Dynamics under Uncertainty: Modeling Simulation and Complexity II
A special issue of Mathematics (ISSN 2227-7390). This special issue belongs to the section "Dynamical Systems".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (28 April 2023) | Viewed by 9649
Special Issue Editors
Interests: multi-criteria decision making problems; computational intelligence; sustainability neuro-fuzzy systems; fuzzy; rough and intuitionistic fuzzy set theory; neutrosophic theory
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: finite element analysis; nano materials; nano technology; materials science; modeling; mathematical modeling; experimentation; ansys; labview, transportatiom; civil engineering; structural engineering; mechanical engineering
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: operations research; optimization; soft computing; uncertainty theory; financial modelling
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
The dynamics of systems have proven to be very powerful tools in understanding the behavior of different natural phenomena throughout the last two centuries. However, the attributes of natural systems are observed to deviate from their classical state due to the effects of different types of uncertainties. In fact, randomness and impreciseness are the two major sources of uncertainties in natural systems. Randomness is modeled by different stochastic processes, and impreciseness can be modeled by fuzzy sets, rough sets, Dempster–Shafer theory, etc.
Generally, symmetry, asymmetry, and antisymmetry are basic characteristics of binary relations used when modeling dynamical systems. Moreover, the notion of symmetry has appeared in many articles about fuzzy sets, rough sets, Dempster–Shafer theory, etc., which are employed in dynamical systems. Hence, the behavior of dynamical systems with uncertain variables, parameters, and functions has recently attracted academic attention. Similarly, the study of the dynamics manifested in complex networks, or an interaction network of individuals, became popular in the last few decades. The study of collective dynamics in complex interaction networks has been proven to be useful to understand collective dynamic phenomena like the emergence of cooperation between rational agents, the synchronization of signals like a flashlight or fireflies, rumor spreading, conscious forming in a social network, etc. Different methods of statistical mechanics are also successfully applied to study such complex systems and to understand the emergence of different collective behavior. When randomness and imprecision coexist in a system, the system is called a hybrid uncertain system. In such a system, the overall uncertainty is an aggregation of both types of uncertainties. However, in the context of modeling the behavior of complex natural systems, it is extremely important to analyze the effect of appropriate uncertainty in order to understand the predictability of different phenomena. Examples of such uncertain dynamical systems could be cited in different levels of the universe ranging from the interaction of quantum particles to the complex interaction of biochemical molecules like signaling in the brain, or even complex social interactions like forming opinions.
This Special Issue will collect high-quality papers addressing uncertain dynamics, their modeling, and their simulation. Submitted papers should not have been previously published or be currently under consideration for publication elsewhere.
We invite authors to submit original research articles that propose novel modeling and simulation of uncertain complex systems in various fields of natural science.
A quick query of Scopus on uncertain dynamics clearly demonstrates a rapid and steady growth of the area as shown in Figure 1.
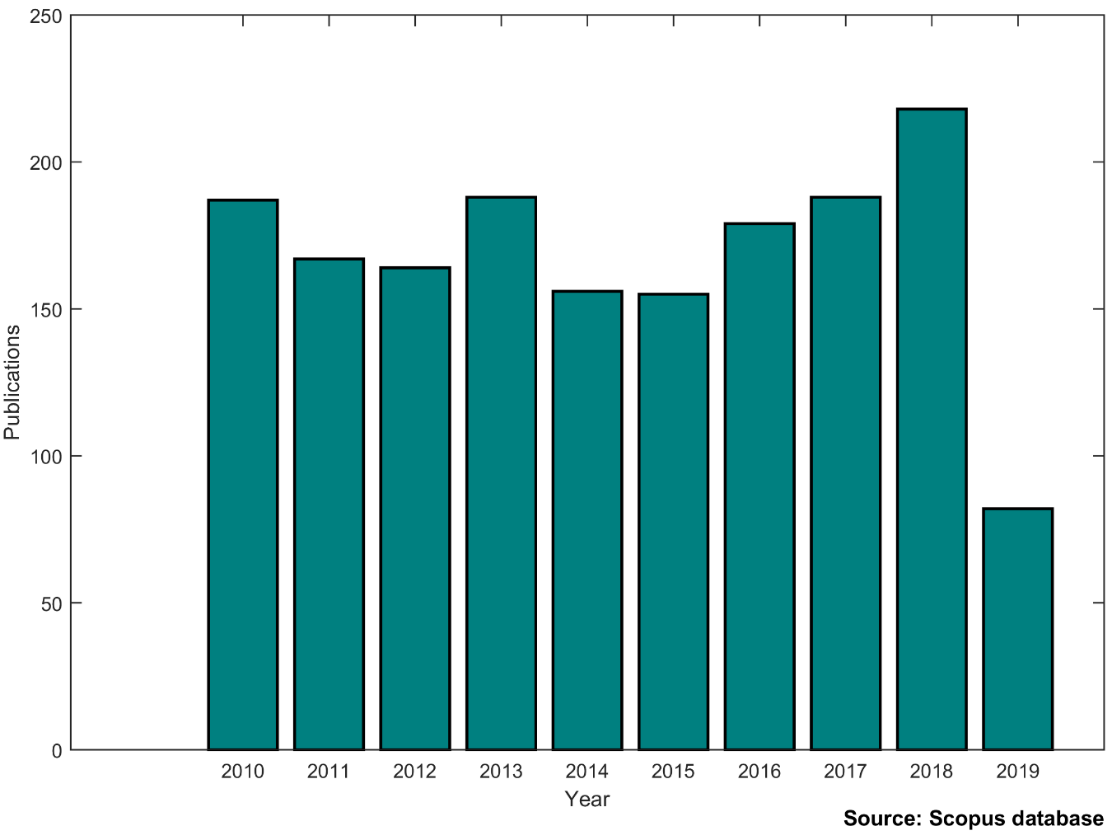
Figure 1. Publications related to uncertain dynamics.
Potential topics include but are not limited to the following:
- Stochastic dynamics, SPDE;
- Random dynamical systems;
- Rough path analysis, random matrix;
- Uncertain dynamics, fuzzy dynamics, rough dynamics;
- Network analysis of complex dynamics;
- Hybrid uncertainty analysis;
- Simulation and complexity of dynamics under uncertainty.
Prof. Dr. Dragan Pamucar
Prof. Dr. Dragan Marinkovic
Prof. Dr. Samarjit Kar
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Mathematics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.






