-
 Electricity Cost Savings in Energy-Intensive Companies: Optimization Framework and Case Study
Electricity Cost Savings in Energy-Intensive Companies: Optimization Framework and Case Study -
 A Composite Index for Tracking the Evolution towards Energy Transition at Urban Scale: The Turin Case Study
A Composite Index for Tracking the Evolution towards Energy Transition at Urban Scale: The Turin Case Study -
 Predictive Energy Management of a Building-Integrated Microgrid: A Case Study
Predictive Energy Management of a Building-Integrated Microgrid: A Case Study -
 Techno-Economic Planning of a Fully Renewable Energy-Based Autonomous Microgrid with Both Single and Hybrid Energy Storage Systems
Techno-Economic Planning of a Fully Renewable Energy-Based Autonomous Microgrid with Both Single and Hybrid Energy Storage Systems -
 Improving the Methodology for Determining the Biomass/Coal Co-Combustion Ratio: Predictive Modeling of the 14C Activity of Pure Biomass
Improving the Methodology for Determining the Biomass/Coal Co-Combustion Ratio: Predictive Modeling of the 14C Activity of Pure Biomass
Journal Description
Energies
Energies
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of related scientific research, technology development, engineering policy, and management studies related to the general field of energy, from technologies of energy supply, conversion, dispatch, and final use to the physical and chemical processes behind such technologies. Energies is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The European Biomass Industry Association (EUBIA), Association of European Renewable Energy Research Centres (EUREC), Institute of Energy and Fuel Processing Technology (ITPE), International Society for Porous Media (InterPore), CYTED and others are affiliated with Energies and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, RePEc, Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Engineering (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 41 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Energies.
- Companion journals for Energies include: Fuels, Gases, Nanoenergy Advances and Solar.
Impact Factor:
3.2 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2022)
Latest Articles
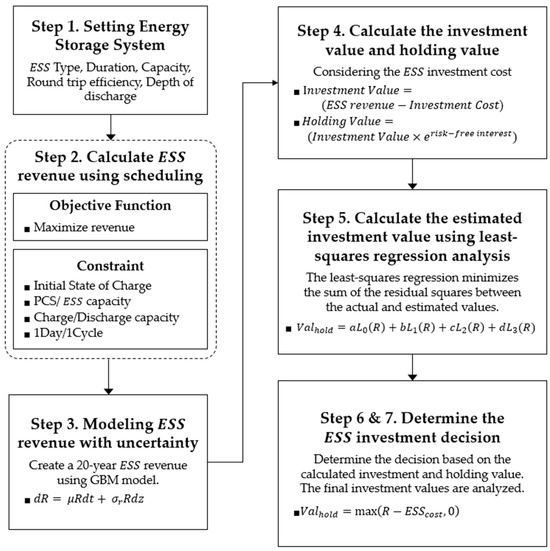
Investment Decision for Long-Term Battery Energy Storage System Using Least Squares Monte Carlo
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2019; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092019 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
The use of renewable energy sources to achieve carbon neutrality is increasing. However, the uncertainty and volatility of renewable resources are causing problems in power systems. Flexible and low-carbon resources such as Energy Storage Systems (ESSs) are essential for solving the problems of
[...] Read more.
The use of renewable energy sources to achieve carbon neutrality is increasing. However, the uncertainty and volatility of renewable resources are causing problems in power systems. Flexible and low-carbon resources such as Energy Storage Systems (ESSs) are essential for solving the problems of power systems and achieving greenhouse gas reduction goals. However, ESSs are not being installed because of Korea’s fuel-based electricity market. To address this issue, this paper presents a method for determining the optimal investment timing of Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESSs) using the Least Squares Monte Carlo (LSMC) method. A case study is conducted considering the System Marginal Price (SMP) and Capacity Payment (CP), which are electricity rates in Korea. Revenue is calculated through the arbitrage of a 10 MW/40 MWh lithium-ion BESS, and linear programming optimization is performed for ESS scheduling to maximize revenue. The ESS revenue with uncertainty is modeled as a stochastic process using Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM), and the optimal time to invest in an ESS is determined using an LSMC simulation considering investment costs. The proposed method can be used as a decision-making tool for ESS investors to provide information on facility investments in arbitrage situations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations and Recent Trends in Power Systems: Smart Grids, Energy Storage Systems and Electric Vehicle Integrations)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Adaptive Comfort Potential in Different Climate Zones of Ecuador Considering Global Warming
by
Evelyn Delgado-Gutierrez, Jacinto Canivell, David Bienvenido-Huertas and Francisco M. Hidalgo-Sánchez
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2017; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092017 (registering DOI) - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Ecuador is a country with several climate zones. However, their behaviour is similar throughout the year, with no peaks of extreme temperatures in the various seasons. This paper is a first approach to study the adaptive comfort behaviour in several areas and populations
[...] Read more.
Ecuador is a country with several climate zones. However, their behaviour is similar throughout the year, with no peaks of extreme temperatures in the various seasons. This paper is a first approach to study the adaptive comfort behaviour in several areas and populations of the country. Considering the ASHRAE 55-2020 model, energy simulation programmes are applied not just to the current climate scenario but also to the climate change scenarios of 2050 and 2100. The results of locations are analysed and compared to determine their performance. Thanks to their climate characteristics, adaptive comfort models could be applied as a passive strategy, using natural ventilation for building indoor comfort improvement, particularly social dwellings. According to previous studies, some prototypes have not considered the climate determinants in each region. Given the geographic situation of the study areas, the adaptive comfort model could be applied in all cases. Percentages of application of natural ventilation and heating and cooling degree hours have similar behaviours according to the climatic region, with a variation greater than 30% among them.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Thermal Comfort and Energy Performance in Building)
Open AccessArticle
Influence of a Precursor Catalyst on the Composition of Products in Catalytic Cracking of Heavy Oil
by
Khoshim Kh. Urazov, Nikita N. Sviridenko, Yulia A. Sviridenko and Veronika R. Utyaganova
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2016; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092016 (registering DOI) - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Heavy oils are characterized by a high content of resins and asphaltenes, which complicates refining and leads to an increase in the cost of refinery products. These components can be strongly adsorbed on the acid sites of a supported catalyst, leading to its
[...] Read more.
Heavy oils are characterized by a high content of resins and asphaltenes, which complicates refining and leads to an increase in the cost of refinery products. These components can be strongly adsorbed on the acid sites of a supported catalyst, leading to its deactivation. Currently, various salts of group 8 metals are being considered for such processes to act as catalysts during oil cracking. At the same time, the nature of the precursor often has a significant impact on the process of refining heavy oil. In this work, catalytic cracking of heavy oil from the Ashalchinskoye field using different precursors (nanodispersed catalysts formed in situ based on NiO) has been studied. The cracking was carried out at 450 °C with a catalyst content from 0.1 to 0.5 wt.%. The catalytic cracking products were analyzed via SARA, GC, XRD and SEM. Nickel acetate and nitrate promote similar yields of by-products, while formate promotes higher yields of gaseous products. Formate and nickel acetate were shown to produce 1.8 and 2.8 wt.% more light fractions than nickel nitrate. When heavy oil is cracked in the presence of Ni(NO3)2∙6H2O, the maximum decrease in sulfur content (2.12 wt.%) is observed compared to other precursors. It has been found that the composition and morphology of the resulting nickel sulfides and compaction products are influenced by the nature of the catalyst precursor. XRD and SEM analyses of coke-containing catalysts indicate the formation of Ni9S8 and Ni0.96S phases during cracking when nickel nitrate is used and the formation of NiS and Ni9S8 when nickel acetate and formate are used.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Development of Unconventional Oil and Gas Fields)
Open AccessArticle
Development of a Genetic Algorithm-Based Control Strategy for Fuel Consumption Optimization in a Mild Hybrid Electrified Vehicle’s Electrified Propulsion System
by
Roberto H. Q. Filho, Rodrigo P. M. Ruiz, Eisenhawer de M. Fernandes, Rosalvo B. Filho and Felipe C. Pimenta
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2015; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092015 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Increasingly stringent pollutant emission regulations and a customer demand for a high-fuel economy drive the modern automotive industry to hurriedly solve the problem of decarbonization and powertrain efficiency, leading R&D towards alternative powertrain solutions and fuels. Electrification, today, plays the biggest role in
[...] Read more.
Increasingly stringent pollutant emission regulations and a customer demand for a high-fuel economy drive the modern automotive industry to hurriedly solve the problem of decarbonization and powertrain efficiency, leading R&D towards alternative powertrain solutions and fuels. Electrification, today, plays the biggest role in the topic, with Mild Hybrid Electrified Vehicles (MHEVs) being the most cost-effective architectures, displaying dominance in smaller markets such as Brazil. One of the biggest challenges for HEVs’ development is the complexity of the hybrid control system, knowing when to actuate the electric machine, and the optimum power delivery, plus the gearshift schedule becomes a hard optimization problem that plays a key role in powertrain efficiency and cost savings for the customer. This paper proposes the implementation of a genetic algorithm (GA) as a machine learning-based control strategy to determine the torque split and the gear engaged for each driving condition of an MHEV operation, aiming to optimize fuel consumption. A quasi-static model of the vehicle was developed in Matlab/Simulink version 2022b, the virtual vehicle was then tested following the FTP75 and HWFET driving cycles. Simulation results indicate that the control decisions taken by the GA are qualitatively coherent for all operation conditions, and even quantitatively coherent in some cases, and that the software has the potential to be used as a control strategy outside the simulation environment, in future steps of development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Performance Analysis and Simulation of Electric Vehicles)
►▼
Show Figures
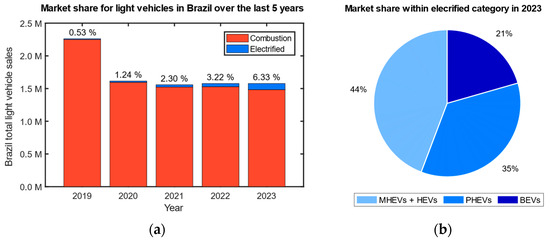
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Applications of Oxyhydrogen, Direct Water Injection, and Early-Intake Valve Closure Technologies on a Petrol Spark Ignition Engine—A Path towards Zero-Emission Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engines
by
Xiangtao Kong and Yaodong Wang
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2014; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092014 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study investigates the performance of a 4-MIX engine utilizing hydrogen combustion in pure oxygen, water injection, and the application of the early-intake valve closure (EIVC) Miller cycle. Transitioning from a standard petrol–oil mix to hydrogen fuel with pure oxygen combustion aims to
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the performance of a 4-MIX engine utilizing hydrogen combustion in pure oxygen, water injection, and the application of the early-intake valve closure (EIVC) Miller cycle. Transitioning from a standard petrol–oil mix to hydrogen fuel with pure oxygen combustion aims to reduce emissions. Performance comparisons between baseline and oxyhydrogen engines showed proportional growth in the energy input rate with increasing rotational speed. The oxyhydrogen engine exhibited smoother reductions in brake torque and thermal efficiency as rotational speed increased compared to the baseline, attributed to hydrogen’s higher heating value. Water injection targeted cylinder and exhaust temperature reduction while maintaining a consistent injected mass. The results indicated a threshold of around 2.5 kg/h for the optimal water injection rate, beyond which positive effects on engine performance emerged. Investigation into the EIVC Miller cycle revealed improvements in brake torque, thermal efficiency, and brake specific fuel consumption as early-intake valve closure increased. Overall, the EIVC model exhibited superior energy efficiency, torque output, and thermal efficiency compared to alternative models, effectively addressing emissions and cylinder temperature concerns.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Hydrogen Energy Technologies, 2nd Volume)
Open AccessReview
A Systematic Review on Fuzzy Decision Support Systems and Multi-Criteria Analysis in Urban Heat Island Management
by
Majda Ćesić, Katarina Rogulj, Jelena Kilić Pamuković and Andrija Krtalić
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2013; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092013 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The phenomenon known as urban heat islands (UHIs) is becoming more common and widespread, especially in large cities and metropolises around the world. The main cause of these temperature variations between the city center and the suburbs is the replacement of large tracts
[...] Read more.
The phenomenon known as urban heat islands (UHIs) is becoming more common and widespread, especially in large cities and metropolises around the world. The main cause of these temperature variations between the city center and the suburbs is the replacement of large tracts of natural land with artificial (built-up) surfaces that absorb solar heat and radiate it back at night. UHIs have been the subject of numerous studies, most of which were about defining the main characteristics, factors, indexes, etc., of UHIs using remote sensing technologies or about determining mitigating activities. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the literature, as well as a bibliometric analysis, to discover research trends related to the application of decision support systems and multi-criteria decision-making for UHI management, with a special emphasis on fuzzy theory. Data collection is conducted using the Scopus bibliographic database. Throughout the literature review, it was found that there were not many studies on multi-criteria analysis and decision support system applications regarding UHIs. The fuzzy theory application was also reviewed, resulting in only a few references. However, this topic is current, with an increase in published papers, and authors see this as an opportunity for improvement and further research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fuzzy Decision Support Systems for Efficient Energy Management)
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Deep Learning-Based Non-Intrusive Thermal Load Monitoring
by
Kazuki Okazawa, Naoya Kaneko, Dafang Zhao, Hiroki Nishikawa, Ittetsu Taniguchi, Francky Catthoor and Takao Onoye
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2012; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092012 (registering DOI) - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM), which provides sufficient load for the energy consumption of an entire building, has become crucial in improving the operation of energy systems. Although NILM can decompose overall energy consumption into individual electrical sub-loads, it struggles to estimate thermal-driven sub-loads
[...] Read more.
Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM), which provides sufficient load for the energy consumption of an entire building, has become crucial in improving the operation of energy systems. Although NILM can decompose overall energy consumption into individual electrical sub-loads, it struggles to estimate thermal-driven sub-loads such as occupants. Previous studies proposed Non-Intrusive Thermal Load Monitoring (NITLM), which disaggregates the overall thermal load into sub-loads; however, these studies evaluated only a single building. The results change for other buildings due to individual building factors, such as floor area, location, and occupancy patterns; thus, it is necessary to analyze how these factors affect the accuracy of disaggregation for accurate monitoring. In this paper, we conduct a fundamental evaluation of NITLM in various realistic office buildings to accurately disaggregate the overall thermal load into sub-loads, focusing on occupant thermal load. Through experiments, we introduce NITLM with deep learning models and evaluate these models using thermal load datasets. These thermal load datasets are generated by a building energy simulation, and its inputs for the simulation were derived from realistic data like HVAC on/off data. Such fundamental evaluation has not been done before, but insights obtained from the comparison of learning models are necessary and useful for improving learning models. Our experimental results shed light on the deep learning-based NITLM models for building-level efficient energy management systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section G: Energy and Buildings)
Open AccessArticle
Estimation of Fuel Properties for the Heavy Fraction of Biomass Pyrolysis Oil Consisting of Proposed Structures for Pyrolytic Lignin and Humins
by
Evan Terrell
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2011; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092011 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The organic component of biomass pyrolysis oils is composed of a light fraction (C2–C4 volatiles, sugar- and lignin-derived monomers) and a less polar heavy fraction (pyrolytic lignin/humins, greater than approximately 200 g/mol). Importantly, this heavy fraction can account for roughly one-third to one-half
[...] Read more.
The organic component of biomass pyrolysis oils is composed of a light fraction (C2–C4 volatiles, sugar- and lignin-derived monomers) and a less polar heavy fraction (pyrolytic lignin/humins, greater than approximately 200 g/mol). Importantly, this heavy fraction can account for roughly one-third to one-half of the total pyrolysis oil. While the composition and characteristics of the light fraction are generally well understood, research is still needed for the characterization of the heavy fraction. Some important thermodynamic fuel properties of this fraction are the heat of combustion, normal boiling point, heat of vaporization, and flash point, which are (computationally) estimated in this work with regularized regression and empirical correlations. The quantification of these properties has implications on downstream utilization, particularly in the context of co-processing bio-oils with plastic and coal liquefaction products and/or crude petroleum. Finally, challenges and opportunities for (experimental) work are discussed for the advancement of sustainable valorization of biomass pyrolysis oils.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section A4: Bio-Energy)
►▼
Show Figures
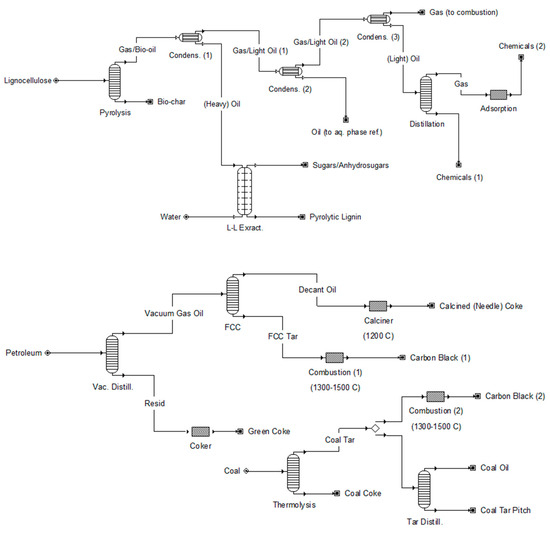
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hartmann–Sprenger Energy Separation Effect for the Quasi-Isothermal Pressure Reduction of Natural Gas: Feasibility Analysis and Numerical Simulation
by
Artem Belousov, Vladimir Lushpeev, Anton Sokolov, Radel Sultanbekov, Yan Tyan, Egor Ovchinnikov, Aleksei Shvets, Vitaliy Bushuev and Shamil Islamov
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2010; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092010 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The present paper provides a brief overview of the existing methods for energy separation and an analysis of the possibility of the practical application of the Hartmann–Sprenger effect to provide quasi-isothermal pressure reduction of natural gas at the facilities within a gas transmission
[...] Read more.
The present paper provides a brief overview of the existing methods for energy separation and an analysis of the possibility of the practical application of the Hartmann–Sprenger effect to provide quasi-isothermal pressure reduction of natural gas at the facilities within a gas transmission system. The recommendations of external authors are analyzed. A variant of a quasi-isothermal pressure regulator is proposed, which assumes the mixing of flows after energy separation. Using a numerical simulation of gas dynamics, it is demonstrated that the position of the resonators can be determined on the basis of calculations of the structure of the underexpanded jet without taking into account the resonator and, accordingly, without the need for time-consuming calculations of the dynamics of the processes. Based on the results of simulating the gas dynamics of two nozzle–resonator pairs installed in a single flow housing, it is shown that, in order to optimize the regulator length, the width of the passage between the two nearest resonators should be greater than or equal to the sum of diameters of the critical sections of the nozzles. Numerical vibroacoustic analysis demonstrated that the most dangerous part of the resonator is the frequency of its natural oscillations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Natural Gas Research and Energy Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Stakeholder Decision Support Based on Multicriteria Assessment: Application to Industrial Waste Heat Recovery for a District Heating Network in Grenoble, France
by
Jaume Fitó and Julien Ramousse
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2009; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092009 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The decarbonization and decentralization of district heating networks lead to the shared use of on-site resources by multiple stakeholders. The optimal design of prospective equipment in such contexts should take into account the preferences and objectives of each stakeholder. This article focuses on
[...] Read more.
The decarbonization and decentralization of district heating networks lead to the shared use of on-site resources by multiple stakeholders. The optimal design of prospective equipment in such contexts should take into account the preferences and objectives of each stakeholder. This article focuses on the adaptation of a 4E multicriteria model (the criteria being energy, exergy, economic, and exergoeconomic) to include and compare the stakeholders’ performance criteria around the technical design. In addition, two graphical supports are proposed that represent and cross-analyze the different stakeholders’ preferred optima. A preliminary implementation of the methodology is illustrated through a study case in France, which features waste heat recovery for district heating utilization. After presenting the results, a discussion is offered on how to complete the methodology with an iterative negotiation procedure to determine the most suitable design. It was concluded, among other considerations, that the relaxation of the stakeholders’ optimality requirements can greatly enable the project’s feasibility. Such a relaxation could be implemented in the form of a joint consortium. In addition, the results showed that stakeholder relaxations of requirements can lead to new solutions that may outperform the best solutions pre-relaxation. Lastly, perspectives are suggested toward verifying whether relaxed requirements from upstream stakeholders might be more impactful than those of downstream stakeholders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Energy Systems in Energy Resilient, Zero/Positive Energy Buildings, Communities and Districts)
►▼
Show Figures
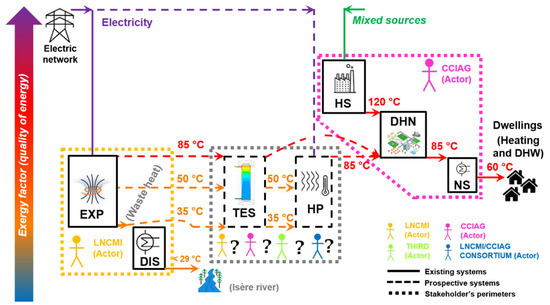
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating Advanced Building Envelopes for Energy Efficiency in Prefab Temporary Post-Disaster Housing
by
Lorenzo Rapone, Afaq A. Butt, Roel C. G. M. Loonen, Giacomo Salvadori and Francesco Leccese
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2008; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092008 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Prefabricated temporary buildings are a promising solution for post-disaster scenarios for their modularity, sustainability and transportation advantages. However, their low thermal mass building envelope shows a fast response to heat flux excitations. This leads to the risk of not meeting the occupant comfort
[...] Read more.
Prefabricated temporary buildings are a promising solution for post-disaster scenarios for their modularity, sustainability and transportation advantages. However, their low thermal mass building envelope shows a fast response to heat flux excitations. This leads to the risk of not meeting the occupant comfort and HVAC energy-saving requirements. The literature shows different measures implementable in opaque surfaces, like vacuum insulation panels (VIPs), phase change materials (PCMs) and switchable coatings, and in transparent surfaces (switchable glazing) to mitigate thermal issues, like overheating, while preserving the limited available internal space. This paper investigates the energy and overheating performance of the mentioned interventions by using building performance simulation tools to assess their effectiveness. The optimization also looks at the transportation flexibility of each intervention to better support the decision maker for manufacturing innovative temporary units. The most energy-efficient measures turn to be VIPs as a better energy solution for winter and PCMs as a better thermal comfort solution for summer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Efficient Low Carbon Buildings and Districts)
►▼
Show Figures
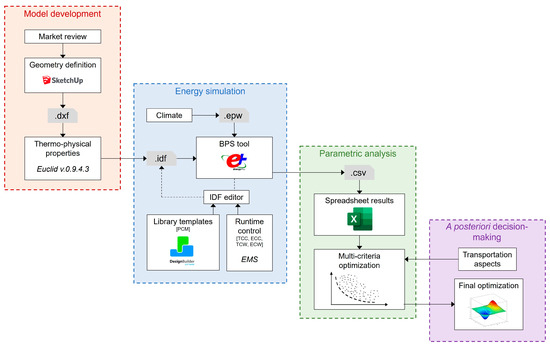
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation on Pollution-Induced Flashovers of In-Service Insulators in Ethiopian Power Transmission Lines
by
Berhanu Zelalem Desta, Mengesha M. Wogari and Stanislaw M. Gubanski
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2007; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092007 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Power transmission lines in Ethiopia are experiencing an alarmingly high frequency of unexplained outages triggered by environmental factors, which significantly undermine the reliability of the country’s power system. This paper presents investigations aiming to identify those among the unexplained fault records that have
[...] Read more.
Power transmission lines in Ethiopia are experiencing an alarmingly high frequency of unexplained outages triggered by environmental factors, which significantly undermine the reliability of the country’s power system. This paper presents investigations aiming to identify those among the unexplained fault records that have been caused by pollution induced flashovers. An identification method is developed, which associates the contextual fault features, such as information about the characteristics of the fault, fault location, and time of day, as well as month of its occurrence with local meteorological/climatic and environmental conditions. A total number of 4231 unexplained faults, recorded between 2015 and 2022, were analyzed. Among them, 1045 faults (24.7%) were identified as being most likely caused by pollution induced flashovers. The entire network suffered from more than 130 pollution-induced flashovers annually with a frequency of about 0.8 faults/100 km/year. The fault frequency strongly differed among the grid regions, being highest in the Northeast and lowest in the Southwest region. Moreover, the performed analyses also concentrated on the evaluation of the pollution performance of various insulator types employed in the network. The results indicate that porcelain insulators have the highest pollution-induced flashover intensity of 1.47 faults/year/1000 units, followed by silicone rubber polymeric composite insulators and glass insulators with the respective intensities of 1.21 and 0.83 faults/year/1000 units. These results indicate that despite the high expectations towards the pollution performance of silicone rubber polymeric insulators, their use in the Ethiopian climatic and environmental conditions appears to be unsatisfactory.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Electrical Engineering, High Voltage and Insulation Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
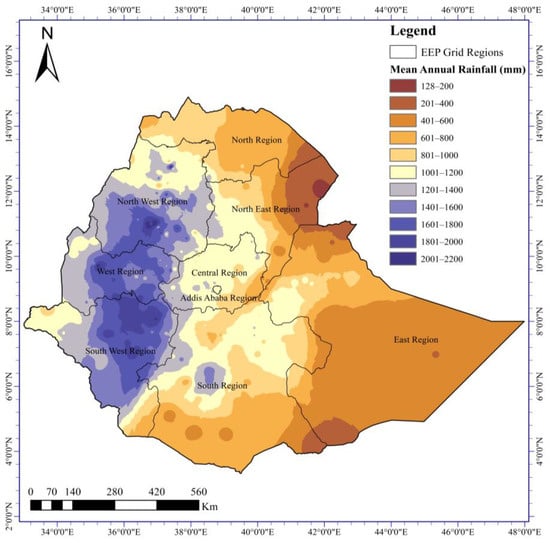
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design of Broadband Doherty Power Amplifier Based on Misaligned Current Phase
by
Yinlong Hu, Decheng Gan and Weimin Shi
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2006; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092006 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
A broadband Doherty power amplifier (DPA) always experiences an efficiency degradation between two efficiency peaks, especially at two side bands. In this study, the efficiency degradation was demonstrated to be caused caused by the in-phase power combining at the saturation power level. To
[...] Read more.
A broadband Doherty power amplifier (DPA) always experiences an efficiency degradation between two efficiency peaks, especially at two side bands. In this study, the efficiency degradation was demonstrated to be caused caused by the in-phase power combining at the saturation power level. To solve this problem, current misalignment was introduced into the broadband DPA design. The carrier and peaking PA have different current phases when performing the power combination at the saturation power level. In this work, it was also demonstrated that the efficiency in the high-power region of a DPA can be improved by elaborately using misaligned current phases. A detailed analysis and the design procedure of a broadband DPA are presented in this paper. And a 1.5–2.45 GHz broadband DPA was implemented and measured. The fabricated DPA achieves a saturation output power of 42.7–44.9 dBm, a saturation drain efficiency (DE) of 62.7–74.1% and a gain of 10.2–13.9 dB over 1.5–2.45 GHz. Moreover, the fabricated DPA also achieves a 6 dB back-off DE of more than 49.1% in the frequency band of interest.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section F3: Power Electronics)
►▼
Show Figures
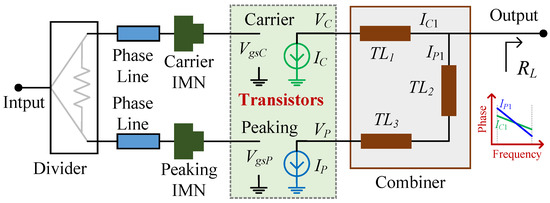
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Proposal and Study of a Pumped Thermal Energy Storage to Improve the Economic Results of a Concentrated Solar Power That Works with a Hybrid Rankine–Brayton Propane Cycle
by
Antonio Jesús Subires, Antonio Rovira and Marta Muñoz
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2005; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092005 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
This work proposes a pumped thermal energy storage (PTES) integrated into the power block of a concentrated solar power plant. The power block operates under a Hybrid Rankine–Brayton (HRB) cycle using propane as the working fluid. During PTES charging, some thermal energy is
[...] Read more.
This work proposes a pumped thermal energy storage (PTES) integrated into the power block of a concentrated solar power plant. The power block operates under a Hybrid Rankine–Brayton (HRB) cycle using propane as the working fluid. During PTES charging, some thermal energy is obtained from a dedicated compressor (additional to that of the HRB cycle), which is stored. During discharge, both compressors (HRB and PTES) are off, restoring the consumed energy and resulting in about a 13% increase in nominal power output. The system is also able to store thermal energy that would otherwise be rejected through the condenser if the PTES were turned off, leading to efficiency improvements in some cases. Considering the 2022 Spanish electricity market prices, the proposed PTES integration with 4 h of storage is feasible. The levelized cost of storage is calculated and compared to those of other PTES systems, achieving around a 40% reduction compared with an equivalent PTES Rankine. These results encourage future studies where the proposed PTES could be integrated into other power cycles that include a recompression process.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Renewable Energy and Energy Storage Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
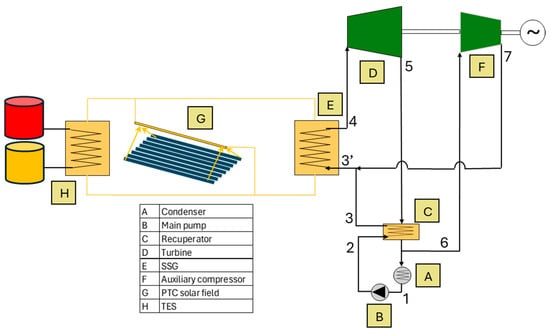
Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Vasistha et al. Exploring the Pivotal Significance of Microalgae-Derived Sustainable Lipid Production: A Critical Review of Green Bioenergy Development. Energies 2023, 16, 531
by
Energies Editorial Office
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2004; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092004 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Following publication [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Study on Traveling Wave Fault Localization of Transmission Line Based on NGO-VMD Algorithm
by
Ke Yu, Xueling Zhu and Wensi Cao
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2003; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092003 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
To address the challenge of inaccurate fault location of variational mode decomposition (VMD) in practical engineering, due to poor choice of mode decomposition number K and quadratic penalty factor α, a traveling wave fault location method using Northern Goshawk optimization algorithm (NGO) to
[...] Read more.
To address the challenge of inaccurate fault location of variational mode decomposition (VMD) in practical engineering, due to poor choice of mode decomposition number K and quadratic penalty factor α, a traveling wave fault location method using Northern Goshawk optimization algorithm (NGO) to optimize VMD was proposed. First, the NGO algorithm is used to optimize VMD, and the optimal K and α are obtained. Secondly, the optimal parameters are inputted into VMD for fault signal decomposition, and the eigenmode components are obtained. Due to the difficulty of identification of the traveling wave head in the process of traveling wave propagation, Hilbert transform is used to determine the time of initial arrival of the traveling wave head at both ends of the line, and the fault location is precisely calculated by using the two-ended traveling wave fault detection formula. Finally, simulation experiments are carried out to verify the accuracy of the proposed location method, which shows that the proposed location method can locate the fault more accurately and has good engineering application value.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section F: Electrical Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
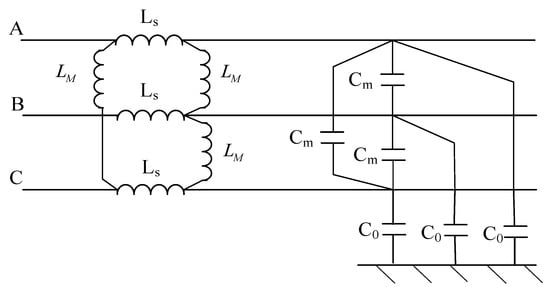
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Harnessing Geothermal Energy Potential from High-Level Nuclear Waste Repositories
by
Dauren Sarsenbayev, Liange Zheng, Dinara Ermakova, Rashid Sharipov and Haruko M. Wainwright
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2002; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092002 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
The disposal of high-level nuclear waste (HLW) has been one of the most challenging issues for nuclear energy utilization. In this study, we have explored the potential of extracting decay heat from HLW, taking advantage of recent advances in the technologies to utilize
[...] Read more.
The disposal of high-level nuclear waste (HLW) has been one of the most challenging issues for nuclear energy utilization. In this study, we have explored the potential of extracting decay heat from HLW, taking advantage of recent advances in the technologies to utilize low-temperature geothermal resources for the co-generation of electricity and heat. Given that geothermal energy entails extracting heat from natural radioactivity within the Earth, we may consider that our approach is to augment it with an anthropogenic geothermal source. Our study—for the first time—introduces a conceptual model of a binary-cycle geothermal system powered by the heat produced by HLW. TOUGHREACT V3.32 software was used to model the heat transfer resulting from radioactive decay to the surrounding geological media. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of employing the organic Rankine cycle (ORC) to generate approximately 108 kWe per HLW canister 30 years after emplacement and a heat pump system to produce 81 kWth of high-potential heat per canister for HVAC purposes within the same timeframe. The proposed facility has the potential to produce carbon-free power while ensuring the safe disposal of radioactive waste and removing the bottleneck in the sustainable use of nuclear energy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section H: Geo-Energy)
Open AccessArticle
A Systematic Investigation into the Optimization of Reactive Power in Distribution Networks Using the Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm–Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
by
Yonggang Wang, Fuxian Li, Ruimin Xiao and Nannan Zhang
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2001; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092001 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
With the expansion of the scale of electric power, high-quality electrical energy remains a crucial aspect of power system management and operation. The generation of reactive power is the primary cause of the decline in electrical energy quality. Therefore, optimization of reactive power
[...] Read more.
With the expansion of the scale of electric power, high-quality electrical energy remains a crucial aspect of power system management and operation. The generation of reactive power is the primary cause of the decline in electrical energy quality. Therefore, optimization of reactive power in the power system becomes particularly important. The primary objective of this article is to create a multi-objective reactive power optimization (MORPO) model for distribution networks. The model aims to minimize reactive power loss, reduce the overall compensation required for reactive power devices, and minimize the total sum of node voltage deviations. To tackle the MORPO problems for distribution networks, the improved sparrow search algorithm–particle swarm optimization (ISSA-PSO) algorithm is proposed. Specifically, two improvements are proposed in this paper. The first is to introduce a chaotic mapping mechanism to enhance the diversity of the population during initialization. The second is to introduce a three-stage differential evolution mechanism to improve the global exploration capability of the algorithm. The proposed algorithm is tested on the IEEE 33-node system and the practical 22-node system. The results indicate a reduction of 32.71% in network losses for the IEEE 33-node system after optimization, and the average voltage of the circuit increases from 0.9485 p.u. to 0.9748 p.u. At the same time, optimization results in a reduction of 44.07% in network losses for the practical 22-node system, and the average voltage of the circuit increases from 0.9838 p.u. to 0.9921 p.u. Therefore, the proposed method exhibits better performance for reducing network losses and enhancing voltage levels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section F: Electrical Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
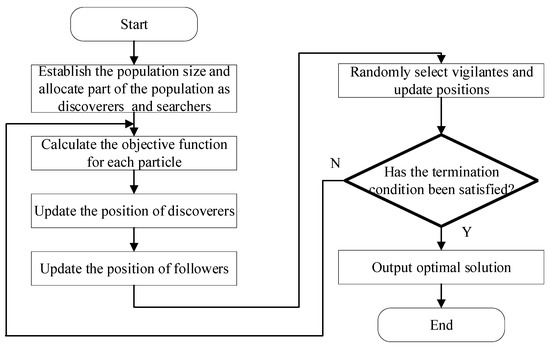
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Automatic Generation Control of a Multi-Area Hybrid Renewable Energy System Using a Proposed Novel GA-Fuzzy Logic Self-Tuning PID Controller
by
Gama Ali, Hamed Aly and Timothy Little
Energies 2024, 17(9), 2000; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17092000 (registering DOI) - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
Human activities overwhelm our environment with CO2 and other global warming issues. The current electricity landscape necessitates a superior, continuous power supply and addressing such environmental concerns. These issues can be resolved by incorporating renewable energy sources (RESs) into the utility grid.
[...] Read more.
Human activities overwhelm our environment with CO2 and other global warming issues. The current electricity landscape necessitates a superior, continuous power supply and addressing such environmental concerns. These issues can be resolved by incorporating renewable energy sources (RESs) into the utility grid. Thus, this paper presents an optimized hybrid fuzzy logic self-tuning PID controller to control the automatic generation control (AGC) of various renewable sources. This controller regulates the frequency deviations of the power system and governs the change in the tie-line load of a multi-area hybrid energy system composed of wind, biomass, and photovoltaic energy sources. MATLAB Simulink software was applied to design and test the system. The PID controller has been tuned using four algorithms, namely, genetic algorithm (GA), pattern search (PS), simulated annealing (SA), and particle swarm optimization (PSO), and we compared the results with the proposed novel optimized PID controller (GA-fuzzy logic self-tuning technique) to validate it. The results show the superiority of the proposed hybrid GA-fuzzy logic self-tuning algorithm over the other algorithms in bringing the power system back to its regular operation. The paper also proposes an operation strategy to lower the utilization of biomass energy in the presence of other renewable energy sources.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Renewable Energy Power Forecasting and Integration)
►▼
Show Figures
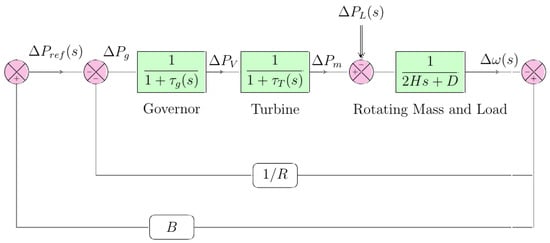
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory (ConvLSTM)-Based Prediction of Voltage Stability in a Microgrid
by
Muhammad Jamshed Abbass, Robert Lis, Muhammad Awais and Tham X. Nguyen
Energies 2024, 17(9), 1999; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/en17091999 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
The maintenance of an uninterrupted electricity supply to meet demand is of paramount importance for maintaining the stable operation of an electrical power system. Machine learning and deep learning play a crucial role in maintaining that stable operation. These algorithms have the ability
[...] Read more.
The maintenance of an uninterrupted electricity supply to meet demand is of paramount importance for maintaining the stable operation of an electrical power system. Machine learning and deep learning play a crucial role in maintaining that stable operation. These algorithms have the ability to acquire knowledge from past data, enabling them to efficiently identify and forecast potential scenarios of instability in the future. This work presents a hybrid convolutional long short-term memory (ConvLSTM) technique for training and predicting nodal voltage stability in an IEEE 14-bus microgrid. Analysis of the findings shows that the suggested ConvLSTM model exhibits the highest level of precision, reaching a value of 97.65%. Furthermore, the ConvLSTM model has been shown to perform better compared to alternative machine learning and deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks, k-nearest neighbors, and support vector machine models, specifically in terms of accurately forecasting voltage stability. The IEEE 14-bus system tests indicate that the suggested method can quickly and accurately determine the stability status of the system. The comparative analysis obtained the results and further justified the efficiency and voltage stability of the proposed model.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Reinforcement Learning in Energy Management of Microgrids and Hybrid Energy Storage Systems)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Energies Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
25 April 2024
Topics Webinar | Shaping Sustainable Futures: Integrating Innovation and Sustainability in Building Design and Retrofitting, 15 May 2024
Topics Webinar | Shaping Sustainable Futures: Integrating Innovation and Sustainability in Building Design and Retrofitting, 15 May 2024

12 April 2024
Meet Us at the 16th International Conference on Hybrid and Organic Photovoltaics, 13–15 May 2024, Valencia, Spain
Meet Us at the 16th International Conference on Hybrid and Organic Photovoltaics, 13–15 May 2024, Valencia, Spain

Topics
Topic in
Energies, JMSE, Oceans, Remote Sensing, Water
Energy from Sea Waves
Topic Editors: Daniele Milone, Vincenzo Franzitta, Domenico Curto, Andrea GuercioDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Batteries, C, Coatings, Energies, Nanomaterials
Advances in Low-Dimensional Materials (LDMs) for Energy Conversion and Storage
Topic Editors: In Soo Kim, Jin Gu KangDeadline: 15 May 2024
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Processes, Solar, Sustainability
Solar Thermal Energy and Photovoltaic Systems, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Pedro Dinis Gaspar, Pedro Dinho da Silva, Luís C. PiresDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electricity, Electronics, Energies, Sensors
Power System Protection
Topic Editors: Seyed Morteza Alizadeh, Akhtar KalamDeadline: 20 June 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Energies
Power Transmission and Distribution Equipment and Systems
Guest Editors: Bilal Asad, Muhammad Naveed IqbalDeadline: 25 April 2024
Special Issue in
Energies
Water Desalination Plants Driven by Hybrid Energy Conversion Systems
Guest Editors: Ekaterina Sokolova, Pietro ZuninoDeadline: 8 May 2024
Special Issue in
Energies
Offshore Wind Support Structure Design
Guest Editor: Mehdi ShokouhianDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Energies
Modeling and Simulation of Floating Offshore Wind Farms
Guest Editor: M. Salman SiddiquiDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Energies
Featured Papers in Electrical Power and Energy System
Collection Editors: Nicu Bizon, Mihai Oproescu, Philippe Poure, Rocío Pérez de Prado, Abdessattar Abdelkefi
Topical Collection in
Energies
Energy Economics and Policy in Developed Countries
Collection Editor: Almas Heshmati
Topical Collection in
Energies
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Advances in Power Converters
Collection Editors: Rosa Anna Mastromauro, Luigi Piegari
Topical Collection in
Energies
Artificial Intelligence and Smart Energy
Collection Editors: Wei-Hsin Chen, Núria Agell, Zhiyong Liu, Ying-Yi Hong