Heterocycles in Drugs and Drug Discovery
A special issue of Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This special issue belongs to the section "Medicinal Chemistry".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (30 November 2022) | Viewed by 4897
Special Issue Editor
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Heterocycles are moieties used often as part of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The reasons for this are varied: heterocyclic fragments add to the API molecule a variety of functionalities, heteroatoms, aromatic or nonaromatic rings, and differences in basicity or hydrophobicity, all properties which can be easily modulated by the correct functionalization of every heterocyclic ring.
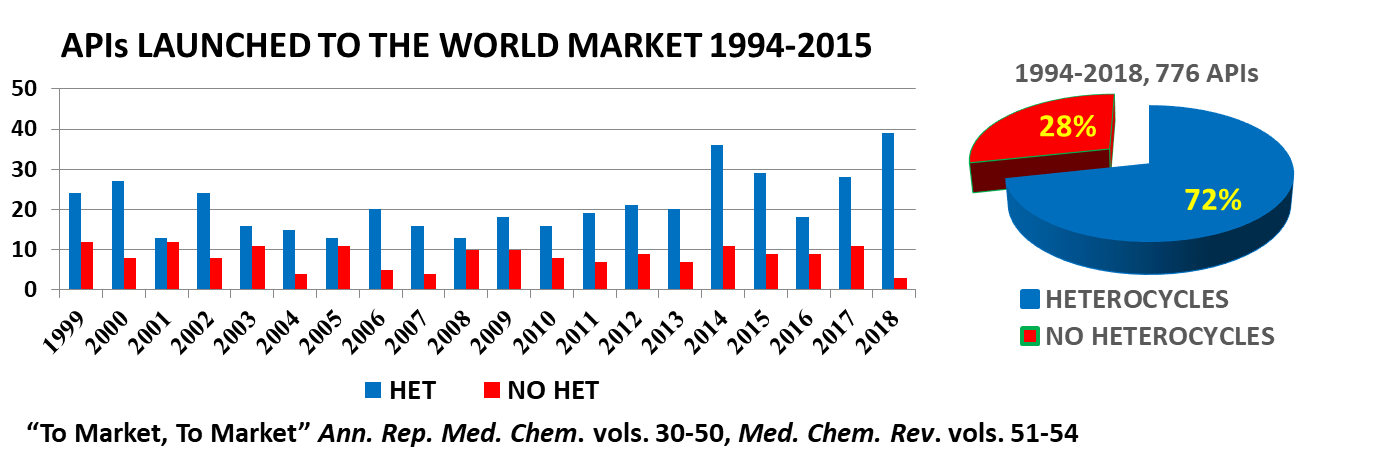
Scheme 1. Heterocyclic and nonheterocyclic APIs launched in the international market.
As shown in Scheme 1, which lists most of the APIs launched in the international market since 1994, more than 70% of the products bear heterocycles in their molecules. Biotech drugs have been counted as nonheterocyclic. The present Special Issue will be devoted to this field, focusing on how heterocycles can be used to develop new APIs. Original research (communications, full papers, and reviews) that discusses drug development of heterocyclic drugs would therefore be welcome.
Prof. Julio Álvarez-Buílla
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- medicinal chemistry
- heterocyclic chemistry
- drug design
- heterocycles
- π-excedent heterocycles
- π-deficient heterocycles






