissue overheating, etc.). Thus, studies focused on light applications, matters used in oral treatments and fundamental studies can enlighten us the interaction process with biological oral tissues and improve the quality of oral treatments. In the oral environment, there are both hard (bone and teeth) and soft (gingival and mucosal tissues) tissues, providing complex functions and aesthetics. Treatment modalities including light energy should specifically target these tissues for the best biological responses and clinical outcomes. Thus, research and clinical studies focused on the application of light on the various oral tissues would enlighten the biological and interactive mechanisms that can eventually improve the quality of treatment for oral conditions and needs.
Prof. Dr. Samir NammourProf. Aldo Brugnera Junior
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Dentistry Journal is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2000 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Light applications
- Light interaction with biological oral tissues
- Clinical applications using a new material
- Interaction between materials and oral tissues
- Case reports
- Basic research including molecular biology
- Properties of light-emitting sources including lasers for oral tissues
- Bio-interactive mechanisms—wavelengths, parameters, indications
- Clinical studies of such applications
- New materials and advantages
- Limitations and risks