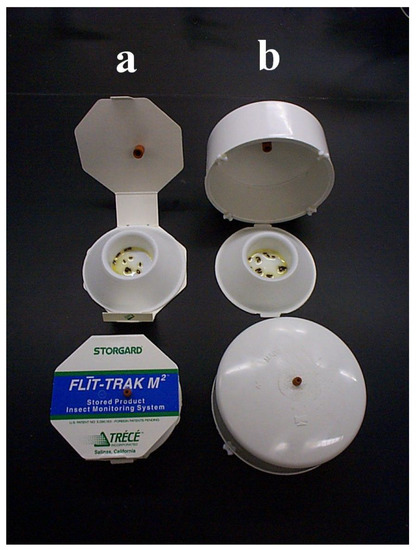
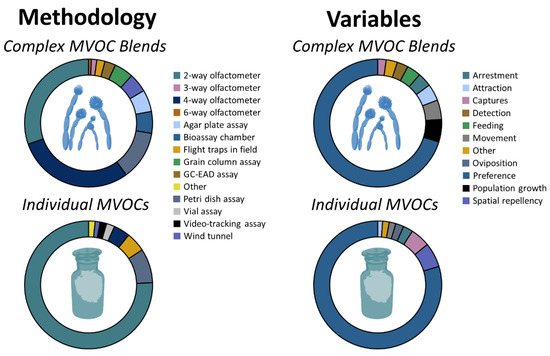
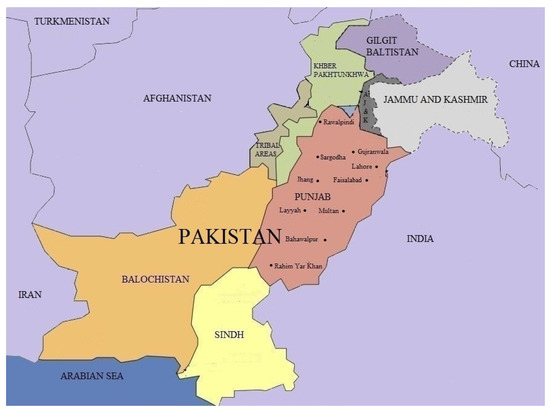
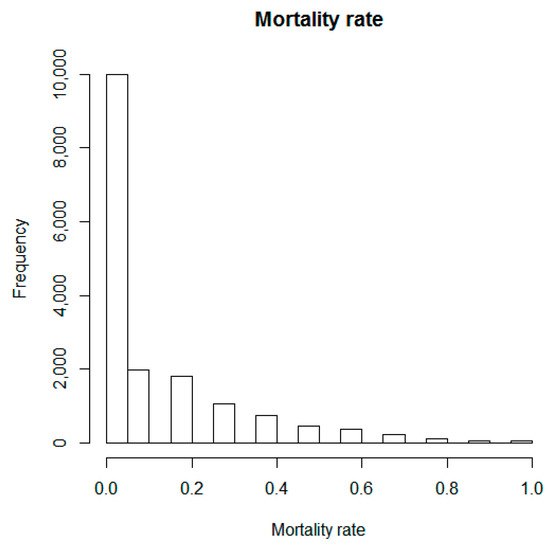
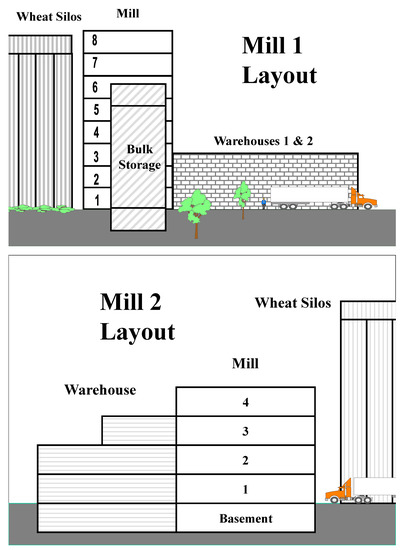
Stored-Product Pests: Biology, Ecology, Behavior and Integrated Management
A topical collection in Insects (ISSN 2075-4450). This collection belongs to the section "Insect Pest and Vector Management".
Viewed by 115420Editor
Interests: stored-product protection; stored-product insect biology; chemical control; non-chemical control; trapping and sampling; taxonomy; aphid parasitoids; forest entomology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
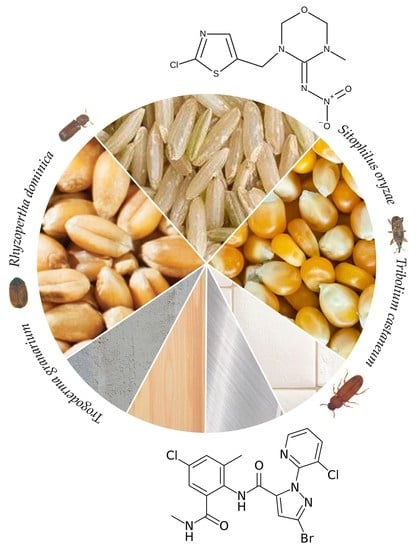
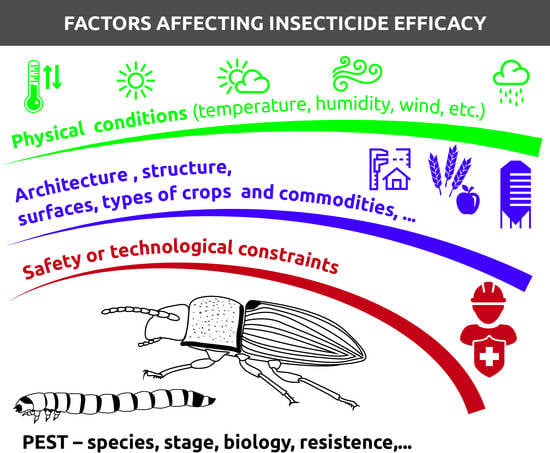
The mass production of goods is linked with a high standard in storage conditions. However, damage from stored-product pests leads to considerable losses worldwide, especially to developing countries. A sure path to confronting these losses is a better understanding of the biology, ecology, and behavior of destructive organisms—either alone or in co-existence—in the complex storage environment as a means to reveal any vulnerabilities during their lifecycles that may be exploited. Consequently, the focused application of management measurements, based on new findings, is expected to be more effective than just following standard protocols. There is an obvious need for novel, cost-effective management tools, which should be available for large-scale applications, given that continuous use of the existing registered formulations is leading to resistance issues. The enrichment and upgrade of our knowledge on the aforementioned aspects will certainly contribute to our available resources to be used against the wide spectrum of noxious species that threaten stored products—a goal that this Topical Collection aims to fulfill.
Dr. Nickolas G. Kavallieratos
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Insects is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- stored-products
- noxious organisms
- control
- biology
- ecology
- behavior