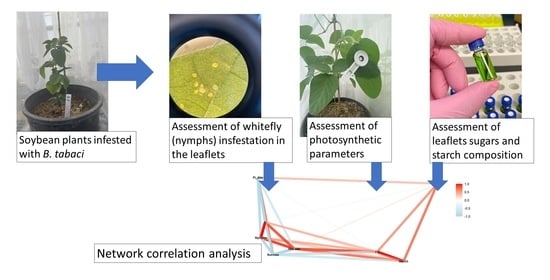
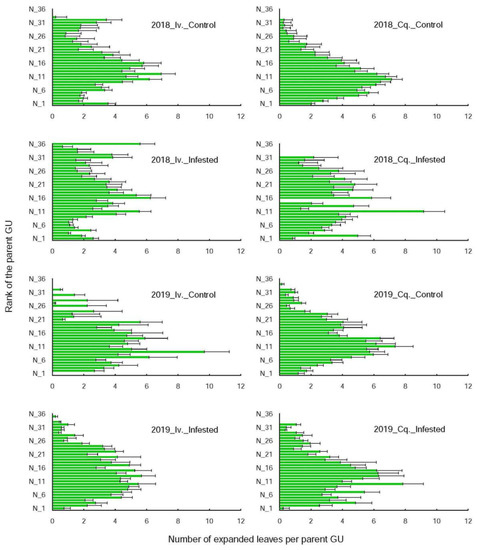
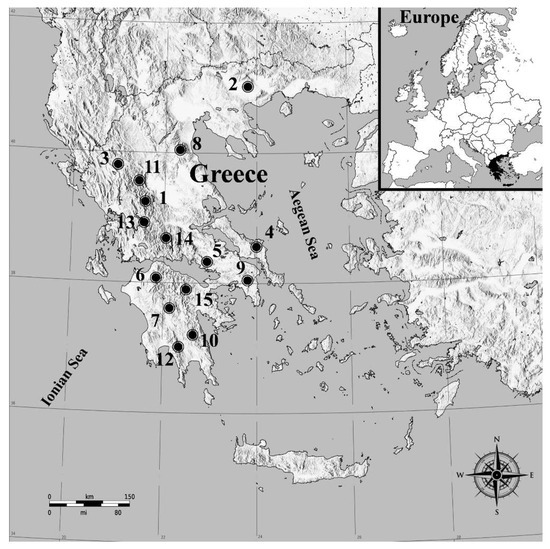
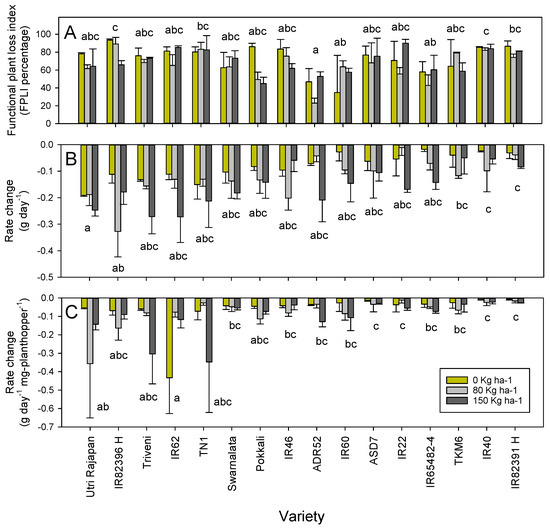
Biology and Management of Sap-Sucking Pests
A topical collection in Insects (ISSN 2075-4450). This collection belongs to the section "Insect Pest and Vector Management".
Viewed by 67827Editors
Interests: stored-product protection; stored-product insect biology; chemical control; non-chemical control; trapping and sampling; taxonomy; aphid parasitoids; forest entomology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: integrated pest management; biological control, environmental science; plant protection; molecular biology; agricultural and applied entomology; insecticide resistance; insect rearing; insect ecology; metabolomics; chemical ecology; tritrophic interactions; plant-insect interactions; plant-microbe-insect interactions; plant defense
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
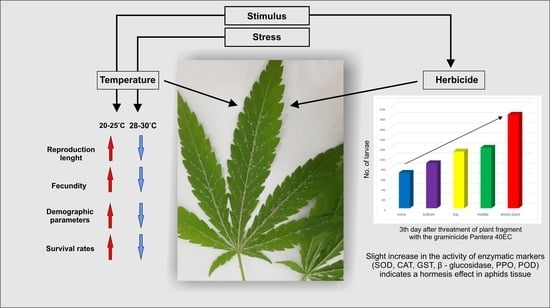
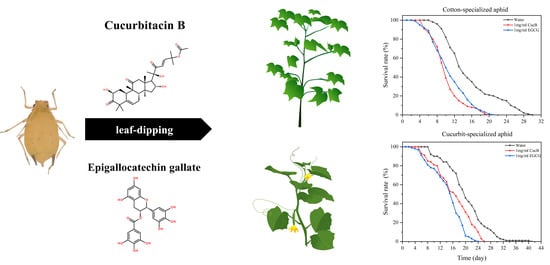
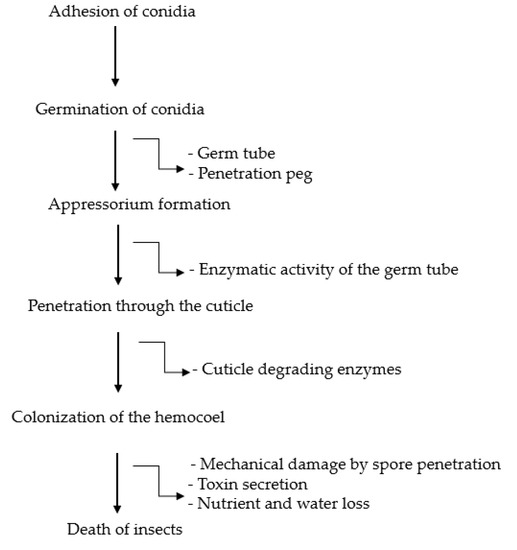
Sap-sucking pests such as brown plant hoppers, whiteflies, aphids, mealybugs, etc. are herbivorous pests that suck the sap (containing vital nutrient-rich assimilates) of plants, yielding detriments in the plants and severely threatening their health. The detriments may not always be severe, however, the fact that the sucking pests can vector viral disease is becoming a serious threat to many major cash crops. Furthermore, as result of sucking nutrient-rich assimilates from the plants, large amounts of sticky feeding residues known as honeydew are produced and deposited on plants. The honeydew then supports the growth of various microbes on plant surfaces, leading to a sooty appearance of infested plants and hence promoting yield losses.
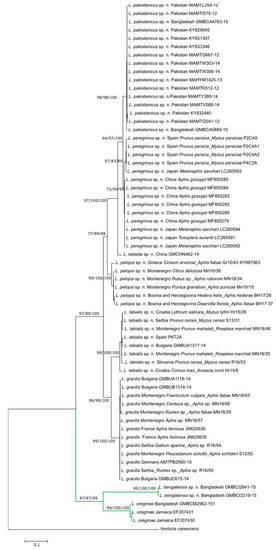
In this Topical Collection, we intend to feature articles that deliberate the biology of the sucking pests; the tritrophic interactions between the sucking pests, the microbes they host, and the plants they attack; the plant defense mechanisms against the sucking pests; the biology, behavior, and ecology of natural enemies against the sucking pests; and the Integrated Pest Management strategies harmonizing environmentally sound biological control agents and conventional methods are all welcomed.
Dr. Nickolas G. Kavallieratos
Dr. David Wari
Dr. Kazumu Kuramitsu
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Insects is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- sap-sucking pest biology
- plant-insect interaction
- plant–microbe–insect interactions
- plant defense mechanisms
- natural enemies
- integrated pest management