Polymers in Agriculture and Food Science (Closed)
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Applications".
Viewed by 6398Editor
Interests: cyclodextrins; nanomaterials; polymers; drug delivery; food; health; environment
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Polymeric materials have recently attracted a great deal of interest from the agro-food industry due to their ability to enable the efficient, sustainable, and massive production of food, as well as its subsequent preservation, thus satisfying the demands of a planet with limited natural resources and a growing population. In this regard, due to their ease of processing and the ability to incorporate different compounds to exert specific activities, natural and synthetic polymers can be tailored to meet specific needs.
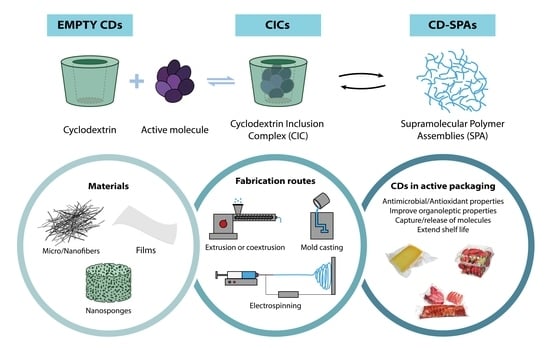
Thus, in food science, researchers have developed suitable materials to improve food quality and safety, or enhance the human health, putting special emphasis on potential migration from the polymer structures or added additives, of analytes that can disrupt or enhance the health of consumers.
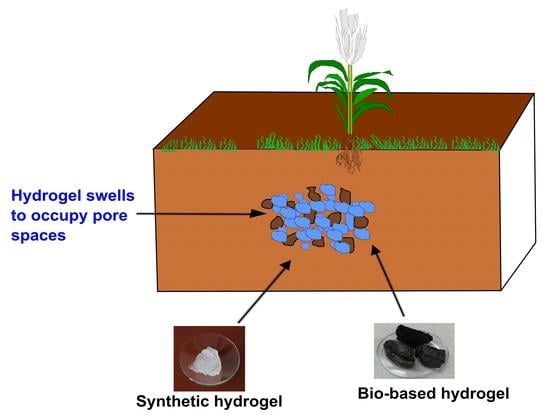
In addition, a pleiad of functionalized polymeric materials have been used to improve treatment effectiveness and crop yield and reduce environmental pollution in agriculture.
In this sense, this Special Issue is planned to bring together a number of original papers and reviews covering (but not restricted to) topics related to the development and application of polymeric systems in the agro-food sector.
Prof. Dr. José Antonio Gabaldón Hernández
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- polymers
- nanocomposites
- food
- agriculture
- controlled release
- absorbent
- packaging-coatings and films
- toxicological studies
- remediation
- future trends
Related Special Issue
- Polymers in Agriculture and Food Science in Polymers (16 articles - displayed below)