Polymeric Adhesives
(Closed)
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Chemistry".
Viewed by 251938
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Antonio Pizzi
Prof. Dr. Antonio Pizzi
 Prof. Dr. Antonio Pizzi
Prof. Dr. Antonio Pizzi
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
LERMAB, Laboratoire d’Etude et de Recherche sur le MAteriau Bois, Université de Lorraine, 27 rue Philippe Seguin, CS60036, 88021 Epinal, France
Interests: polycondensation; resins; adhesives; thermosetting polymers for adhesives; natural polymers for industrial use; fibrous and wood composites; polymeric wood constituents (cellulose, lignin, tannins)
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Today’s intense search for adhesives of superior performance and lower cost, but based on novel approaches, is evident in both the fields of synthetic polymeric adhesives, as well as for adhesives from renewable polymeric materials. This Topical Collection is aimed at collecting cutting-edge original research papers and reviews on the main areas where novel approaches, conceptual or applied, are taken to the fundamental chemistry, mechanisms, applications and technologies of polyurethanes, epoxies, acrylics and many other synthetic adhesives be it oil-derived, coal-derived, inorganic binders or moreover biosourced polymeric adhesives from renewable materials. Mixed synthetic/biosourced adhesives are also aimed at as a particularly lively field of interest. The Collection is aimed at collecting cutting-edge research on all adhesive types under development throughout the vast variety of adhesives in use today, from acrylics to epoxies, to polyurethanes and isocyanates, phenolics and aminoplastics and many others.
Both original contributions and reviews are welcome.
Prof. Dr. Antonio Pizzi
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
-
Synthetic adhesives
-
Biosourced adhesives
-
Mixed Synthetic/biosourced adhesives
-
Adhesion, synthesis and cross-linking mechanisms
-
Novel concepts in adhesion and adhesives
-
Novel or improved adhesive technologies
-
Adhesives application technologies
-
Polyurethane and isocyanate adhesives
-
Acrylic adhesives
-
Epoxy adhesives
-
Phenolic adhesives
-
Aminoplastic adhesives
-
Furanic adhesives
-
Polyvinyl and EVA adhesives
-
Unsaturated polyester adhesives
-
Hot-melt adhesives
-
Anaerobic and aerobic adhesives
-
Cyanoacrylate adhesives
-
Silicone adhesives and sealants
-
Pressure sensitive adhesives
-
Electrically conducting adhesives
-
Rubber adhesives
-
Protein adhesives
Related Special Issues
Published Papers (35 papers)
Open AccessReview
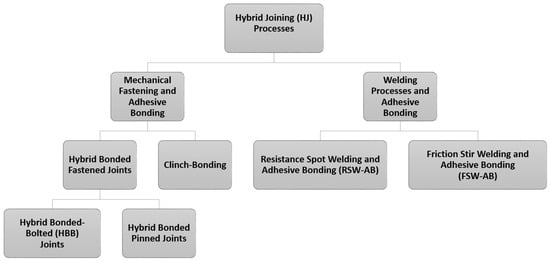
A Review of Structural Adhesive Joints in Hybrid Joining Processes
by
Sofia Maggiore, Mariana D. Banea, Paola Stagnaro and Giorgio Luciano
Cited by 49 | Viewed by 5291
Abstract
Hybrid joining (HJ) is the combination of two or more joining techniques to produce joints with enhanced properties in comparison to those obtained from their parent techniques. Their adoption is widespread (metal to metal joint, composite to composite and composite to metal) and
[...] Read more.
Hybrid joining (HJ) is the combination of two or more joining techniques to produce joints with enhanced properties in comparison to those obtained from their parent techniques. Their adoption is widespread (metal to metal joint, composite to composite and composite to metal) and is present in a vast range of applications including all industrial sectors, from automotive to aerospace, including naval, construction, mechanical and utilities. The objective of this literature review is to summarize the existing research on hybrid joining processes incorporating structural adhesives highlighting their field of application and to present the recent development in this field. To achieve this goal, the first part presents an introduction on the main class of adhesives, subdivided by their chemical nature (epoxy, polyurethane, acrylic and cyanoacrylate, anaerobic and high-temperature adhesives) The second part describes the most commonly used Hybrid Joining (HJ) techniques (mechanical fastening and adhesive bonding, welding processes and adhesive bonding) The third part of the review is about the application of adhesives in dependence of performance, advantage and disadvantage in the hybrid joining processes. Finally, conclusions and an outlook on critical challenges, future perspectives and research activities are summarized. It was concluded that the use of hybrid joining technology could be considered as a potential solution in various industries, in order to reduce the mass as well as the manufacturing cost.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Compounds Based on Bisphenol a Aged in Aqueous Environments
by
Anna Rudawska
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 2112
Abstract
(1) Background: The aim of the work is to determine the influence of selected aqueous environments of various types of liquids on the strength of adhesive compositions prepared from epoxy resin based on bisphenol A combined with two different curing agents: tritethylenetetramine and
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: The aim of the work is to determine the influence of selected aqueous environments of various types of liquids on the strength of adhesive compositions prepared from epoxy resin based on bisphenol A combined with two different curing agents: tritethylenetetramine and polyaminoamide C. (2) Methods: The cured epoxy adhesive compounds samples were seasoned in four aqueous environments of the liquid: rainwater, demineralized water, tap water, and a sweetened drink. Three variants of the aging time in the above-mentioned operating environments were adopted: one month, two months, and three months. After the specified maturing time, samples of epoxy adhesive compositions were subjected to the strength tests on the Zwick/Roell 150 testing machine, which is in accordance with ISO 604 standard, determining the compressive strength. (3) Results: On the basis of the obtained strength test results and their analysis, it was noticed, inter alia, that the strength of the epoxy compounds decreases with the aging time in all used aqueous environments. Moreover, in the case of both types of the epoxy compounds, the highest strength was achieved after aging in demineralized water.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Long-Term Formaldehyde Emission Potential from UF- and NAF-Bonded Particleboards
by
Charles R. Frihart, Timothy L. Chaffee and James M. Wescott
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3275
Abstract
As a result of the dominance of urea formaldehyde (UF)-bonded particleboard, it seemed worthwhile to examine formaldehyde emissions years after production. A California Air Resources Board (CARB) phase II-compliant commercial particleboard produced with a UF resin adhesive was compared to a no-added formaldehyde
[...] Read more.
As a result of the dominance of urea formaldehyde (UF)-bonded particleboard, it seemed worthwhile to examine formaldehyde emissions years after production. A California Air Resources Board (CARB) phase II-compliant commercial particleboard produced with a UF resin adhesive was compared to a no-added formaldehyde (NAF)-particleboard produced with Soyad™ adhesive resin for formaldehyde emissions during exposure to elevated humidity and temperature conditions after being in a room at 21 ± 1.9 °C, 50 ± 3.3% relative humidity for 3.5 years. A modified version of EN 717-3 was used to collect formaldehyde emissions under typical along with higher temperature and humidity conditions. The formaldehyde emissions from the commercial particleboard panel bonded with a UF adhesive even after the 3.5 years of exposure greatly increased only during exposure of the panels to elevated heat and humidity compared to typical testing conditions. The amounts were the same as those with the previous shorter-term study. In contrast, formaldehyde emissions from the NAF-bonded particleboard were not as susceptible (in absolute terms) to increases in temperature and relative humidity conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
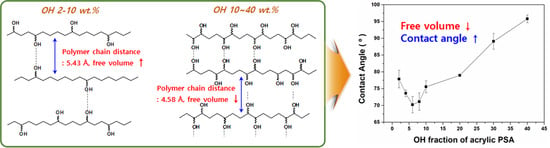
Change of Characterization and Film Morphology Based on Acrylic Pressure Sensitive Adhesives by Hydrophilic Derivative Ratio
by
Woong Cheol Seok, Jong Tae Leem, Ju Hui Kang, Young Jun Kim, Sangkug Lee and Ho Jun Song
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4576
Abstract
Hydrophilic acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) were synthesized by controlling the contents of 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (EHA), isobornyl acrylate (IBOA), and 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA); especially, the characteristic change of the HEA content was analyzed. Surface contact angle of acrylic PSA film decreased from 77.87° to
[...] Read more.
Hydrophilic acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) were synthesized by controlling the contents of 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (EHA), isobornyl acrylate (IBOA), and 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA); especially, the characteristic change of the HEA content was analyzed. Surface contact angle of acrylic PSA film decreased from 77.87° to 70.23° in the case of Acryl-2 to Acryl-8 (below HEA 10 wt %). However, the surface contact angle of Acryl-10 to Acryl-40 (HEA 10 wt % to 40 wt %) increased up to 92.29°, indicating hydrophobicity. All acrylic PSA films showed high adhesive force above 1800 gf/25 mm. According to X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurement, hydrophilic acrylic PSAs exhibited amorphous property and it was confirmed that the morphology of acrylic PSA film was significantly affected by the flexibility of the polymer chain and the strength of hydrogen bonding. The affinity with hydrophilic materials for acrylic PSA films was evaluated by T-type peel test, confirming that the affinity with hydrophilic materials is determined by the hydrophilicity of the acrylic PSA film. The synthesized acrylic PSA film is non-toxic regardless of the hydrophilicity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
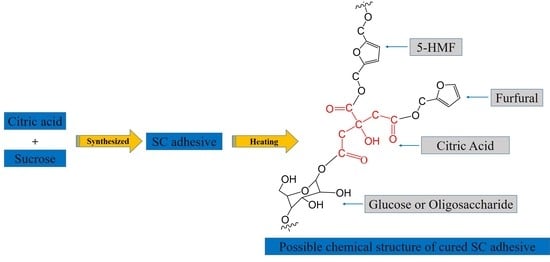
Further Exploration of Sucrose–Citric Acid Adhesive: Investigation of Optimal Hot-Pressing Conditions for Plywood and Curing Behavior
by
Zhongyuan Zhao, Shunsuke Sakai, Di Wu, Zhen Chen, Nan Zhu, Caoxing Huang, Shijing Sun, Min Zhang, Kenji Umemura and Qiang Yong
Cited by 47 | Viewed by 5599
Abstract
In previous research, sucrose and citric acid were used to synthesize an eco-friendly plywood adhesive. Herein, further research was performed to determine the optimal hot-pressing conditions and curing behavior of a sucrose-citric acid (SC) adhesive. The results of dry and wet shear strength
[...] Read more.
In previous research, sucrose and citric acid were used to synthesize an eco-friendly plywood adhesive. Herein, further research was performed to determine the optimal hot-pressing conditions and curing behavior of a sucrose-citric acid (SC) adhesive. The results of dry and wet shear strength measurements showed that the optimal hot-pressing temperature, hot-pressing time, and spread rate of plywood samples bonded by the SC adhesive were 190 °C, 7 min, and 140 g/m
2, respectively. When plywood was bonded at the optimal hot-pressing conditions, the wet shear strength met the requirements of the China National Standard GB/T 9846-2015. Thermal analysis showed that the thermal degradation and endothermic reaction temperatures of the SC 25/75 adhesive were lower than either sucrose or citric acid individually. In addition, the insoluble mass proportion increased with the heating temperature and time. The Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometr (Py-GC/MS) analysis confirmed that the SC adhesive was cured by the reaction between furan compounds, saccharide, and citric acid, and the resulting polymer appeared to be joined by ether linkages.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
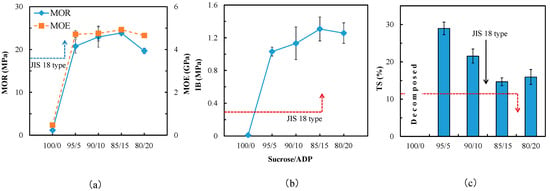
A Novel Eco-Friendly Wood Adhesive Composed by Sucrose and Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate
by
Zhongyuan Zhao, Shin Hayashi, Wei Xu, Zhihui Wu, Soichi Tanaka, Shijing Sun, Min Zhang, Kozo Kanayama and Kenji Umemura
Cited by 40 | Viewed by 4673
Abstract
Development of a bio-based wood adhesive is a significant goal for several wood-based material industries. In this study, a novel adhesive based upon sucrose and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) was formulated in hopes of furthering this industrial goal through realization of a sustainable
[...] Read more.
Development of a bio-based wood adhesive is a significant goal for several wood-based material industries. In this study, a novel adhesive based upon sucrose and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) was formulated in hopes of furthering this industrial goal through realization of a sustainable adhesive with mechanical properties and water resistance comparable to the synthetic resins used today. Finished particleboards exhibited excellent mechanical properties and water resistance at the revealed optimal adhesive conditions. In fact, the board properties fulfilled in principle the requirements of JIS A 5908 18 type standard, however this occured at production conditions for the actual state of development as reported here, which are still different to usual industrial conditions. Thermal analysis revealed addition of ADP resulted in decreases to the thermal thresholds associated with degradation and curing of sucrose. Spectral results of FT-IR elucidated that furanic ring chemistry was involved during adhesive curing. A possible polycondensation reaction pathway was proposed from this data in an attempt to explain why the adhesive exhibited such favorable bonding properties.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
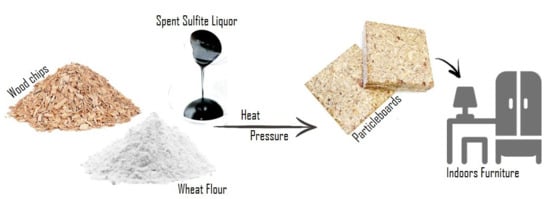
Biosourced Binder for Wood Particleboards Based on Spent Sulfite Liquor and Wheat Flour
by
Ana M. Ferreira, João Pereira, Margarida Almeida, João Ferra, Nádia Paiva, Jorge Martins, Fernão D. Magalhães and Luísa H. Carvalho
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 6795
Abstract
Currently, the majority of binders used in wood particleboard (PB) manufacturing are formaldehyde-based synthetic resins. Because of the toxicity of formaldehyde, there is a strong demand for eco-friendly alternatives with similar performances and economic viability. In this work, thick spent sulfite liquor (TSSL),
[...] Read more.
Currently, the majority of binders used in wood particleboard (PB) manufacturing are formaldehyde-based synthetic resins. Because of the toxicity of formaldehyde, there is a strong demand for eco-friendly alternatives with similar performances and economic viability. In this work, thick spent sulfite liquor (TSSL), an industrial byproduct from sulfite pulp mills, is proposed as a binder for fully bio-based PBs. The results showed that PBs bound with TSSL present appropriate mechanical performance, which was further improved when TSSL was combined with wheat flour at an 84:16 dry weight ratio and preheated to 94 °C prior to application. For 13.2% binder content per dry wood weight, the PB internal bond strength was 0.46 N mm
−2, which is above the standard requirements for PB type P2 (0.35 N mm
−2). Optical microscopy showed that TSSL hinders the gelatinization of starch granules during preheating, allowing the binder mixture to maintain a low viscosity suitable for combination with wood particles and PB production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
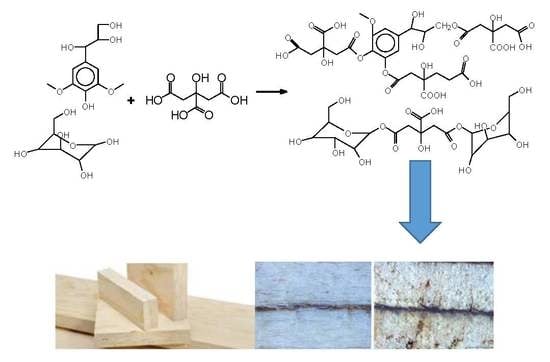
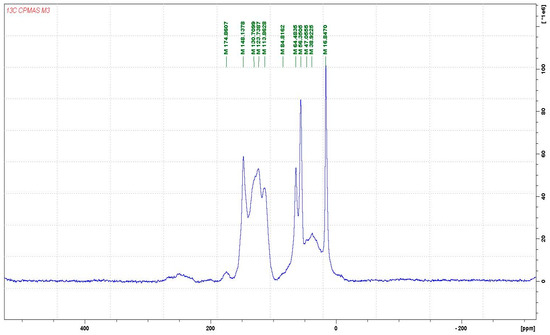
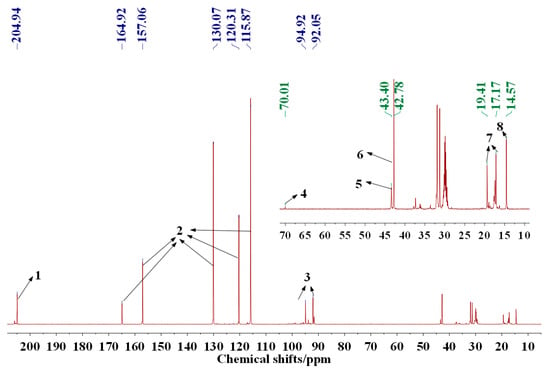
Reactions with Wood Carbohydrates and Lignin of Citric Acid as a Bond Promoter of Wood Veneer Panels
by
Claudio Del Menezzi, Siham Amirou, Antonio Pizzi, Xuedong Xi and Luc Delmotte
Cited by 50 | Viewed by 5856
Abstract
The reaction of citric acid with wood veneers was studied by Cross Polarization Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (CP MAS
13C NMR) and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight (MALDI ToF) mass spectrometry. The analysis showed that reactions of
[...] Read more.
The reaction of citric acid with wood veneers was studied by Cross Polarization Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (CP MAS
13C NMR) and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight (MALDI ToF) mass spectrometry. The analysis showed that reactions of citric acid occurred with both lignin and carbohydrate constituents of wood. The reactions occurring are esterifications between the carboxylic acid functions of citric acid and the numerous aromatic and aliphatic hydroxyl groups of the main wood constituents. Reaction of citric acid with glucose as a simple model compound of carbohydrates hydroxyl groups also yielded reactions leading to linear and branched oligomers by esterification. The result indicate that the reactions of esterification are accompanied in parallel by some internal rearrangements of lignin. The applied results on bonding wide flat wood surfaces such as veneers to obtain LVL panels yielded excellent strength results even if the conditions of pressing were more drastic than what is usual for this application. The applied bonding results have shown that citric acid has great potential to be used as a bio-binder for wood veneers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
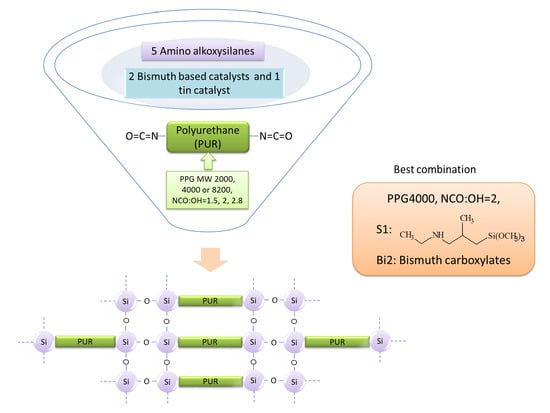
The Synthesis of Low-Viscosity Organotin-Free Moisture-Curable Silane-Terminated Poly(Urethane-Urea)s
by
Chen Tan, Viivi Luona, Teija Tirri and Carl-Eric Wilen
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 6098
Abstract
This work explores the possibility of synthesizing moisture-curable silane-terminated poly(urethane-urea)s (SPURs) of low viscosity. First, NCO-terminated urethane prepolymers were prepared, followed by silane end-capping. The impact of polyol molecular weight and the ratio of isocyanate to polyol (NCO/OH) on viscosity and the properties
[...] Read more.
This work explores the possibility of synthesizing moisture-curable silane-terminated poly(urethane-urea)s (SPURs) of low viscosity. First, NCO-terminated urethane prepolymers were prepared, followed by silane end-capping. The impact of polyol molecular weight and the ratio of isocyanate to polyol (NCO/OH) on viscosity and the properties of SPUR were examined. As alternatives to the organotin catalysts traditionally used for the polyurethane synthesis and curing processes, bismuth carboxylate catalysts were evaluated. In addition, the effect of organofunctional groups in the aminosilane structure (R1–NH–R2–Si(OR3)
3), i.e., R1 (alkyl, aryl or trimethoxysilyl-propyl), the spacer R2 (α or γ) and alkyl group R3 (methyl or ethyl), was examined. The chemical and physical structures of the SPUR were investigated by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and the mechanical properties were evaluated by tensile tests. The results reveal that silane-terminated, moisture-curable polyurethanes can be successfully synthesized and cured with bismuth carboxylate catalysts. SPUR exhibiting low viscosity, with adequate tensile strength and elongation can be prepared using environmentally benign bismuth carboxylate catalyst having a high metal content of 19%–21%, by utilizing secondary aminosilane end-cappers and an optimal combination of the polyol molecular weight and NCO/OH ratio.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Characterization of the Low Molar Ratio Urea–Formaldehyde Resin with 13C NMR and ESI–MS: Negative Effects of the Post-Added Urea on the Urea–Formaldehyde Polymers
by
Hui Wang, Ming Cao, Taohong Li, Long Yang, Zhigang Duan, Xiaojian Zhou and Guanben Du
Cited by 48 | Viewed by 7495
Abstract
The structural changes during three-step synthesis of low-molar ratio urea–formaldehyde (UF) resin were tracked by quantitative
13C nuclear magnetic resonance (
13C NMR) analysis and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI–MS). Condensations that produced polymers were found to be linked by ether bonds
[...] Read more.
The structural changes during three-step synthesis of low-molar ratio urea–formaldehyde (UF) resin were tracked by quantitative
13C nuclear magnetic resonance (
13C NMR) analysis and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI–MS). Condensations that produced polymers were found to be linked by ether bonds in addition to hydroxymethylation reactions at the first alkaline stage with a formaldehyde to urea ratio of 2:1. Considerable formation of branched methylene linkages, with the highest content among all the condensed structures, was the key feature of the acidic stage. Notable changes were observed for the chemical structures and molecular masses of the resin components after the formaldehyde to urea molar ratio was lowered to 1.2 by adding post-urea at the final alkaline stage. Specifically, most of the branched hydroxymethyl groups on the polymers were cleaved, resulting in a significant decrease in the branching degree of the polymers. The performance degradation of the UF resin was attributed to this debranching effect and the production of components with low molecular masses. Based on the observations, the curing pattern of low molar ratio UF resin was postulated and branched polymeric formaldehyde catcher bearing urea-reactivity was proposed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
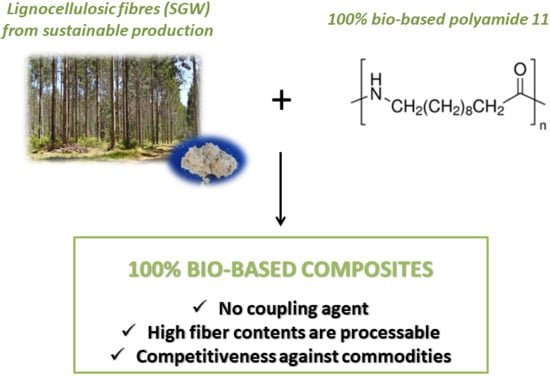
Towards More Sustainable Material Formulations: A Comparative Assessment of PA11-SGW Flexural Performance versus Oil-Based Composites
by
Helena Oliver-Ortega, José Alberto Méndez, Rafel Reixach, Francesc Xavier Espinach, Mònica Ardanuy and Pere Mutjé
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 5096
Abstract
The replacement of commodity polyolefin, reinforced with glass fiber (GF), by greener alternatives has been a topic of research in recent years. Cellulose fibers have shown, under certain conditions, enough tensile capacities to replace GF, achieving competitive mechanical properties. However, if the objective
[...] Read more.
The replacement of commodity polyolefin, reinforced with glass fiber (GF), by greener alternatives has been a topic of research in recent years. Cellulose fibers have shown, under certain conditions, enough tensile capacities to replace GF, achieving competitive mechanical properties. However, if the objective is the production of environmentally friendlier composites, it is necessary to replace oil-derived polymer matrices by bio-based or biodegradable ones, depending on the application. Polyamide 11 (PA11) is a totally bio-based polyamide that can be reinforced with cellulosic fibers. Composites based on this polymer have demonstrated enough tensile strength, as well as stiffness, to replace GF-reinforced polypropylene (PP). However, flexural properties are of high interest for engineering applications. Due to the specific character of short-fiber-reinforced composites, significant differences are expected between the tensile and flexural properties. These differences encourage the study of the flexural properties of a material prior to the design or development of a new product. Despite the importance of the flexural strength, there are few works devoted to its study in the case of PA11-based composites. In this work, an in-depth study of the flexural strength of PA11 composites, reinforced with Stoneground wood (SGW) from softwood, is presented. Additionally, the results are compared with those of PP-based composites. The results showed that the SGW fibers had lower strengthening capacity reinforcing PA11 than PP. Moreover, the flexural strength of PA11-SGW composites was similar to that of PP-GF composites.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
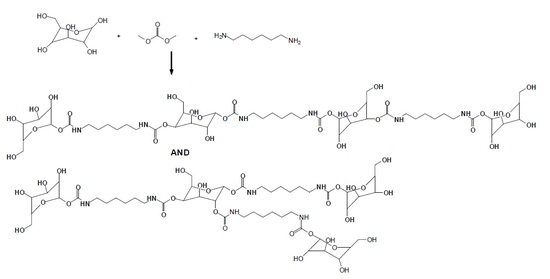
Isocyanate-Free Polyurethane Coatings and Adhesives from Mono- and Di-Saccharides
by
Xuedong Xi, Antonio Pizzi and Luc Delmotte
Cited by 64 | Viewed by 8837
Abstract
Mostly biosourced non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPU) were prepared from mono- and disaccharides, namely glucose and sucrose, reacted with dimethyl carbonate and hexamethylene diamine. The main aim of this research was to show that NIPU can be prepared from mono- and disaccharides, this just being
[...] Read more.
Mostly biosourced non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPU) were prepared from mono- and disaccharides, namely glucose and sucrose, reacted with dimethyl carbonate and hexamethylene diamine. The main aim of this research was to show that NIPU can be prepared from mono- and disaccharides, this just being an initial exploratory work and its sole main aim. The oligomers obtained were detected by MALDI-ToF, CP-MAS
13C NMR, and FTIR spectrometries. The glucose-derived NIPU were shown to harden at a markedly lower temperature than the sucrose-derived ones and to be easier to handle and spread. The NIPU obtained were applied as wood and steel surface coatings and tested by the sessile drop test (on wood) and cross-cut test (on steel) with encouraging results. The glucose NIPU gave good surface coating results already at 103 °C, while the sucrose NIPU yielded good results only at a markedly higher temperature of hardening. The NIPU saccharide resins were also tested as thermosetting wood joint adhesives with the glucose NIPU yielding very encouraging results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
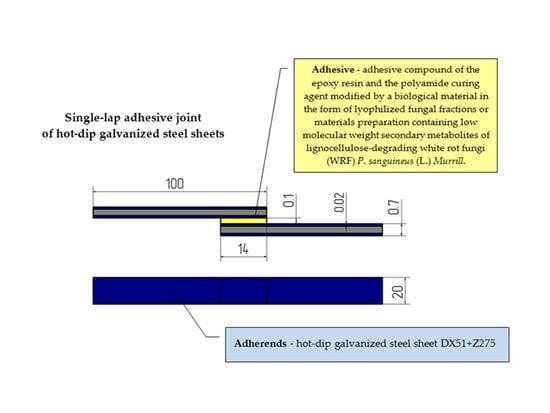
The Influence of Adhesive Compounds Biochemical Modification on the Mechanical Properties of Adhesive Joints
by
Anna Rudawska, Izabela Haniecka, Magdalena Jaszek and Dawid Stefaniuk
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 4648
Abstract
The main purpose of this paper was to determine the effect of biochemical modification of epoxy adhesive compounds on the mechanical properties of hot-dip galvanized steel sheet DX51+Z275 adhesive joints. The epoxy adhesives (resin and curing agent) were biochemically modified by lyophilized fungal
[...] Read more.
The main purpose of this paper was to determine the effect of biochemical modification of epoxy adhesive compounds on the mechanical properties of hot-dip galvanized steel sheet DX51+Z275 adhesive joints. The epoxy adhesives (resin and curing agent) were biochemically modified by lyophilized fungal metabolites (in the form of lyophilized fungal fractions or materials preparation containing low molecular weight secondary metabolites of lignocellulose-degrading white rot fungi (WRF)
Pycnoporus sanguineus (L.)
Murrill and prepared by two methods). The epoxy adhesives (epoxy resin Epidian 53 and poliaminoamide curing agent PAC) were biochemical modified by lyophilized fungal metabolites and prepared by two methods. In the first method (Method I), the epoxy resin and the curing agent were mixed with the fungal material in the desired concentration. In the second method (Method II), the resin was mixed with mortar-grounded lyophilized post-culture liquid of the desired concentration and after following thorough mixing, a suitable amount of the poliaminoamide curing agent was added. The single-lap adhesive joints were prepared by modified epoxy adhesive compounds and were cured in various climatic factors. The specimens of adhesive joints were cured at single stage at the same temperature and humidity as during adhesive bonding (Variant A and Variant B). At the second stage, Method I adhesive joints were seasoned for two months at the temperature of 50 °C and 50% humidity in a climate test chamber (Variant C). The shear strength tests of the single-lap adhesive joints were performed using a Zwick/Roell Z150 testing machine in accordance with the DIN EN 1465 standard. The analysis of results revealed that the addition of the biological modifier can lead to reduced adhesive joint strength in ambient conditions, yet at elevated temperature and the higher humidity it results in a significant increase in adhesive joint strength.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
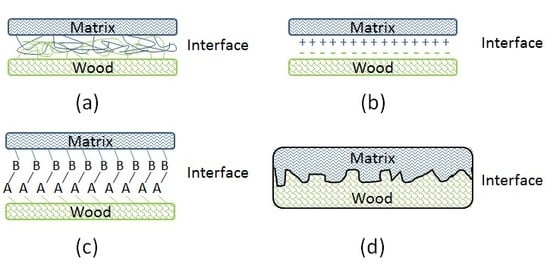
Revealing the Interface Structure and Bonding Mechanism of Coupling Agent Treated WPC
by
Jiuping Rao, Yonghui Zhou and Mizi Fan
Cited by 49 | Viewed by 7306
Abstract
This paper presents the interfacial optimisation of wood plastic composites (WPC) based on recycled wood flour and polyethylene by employing maleated and silane coupling agents. The effect of the incorporation of the coupling agents on the variation of chemical structure of the composites
[...] Read more.
This paper presents the interfacial optimisation of wood plastic composites (WPC) based on recycled wood flour and polyethylene by employing maleated and silane coupling agents. The effect of the incorporation of the coupling agents on the variation of chemical structure of the composites were investigated by Attenuated total reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) and Solid state
13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy (NMR) analyses. The results revealed the chemical reactions that occurred between the coupling agents and raw materials, which thus contributed to the enhancement of compatibility and interfacial adhesion between the constituents of WPC. NMR results also indicated that there existed the transformation of crystalline cellulose to an amorphous state during the coupling agent treatments, reflecting the inferior resonance of crystalline carbohydrates. Fluorescence Microscope (FM) and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analyses showed the improvements of wood particle dispersion and wettability, compatibility of the constituents, and resin penetration, and impregnation of the composites after the coupling agent treatments. The optimised interface of the composites was attributed to interdiffusion, electrostatic adhesion, chemical reactions, and mechanical interlocking bonding mechanisms.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
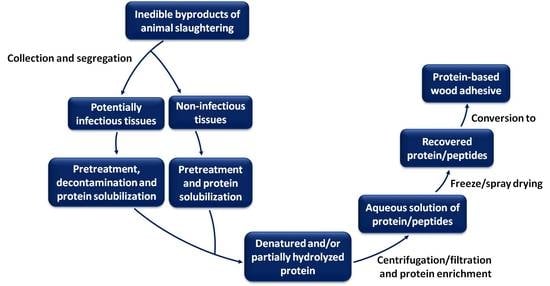
Utilization of Slaughterhouse Waste in Value-Added Applications: Recent Advances in the Development of Wood Adhesives
by
Birendra B. Adhikari, Michael Chae and David C. Bressler
Cited by 78 | Viewed by 9577
Abstract
Globally, slaughterhouses generate large volumes of animal byproducts. While these byproducts are an important resource of industrial protein that could potentially be utilized in various value-added applications, they are currently either underutilized in high-value applications or being used for production of relatively low-value
[...] Read more.
Globally, slaughterhouses generate large volumes of animal byproducts. While these byproducts are an important resource of industrial protein that could potentially be utilized in various value-added applications, they are currently either underutilized in high-value applications or being used for production of relatively low-value products such as animal feed and pet food. Furthermore, some of the byproducts of animal slaughtering cannot enter food and feed chains and thus their disposal possesses a serious environmental concern. An innovative utilization of the proteinaceous waste generated by slaughterhouses comprises of waste processing to extract proteins, which are then incorporated into industrial processes to produce value-added bio-based products. In this report, we review the current processes for extraction of protein from proteinaceous waste of slaughterhouses, and utilization of the recovered protein in the development of protein-based wood adhesives.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
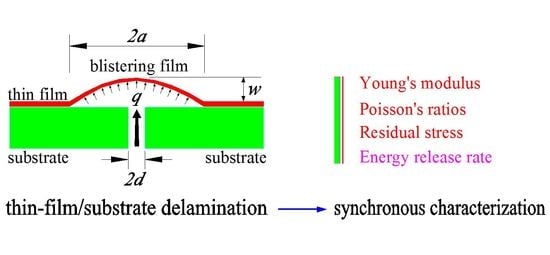
Theoretical Study on Synchronous Characterization of Surface and Interfacial Mechanical Properties of Thin-Film/Substrate Systems with Residual Stress Based on Pressure Blister Test Technique
by
Zhi-xin Yang, Jun-yi Sun, Ke Li, Yong-sheng Lian, Xiao-ting He and Zhou-lian Zheng
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 5757
Abstract
In this study, based on the pressure blister test technique, a theoretical study on the synchronous characterization of surface and interfacial mechanical properties of thin-film/substrate systems with residual stress was presented, where the problem of axisymmetric deformation of a blistering film with initial
[...] Read more.
In this study, based on the pressure blister test technique, a theoretical study on the synchronous characterization of surface and interfacial mechanical properties of thin-film/substrate systems with residual stress was presented, where the problem of axisymmetric deformation of a blistering film with initial stress was analytically solved and its closed-form solution was presented. The expressions to determine Poisson’s ratios, Young’s modulus, and residual stress of surface thin films were derived; the work done by the applied external load and the elastic energy stored in the blistering thin film were analyzed in detail and their expressions were derived; and the interfacial adhesion energy released per unit delamination area of thin-film/substrate (i.e., energy release rate) was finally presented. The synchronous characterization technique presented here has theoretically made a big step forward, due to the consideration for the residual stress in surface thin films.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
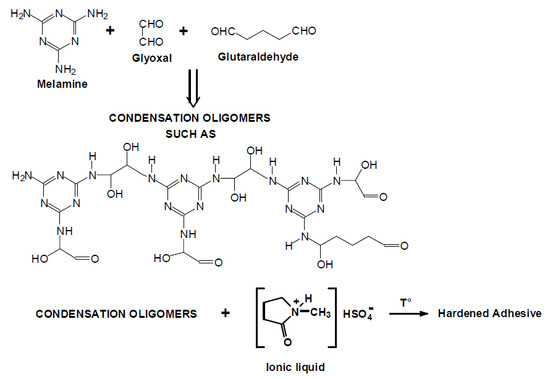
Melamine–Glyoxal–Glutaraldehyde Wood Panel Adhesives without Formaldehyde
by
Xuedong Xi, Antonio Pizzi and Siham Amirou
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 9789
Abstract
(MGG’) resin adhesives for bonding wood panels were prepared by a single step procedure, namely reacting melamine with glyoxal and simultaneously with a much smaller proportion of glutaraldehyde. No formaldehyde was used. The inherent slow hardening of this resin was overcome by the
[...] Read more.
(MGG’) resin adhesives for bonding wood panels were prepared by a single step procedure, namely reacting melamine with glyoxal and simultaneously with a much smaller proportion of glutaraldehyde. No formaldehyde was used. The inherent slow hardening of this resin was overcome by the addition of
N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone hydrogen sulphate ionic liquid as the adhesive hardener in the glue mix. The plywood strength results obtained were comparable with those obtained with melamine–formaldehyde resins pressed under the same conditions. Matrix assisted laser desorption ionisation time of flight (MALDI ToF) and Fourier transform Infrared (FTIR) analysis allowed the identification of the main oligomer species obtained and of the different types of linkages formed, as well as to indicate the multifaceted role of the ionic liquid. These resins are proposed as a suitable substitute for equivalent formaldehyde-based resins.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
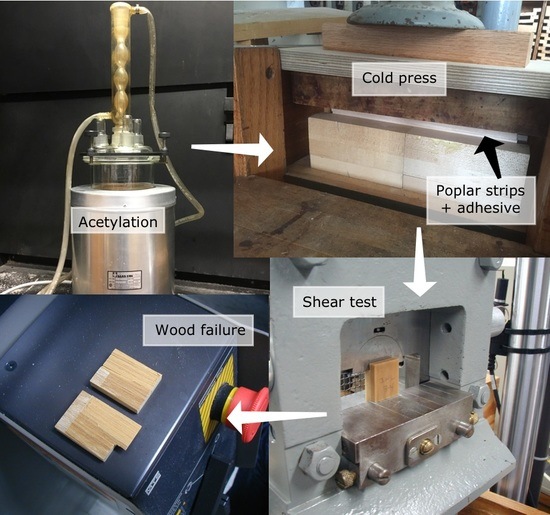
Adhesives for Achieving Durable Bonds with Acetylated Wood
by
Charles R. Frihart, Rishawn Brandon, James F. Beecher and Rebecca E. Ibach
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 5425
Abstract
Acetylation of wood imparts moisture durability, decay resistance, and dimensional stability to wood; however, making durable adhesive bonds with acetylated wood can be more difficult than with unmodified wood. The usual explanation is that the acetylated surface has fewer hydroxyl groups, resulting in
[...] Read more.
Acetylation of wood imparts moisture durability, decay resistance, and dimensional stability to wood; however, making durable adhesive bonds with acetylated wood can be more difficult than with unmodified wood. The usual explanation is that the acetylated surface has fewer hydroxyl groups, resulting in a harder-to-wet surface and in fewer hydrogen bonds between wood and adhesive. This concept was evaluated using four different adhesives (resorcinol–formaldehyde, emulsion polymer isocyanate, epoxy, and melamine–formaldehyde) with unmodified wood, acetylated wood, and acetylated wood that had been planed. Strikingly, acetylation did not hinder adhesive bonds with a waterborne resorcinol–formaldehyde adhesive that bonded equally well to both unmodified and acetylated yellow poplar. An epoxy adhesive bonded better to the acetylated wood than to the unmodified wood, in contrast to an emulsion polymer isocyanate, which gave less durable bonds to acetylated than to unmodified wood. Planing of the acetylated wood surface prior to bonding reduced bond durability for the epoxy adhesive and increased the amount of surface hydroxyl groups, as measured using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis of the trifluoroacetic anhydride-treated wood. These experiments showed that wood modification is useful in understanding wood-adhesive interactions, in addition to determining how to develop adhesives for acetylated woods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Bio-Inspired Polymeric Structures with Special Wettability and Their Applications: An Overview
by
Zihe Pan, Fangqin Cheng and Boxin Zhao
Cited by 45 | Viewed by 14454
Abstract
It is not unusual for humans to be inspired by natural phenomena to develop new advanced materials; such materials are called bio-inspired materials. Interest in bio-inspired polymeric superhydrophilic, superhydrophobic, and superoleophobic materials has substantially increased over the last few decades, as has improvement
[...] Read more.
It is not unusual for humans to be inspired by natural phenomena to develop new advanced materials; such materials are called bio-inspired materials. Interest in bio-inspired polymeric superhydrophilic, superhydrophobic, and superoleophobic materials has substantially increased over the last few decades, as has improvement in the related technologies. This review reports the latest developments in bio-inspired polymeric structures with desired wettability that have occurred by mimicking the structures of lotus leaf, rose petals, and the wings and shells of various creatures. The intrinsic role of surface chemistry and structure on delivering superhydrophilicity, superhydrophobicity, and superoleophobicity has been extensively explored. Typical polymers, commonly used structures, and techniques involved in developing bio-inspired surfaces with desired wettability are discussed. Additionally, the latest applications of bio-inspired structures with desired wettability in human activities are also introduced.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
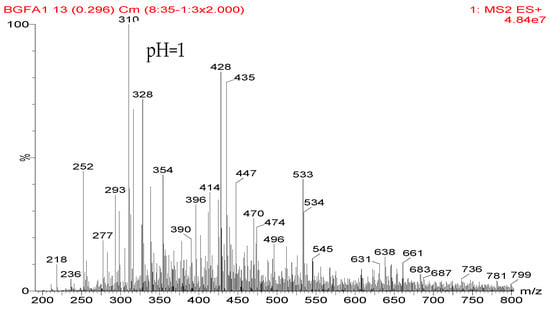
The Reaction between Furfuryl Alcohol and Model Compound of Protein
by
Jiankun Liang, Zhigang Wu, Hong Lei, Xuedong Xi, Taohong Li and Guanben Du
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 5298
Abstract
To guide the preparation of protein-based adhesive, especially the soy-based adhesive, the reaction between a simple dipeptide
N-(2)-
l-alanyl-
l-glutamine (AG), being used as a model compound of protein, and its cross-linker furfuryl alcohol were studied in this paper. The
[...] Read more.
To guide the preparation of protein-based adhesive, especially the soy-based adhesive, the reaction between a simple dipeptide
N-(2)-
l-alanyl-
l-glutamine (AG), being used as a model compound of protein, and its cross-linker furfuryl alcohol were studied in this paper. The products that were prepared with furfuryl alcohol and AG under different pHs were analyzed by ESI-MS,
13C NMR, and FT-IR. It was found that the medium environment had great effects on the competition of the co-condensation reaction between furfuryl alcohol and AG and self-condensation reaction of furfuryl alcohol molecules in the mixing system with furfuryl alcohol and AG. Under alkaline conditions, both co- and self-condensation were not obviously detected. Only when the value of pH was higher than 11, were a few co-condensation reaction products gotten. The reaction occurred mainly between furfuryl alcohol and the primary amido groups of AG. Under acid conditions, both co- and self-condensation were observed. The more acid the preparation conditions were, the easier to be observed the self-condensation of furfuryl alcohol molecules would be than the co-condensation between furfuryl alcohol and AG. When the value of pH was higher than 5, both co- and self-condensation were not outstanding. In this study, under pH 3, the co- and self-condensation found equilibrium. There was a great possibility for the primary amido and aliphatic amino groups of AG molecules to react with furfuryl alcohol molecules. No reaction was detected between the secondary amido groups of AG and furfuryl alcohol.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact Resistance Enhancement by Adding Core-Shell Particle to Epoxy Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polymer
by
Shuiping Li, Qisheng Wu, Huajun Zhu, Qing Lin and Chengshuang Wang
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 5740
Abstract
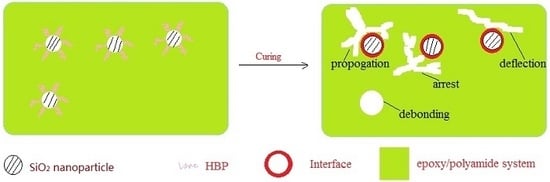
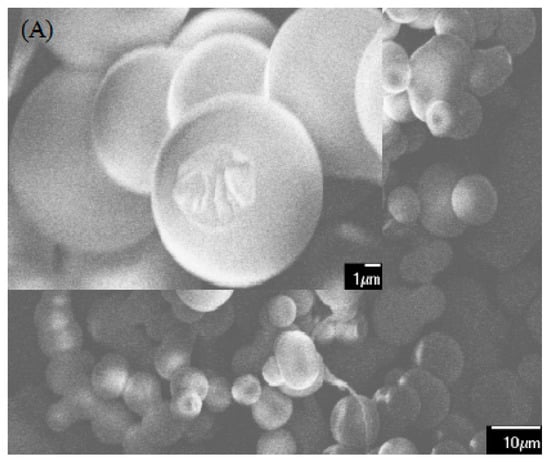
A core-shell particle was fabricated by grafting amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer to the surface of silica nanoparticles. The influences of core-shell particle contents on the tensile and impact strength of the epoxy thermosets modified with amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer were discussed in detail. For comparison,
[...] Read more.
A core-shell particle was fabricated by grafting amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer to the surface of silica nanoparticles. The influences of core-shell particle contents on the tensile and impact strength of the epoxy thermosets modified with amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer were discussed in detail. For comparison, core-shell particle was added into the epoxy/polyamide system for toughness improvement. Results from tensile and impact tests are provided. The introduction of core-shell particle into the epoxy/polyamide systems just slightly enhanced the tensile and impact strength. The incorporation of 3 wt % core-shell particle could substantially improve the tensile and impact strength of epoxy/amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer thermosets. Field emission-scanning electron microscope images of the impact fracture surfaces showed that the excellent impact resistance of epoxy/amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer/core-shell particle thermosets may be attributed to the synergistic effect of shearing deformation and crack pinning/propagation, which is induced by the good compatibility between epoxy matrix and core-shell particle in the presence of amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design Analysis of Adhesively Bonded Structures
by
Ee-Hua Wong and Johan Liu
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3674
Abstract
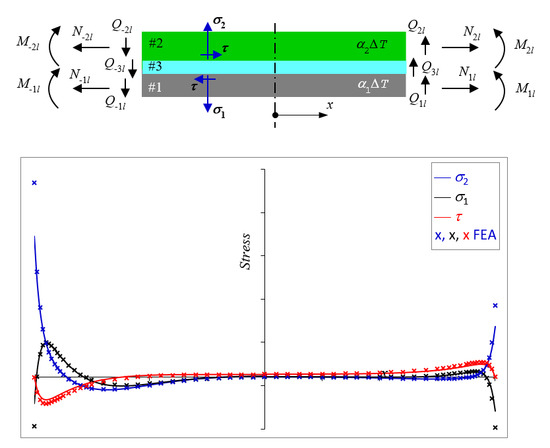
The existing analytical solutions for the peeling and shearing stresses in polymeric adhesively bonded structures are either too inaccurate or too complex for adoption by practicing engineers. This manuscript presents a closed-form solution that is reasonably accurate yet simple and concise enough to
[...] Read more.
The existing analytical solutions for the peeling and shearing stresses in polymeric adhesively bonded structures are either too inaccurate or too complex for adoption by practicing engineers. This manuscript presents a closed-form solution that is reasonably accurate yet simple and concise enough to be adopted by practicing engineers for design analysis and exploration. Analysis of these concise solutions have yielded insightful design guidelines: (i) the magnitude of peeling stress is generally higher than that of shearing stress; (ii) the peeling stress in a balanced structure may be reduced most effectively by reducing the elastic modulus of the adherends or by increasing the adhesive-to-adherend thickness ratio and less effectively by reducing the elastic modulus of the adhesive; and (iii) the peeling stress in an unbalanced structure may be reduced by increasing the in-plane compliance of the structure, which may be implemented most effectively by reducing the thicknesses of the adherends and less effectively by reducing the elastic modulus of the adherends.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effect of MAH-g-PLA on the Properties of Wood Fiber/Polylactic Acid Composites
by
Lei Zhang, Shanshan Lv, Ce Sun, Lu Wan, Haiyan Tan and Yanhua Zhang
Cited by 78 | Viewed by 7859
Abstract
Maleic anhydride (MAH) was used as the grafting monomer, which was prepared by melt grafting reaction in the twin screw extruder with dicumyl peroxide (DCP) as the initiator, polylactic acid grafted with maleic anhydride (MAH-g-PLA) was successfully prepared as the interface compatibilizer. The
[...] Read more.
Maleic anhydride (MAH) was used as the grafting monomer, which was prepared by melt grafting reaction in the twin screw extruder with dicumyl peroxide (DCP) as the initiator, polylactic acid grafted with maleic anhydride (MAH-g-PLA) was successfully prepared as the interface compatibilizer. The PLA/Wood fiber/MAH-g-PLA composites were prepared by melt blending and injection molding with different proportions of compatibilizer added, within which PLA was for the matrix phase and wood fiber was for the reinforcing phase. The crystallinity, microstructure, thermal stability and dynamic thermomechanical property of the composites were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), thermo gravimetric analyzer (TGA) and dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMA). Furthermore, the mechanical and water absorption properties of the composites were also characterized. Results showed that the tensile strength and flexural strength of the composites attained the highest at 30% MAH-g-PLA added, where the crystallinity of the composites also showed the highest value. DMA results showed that the addition of MAH-g-PLA interfacial compatibilizer increased the loss modulus of the composites and improved the toughness. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that when the MAH-g-PLA was used, wood fiber is well dispersed in the PLA matrix phase, and that the interfacial compatibility between the matrix and the enhanced phase was improved. Therefore, the addition of MAH-g-PLA could improve the interfacial compatibility of PLA/Wood fiber composites and improve the mechanical properties of the composites.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Characterization and Performance of Soy-Based Adhesives Cured with Epoxy Resin
by
Nairong Chen, Peitao Zheng, Qinzhi Zeng, Qiaojia Lin and Jiuping Rao
Cited by 55 | Viewed by 5656
Abstract
Soy-based adhesives have attracted much attention recently because they are environmentally safe, low cost, and readily available. To improve the gluability and water resistance of soy-based adhesives, we prepared an enzyme-treated soy-based adhesive modified with an epoxy resin. We investigated the wet shear
[...] Read more.
Soy-based adhesives have attracted much attention recently because they are environmentally safe, low cost, and readily available. To improve the gluability and water resistance of soy-based adhesives, we prepared an enzyme-treated soy-based adhesive modified with an epoxy resin. We investigated the wet shear strength of plywood bonded with the modified adhesive using the boiling-water test. Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and
1H nuclear magnetic resonance analysis were used to characterize the reaction between epoxy groups and –NH
2 groups in the modified soy-based adhesives. FTIR analysis confirmed the cross-linking structure in the cured adhesives. Viscosity and the solid content of soy-based adhesives gradually increased with the increasing amount of epoxy resin, but had little effect on its operability. Wet shear strength of plywood samples increased as the amount of epoxy resin was increased, whereas the inverse trend was observed regarding the water absorption of cured adhesives. Compared to an unmodified adhesive, the addition of 30% of epoxy resin increased the wet shear strength of plywood samples by 58.3% (0.95 MPa), meeting the requirement of the Chinese National Standard for exterior plywood. Differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis showed the improved thermostability of the cured adhesives after curing at 160 °C. These results suggest that epoxy resin could effectively improve the performance of enzyme-treated soy-based adhesives, which might provide a new option for the preparation of soy-based adhesives with high gluability and water resistance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Mechanism of Base-Catalyzed Resorcinol-Formaldehyde and Phenol-Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Condensation Reactions: A Theoretical Study
by
Taohong Li, Ming Cao, Jiankun Liang, Xiaoguang Xie and Guanben Du
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 18096
Abstract
The base-catalyzed resorcinol-formaldehyde condensation reactions were theoretically investigated in this study by employing a quantum chemistry method. The condensation reaction includes two steps: (1) formation of the quinonemethide (QM) intermediate from hydroxymethylresorcinol; (2) Michael addition between the quinonemethide and resorcinol anion. The first
[...] Read more.
The base-catalyzed resorcinol-formaldehyde condensation reactions were theoretically investigated in this study by employing a quantum chemistry method. The condensation reaction includes two steps: (1) formation of the quinonemethide (QM) intermediate from hydroxymethylresorcinol; (2) Michael addition between the quinonemethide and resorcinol anion. The first step is the rate-determining step. Two mechanisms, unimolecular elimination of the conjugate base (E1cb) and water-aided elimination (WAE), were identified for the formation of QM. The hydroxymethylresorcinol anion produces neutral QM while the dianion produces a quinonemethide anion (QMA). The calculated potential energy barriers suggested that the QMA formation is much more favorable. Although resorcinol-formaldehyde and phenol-formaldehyde condensations share a common mechanism, the former would be faster if the QMA participates in condensations. The potential energy barriers for formation of 2-QM, 4-QM, 6-QM, 2-QMA, and 4-QMA were calculated. The results show that the formations of 6-QM and 4-QMA have relatively lower energy barriers. This rationalized previous experimental observations that the 2,4-(2,6-) and 6,6′-(4,4′-) methylene linkages were dominant, whereas the 2,2′-linkage was almost absent. The resorcinol-phenol-formaldehyde co-condensations were also calculated. The cold-setting characteristic of phenol-resorcinol-formaldehyde co-condensed resin can be attributed to participation of resorcinol quinonemethides in condensations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
Synthesis of Humin-Phenol-Formaldehyde Adhesive
by
Shimin Kang, Jinxia Fu, Gang Zhang, Wentao Zhang, Huibin Yin and Yongjun Xu
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 6842
Abstract
Humins are low-value-added byproducts from the biomass acid hydrolysis process. In the present work, humins were first employed as a phenol replacement for synthesis of modified phenol-formaldehyde adhesives through a two-step process. In this process, humins were first utilized to obtain alkaline soluble
[...] Read more.
Humins are low-value-added byproducts from the biomass acid hydrolysis process. In the present work, humins were first employed as a phenol replacement for synthesis of modified phenol-formaldehyde adhesives through a two-step process. In this process, humins were first utilized to obtain alkaline soluble products, mainly consisting of phenolics, through a hydrothermal process. The obtained alkaline soluble products then reacted with phenol and formaldehyde to produce humin-phenol-formaldehyde adhesive (HPFA). The physicochemical properties of HPFA, including viscosity, bonding strength, pH, free formaldehyde level, free phenol level and solid content, met the requirements of the GB/T 14732-2006 Chinese National Standard.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Theoretical Study on Decomposition Mechanism of Insulating Epoxy Resin Cured by Anhydride
by
Xiaoxing Zhang, Yunjian Wu, Xiaoyu Chen, Hao Wen and Song Xiao
Cited by 39 | Viewed by 7633
Abstract
High temperatures caused by partial discharge results in the decomposition of insulating epoxy resins in electrical equipment. In this paper, the ReaxFF force field is used to investigate the decomposition process of epoxy resins cured by anhydride and the formation mechanisms of small-molecule
[...] Read more.
High temperatures caused by partial discharge results in the decomposition of insulating epoxy resins in electrical equipment. In this paper, the ReaxFF force field is used to investigate the decomposition process of epoxy resins cured by anhydride and the formation mechanisms of small-molecule gases. Results show that the initiation reaction is the cleavage of an ester bond linked with an epoxy resin. Produced by the decomposition of ester groups, CO
2 is the first and most abundant product. Meanwhile, CH
2O can be generated through three main ways, although the process still depends on the decomposition of epoxy functional groups. H
2O is produced by free radical collision and dehydration. The production of small-molecule gases has the following sequence: CO
2, CH
2O, CO, and H
2O. The produced gases have the following order according to amount: CO
2, CH
2O, H
2O, and CO.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Improve Performance of Soy Flour-Based Adhesive with a Lignin-Based Resin
by
Xiaochun Zhang, Yuding Zhu, Youming Yu and Jiangang Song
Cited by 55 | Viewed by 7311
Abstract
A lignin-based resin (LB) was used to improve the performance of soy flour-based adhesives. Soy flour (SF), polyamidoamine-epichlorohydrin (PAE), and LB were used to develop a plywood adhesive. The solid content and viscosity of the adhesive, the functional groups, the thermo-stability, and the
[...] Read more.
A lignin-based resin (LB) was used to improve the performance of soy flour-based adhesives. Soy flour (SF), polyamidoamine-epichlorohydrin (PAE), and LB were used to develop a plywood adhesive. The solid content and viscosity of the adhesive, the functional groups, the thermo-stability, and the crystallinity of the cured adhesives were characterized, and the performance of the resultant adhesive was evaluated by fabricating three-ply plywood. Results showed that the LB and PAE mixture used to modify the SF adhesive improved both dry and wet bond strength by 66.3% and 184.2%, respectively. Therefore, the PAE improved the wet bond strength, and the LB improved the dry bond strength. The improvement was attributed to: (1) the reaction of LB/PAE with the functions of the soy protein to form a cross-linking network; (2) a polycondensation reaction between the LB molecules improved the crosslinking density of the adhesive to form an interpenetration structure with cross-linked proteins; and (3) the easy penetration of the LB into the wood surface that enhanced interlocking between the wood and adhesive. Furthermore, the denser structure created by the LB and the PAE mixture improved thermal stability and decreased the crystallinity of the cured adhesive. The use of the LB and the PAE mixture increased the solid content by 35.5%, while still making its viscosity acceptable for industrial applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
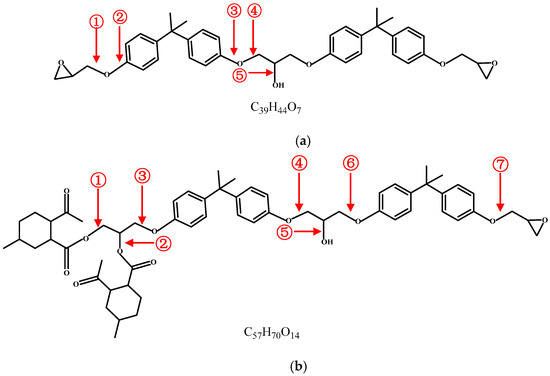
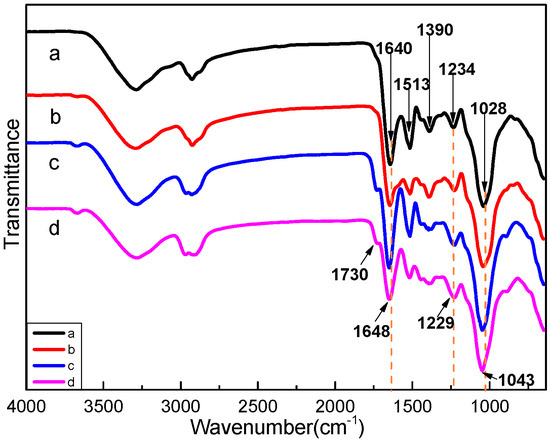
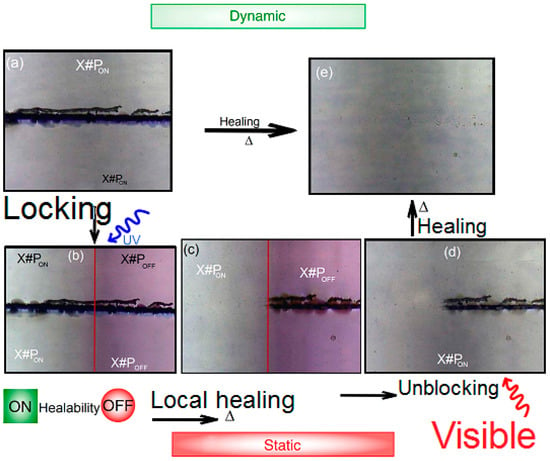
Controlled Light Cross-Linking Technique to Prepare Healable Materials
by
Soliman Abdalla, Fahad Al-Marzouki, Abdullah Obaid and Fatma Bahabri
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 6305
|
Retraction
Abstract
Detection of defects, damages and cracks in structural polymers is very difficult, and even if they are detected, they will be very hard to be repaired. This is because different kinds of stress can reduce the mechanical efficiency of structural and functional thermosetting
[...] Read more.
Detection of defects, damages and cracks in structural polymers is very difficult, and even if they are detected, they will be very hard to be repaired. This is because different kinds of stress can reduce the mechanical efficiency of structural and functional thermosetting composite materials and they can damage the polymer matrix, thus reducing the purposed properties. General healing processes use thermal energy “alone” to heal these materials, thus impairing the intended properties of the materials. Therefore, we present a thermal healing ability that can be switched-on and/or -off at desire using illumination by photon energy (visible and ultra violet). By this technique, one can control local heal while keeping the efficiency of the material nearly unchanged. Furan-based cross-linker chemically reacts (forward- and reverse-reaction) with short-chains of maleimide-substituted poly(lauryl methacrylate) to form robust chemical bonds. This permits us to perform local control over thermally induced de- and/or re-cross-linking techniques. One can extend and apply this technique to cover micro-devices, coating-techniques, fine lithography, micro- and nano-fabrication processes, etc. Therefore, the present work developed a suitable technology with structural polymeric material, which has the ability to self-heal cracks (and damages) and recover structural function.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
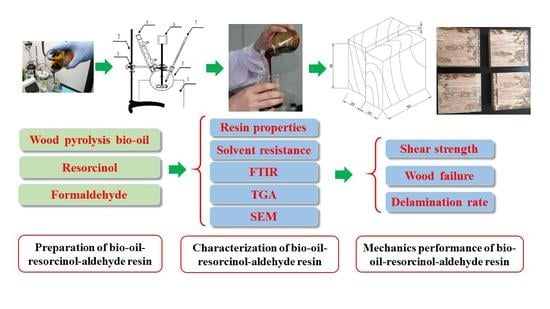
The Preparation and Characterization of Pyrolysis Bio-Oil-Resorcinol-Aldehyde Resin Cold-Set Adhesives for Wood Construction
by
Xueyong Ren, Hongzhen Cai, Hongshuang Du and Jianmin Chang
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 9870
Abstract
Resorcinol-formaldehyde (RF) resin is a kind of excellent exterior-grade wood structural adhesive, which can be conveniently cold-set for various applications. In order to decrease the production cost, pyrolysis bio-oil from renewable bioresources was used to replace resorcinol to synthesize the bio-oil-resorcinol-aldehyde (BRF) resin.
[...] Read more.
Resorcinol-formaldehyde (RF) resin is a kind of excellent exterior-grade wood structural adhesive, which can be conveniently cold-set for various applications. In order to decrease the production cost, pyrolysis bio-oil from renewable bioresources was used to replace resorcinol to synthesize the bio-oil-resorcinol-aldehyde (BRF) resin. The effect of replacing resorcinol with bio-oil on the properties, bonding performance, and characterization of resorcinol-aldehyde resin was comparatively investigated. A higher solid content and viscosity, albeit a lower shear strength, was found when the replacement ratio of bio-oil increased. The bonding performance of BRF with 10 and 20 wt % bio-oil was close to that of the pure RF resin. However, the trends of being less cross-linked, more easily decomposed, but more porous were found when the substitution ratio of bio-oil was higher than 20 wt %. Interestingly, it was found that the wood failure values of the BRF resins with bio-oil of no more than 20 wt % were slightly higher than that of the pure RF resin. On the whole, BRF resins with 20 wt % bio-oil is recommended as a wood structural adhesive, comprehensively considering the bio-oil substitution ratio and resin properties. The results obtained here showed that pyrolysis bio-oil is a promising green raw material for the production of RF resin with lower cost.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Cross-Linking Reaction of Lignin with Triethyl Phosphate by MALDI-TOF and 13C NMR
by
María Cecilia Basso, Antonio Pizzi, Luc Delmotte and Soliman Abdalla
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 7783
Abstract
The reaction of condensation and cross-linking of desulfurized kraft lignin with triethyl phosphate (TEP) was explored. Catechol, a simple model of the aromatic ring of lignin, and glycerol, a model compound of the aliphatic hydroyl groups of the side chain of lignin, were
[...] Read more.
The reaction of condensation and cross-linking of desulfurized kraft lignin with triethyl phosphate (TEP) was explored. Catechol, a simple model of the aromatic ring of lignin, and glycerol, a model compound of the aliphatic hydroyl groups of the side chain of lignin, were employed under similar reaction conditions. Solid state cross-polarisation/magic-angle spinning (CP-MAS)
13C NMR and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) spectroscopy studies showed that polycondensation occurs on phenolic hydroxyl groups of lignin, as well as on aliphatic hydroxyls groups of its side chain. The reactions appear to be favoured by higher temperatures and in the presence of ammonia. Preliminary adhesion tests on wood shown good hydrophobicity properties of the surface treated with lignin-TEP-based resin. Initial application tests carried out at high temperature demonstrated as good performance as metallic coating.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
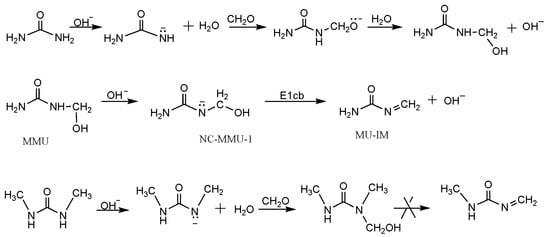
New Mechanism Proposed for the Base-Catalyzed Urea–Formaldehyde Condensation Reactions: A Theoretical Study
by
Taohong Li, Ming Cao, Jiankun Liang, Xiaoguang Xie and Guanben Du
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 9766
Abstract
Base-catalyzed urea–formaldehyde condensation reactions were investigated by using a quantum chemistry method. It was found that monomethylolurea or
N,
N’-dimethylolurea can produce the methyleneurea intermediate (–HN–CO–N=CH
2) with the catalysis of base. The E1cb (unimolecular elimination of conjugate base) mechanism
[...] Read more.
Base-catalyzed urea–formaldehyde condensation reactions were investigated by using a quantum chemistry method. It was found that monomethylolurea or
N,
N’-dimethylolurea can produce the methyleneurea intermediate (–HN–CO–N=CH
2) with the catalysis of base. The E1cb (unimolecular elimination of conjugate base) mechanism was identified for the formation of such an intermediate. The potential energy barrier was theoretically predicted to be 59.6 kJ/mol for the E1cb step, which is about half of that of previously proposed S
N2 (bimolecular nucleophilic substitution) mechanism. In the subsequentcondensation reactions, Michael addition reactions that lead to different condensed structures can occur between the methyleneurea intermediate and the anions produced from methylolureas under alkaline conditions. Based on the theoretical calculations on the kinetics and thermodynamics of the selected reactions, the competitive formations of methylene linkages, ether linkages and uron were discussed in combination with our previous experimental observations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
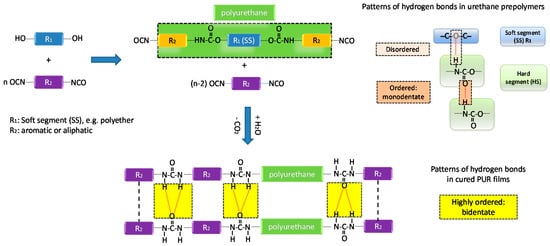
Investigation on the Influence of Chain Extenders on the Performance of One-Component Moisture-Curable Polyurethane Adhesives
by
Chen Tan, Teija Tirri and Carl-Eric Wilen
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 8748
Abstract
In this work, a number of chain extended moisture-curable urethane prepolymers were synthesized in order to develop isocyanate terminated urethane prepolymer formulations that would simultaneously display both high adhesive strength and low viscosity. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (
1H-NMR), size exclusion
[...] Read more.
In this work, a number of chain extended moisture-curable urethane prepolymers were synthesized in order to develop isocyanate terminated urethane prepolymer formulations that would simultaneously display both high adhesive strength and low viscosity. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (
1H-NMR), size exclusion chromatography (SEC), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and Brookfield viscometry were utilized for characterizing the prepared urethane prepolymers. In addition, the adhesion strength of the cured prepolymers was determined by tensile shear strength test according to the DIN EN (Deutsches Institut für Normung, the German Institute for Standardization) 1465 standard. Especially, the role of different types of linear (butanediol, pentanediol) and branched chain extenders (dipropyleneglycol (di-PPG), tripropyleneglycol (tri-PPG) and the influence of their dosage on the degree of microphase separation between hard segments (HS) and soft segments (SS) in urethane prepolymers were studied. Furthermore, the benefits of utilizing either a one-step versus a two-step polymerization process were investigated. The results revealed that the extent of phase separation of different urethane prepolymers was dependent on the extent of hydrogen bonding interactions which was extensively studied by attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR). The incorporation of branched chain extenders (di-PPG and tri-PPG) did not result in notable phase separation between hard segments and soft segments, while linear chain extenders (pentanediol and butanediol) readily promoted phase separation. The degree of phase separation was particularly pronounced for butanediol, and when the linear chain extender ratio was higher than or equal to 0.74. Compared with a two-stage process, one-stage process produced more randomly distributed polymer chains with highly dispersed hard segments. Thus, urethane prepolymers exhibiting strong adhesive strength with simultaneously low viscosity were successfully developed by systematic adjustment of structural parameters.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Soy-Based Adhesive Cross-Linked by Phenol-Formaldehyde-Glutaraldehyde
by
Zhigang Wu, Xuedong Xi, Hong Lei and Guanben Du
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 7077
Abstract
To prepare a low-formaldehyde soy-based adhesive with good water resistance, phenol-formaldehyde modified with glutaraldehyde (PFG) with lower free phenol and free formaldehyde contents was used to cross-link the soy-based adhesive. The results showed that the mechanical properties and water resistance of plywood prepared
[...] Read more.
To prepare a low-formaldehyde soy-based adhesive with good water resistance, phenol-formaldehyde modified with glutaraldehyde (PFG) with lower free phenol and free formaldehyde contents was used to cross-link the soy-based adhesive. The results showed that the mechanical properties and water resistance of plywood prepared with soy-based adhesive with PFG was better than that of plywood with the same amount of phenol-formaldehyde (PF). The reaction between phenol and glutaraldehyde was proved by
13C-NMR. Under the optimized preparation conditions for plywood, that is to say, press temperature 160 °C, press time 4 min and resin loading 320 g·m
−2, type I plywood could be prepared with 9% PFG as a cross-linker of soy-based adhesive. The Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) result confirmed the cross-linking reaction between soy-based adhesive and PFG or PF. The activation energy of soy-based adhesive with cross-linker PFG was higher than that with PF resin.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
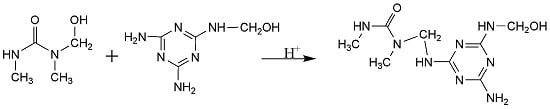
The Influence of pH on the Melamine-Dimethylurea-Formaldehyde Co-Condensations: A Quantitative 13C-NMR Study
by
Ming Cao, Taohong Li, Jiankun Liang and Guanben Du
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 7712
Abstract
1,3-dimethylurea (DMU) was used to mimic urea and to model melamine-urea-formaldehyde (MUF) co-condensation reactions. The products of 1,3-dimethylurea-formaldehyde (DMUF), melamine-formaldehyde (MF), and melamine-1,3-dimethylurea-formaldehyde (MDMUF) reactions under alkaline and weak acidic conditions were compared by performing quantitative carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (
13C-NMR)
[...] Read more.
1,3-dimethylurea (DMU) was used to mimic urea and to model melamine-urea-formaldehyde (MUF) co-condensation reactions. The products of 1,3-dimethylurea-formaldehyde (DMUF), melamine-formaldehyde (MF), and melamine-1,3-dimethylurea-formaldehyde (MDMUF) reactions under alkaline and weak acidic conditions were compared by performing quantitative carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (
13C-NMR) analysis. The effect of pH on the co-condensation reactions was clarified. With the presence of the methyl groups in DMU, the appearance or absence of the featured signal at 54–55 ppm can be used to identify the co-condensed methylene linkage –N(–CH
3) –CH
2–NH–. Under alkaline condition, MDMUF reactions produced primarily MF polymers and the featured signal at 54–55 ppm was absent. Even though the co-condensations concurrently occurred, undistinguishable and very minor condensed structures with ether linkage were formed. Differently, under weak acidic condition, the relative content of co-condensed methylene carbons accounts for over 40%, indicating the MDMUF co-condensation reactions were much more competitive than the self-condensations. The formation of reactive carbocation intermediate was proposed to rationalize the results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures