-
 Integrated and Hybrid Processes for the Treatment of Actual Wastewaters Containing Micropollutants: A Review on Recent Advances
Integrated and Hybrid Processes for the Treatment of Actual Wastewaters Containing Micropollutants: A Review on Recent Advances -
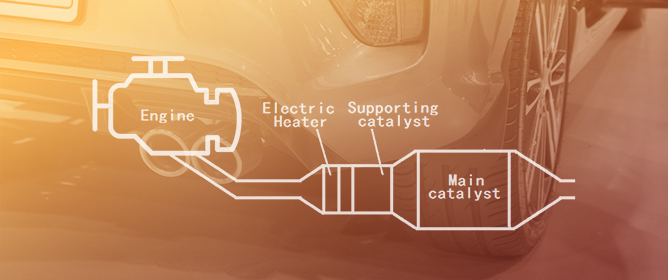 Applications of Electric Heating Technology in Vehicle Exhaust Pollution Control
Applications of Electric Heating Technology in Vehicle Exhaust Pollution Control -
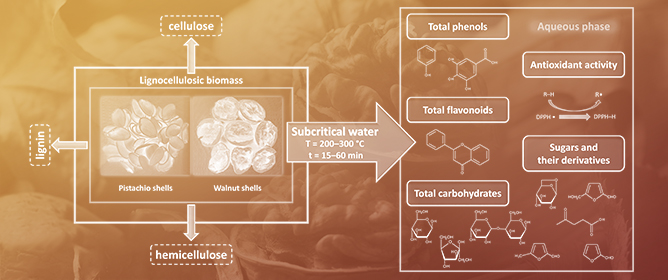 The Conversion of Pistachio and Walnut Shell Waste into Valuable Components with Subcritical Water
The Conversion of Pistachio and Walnut Shell Waste into Valuable Components with Subcritical Water -
 Thermal Stabilization of Lipases Bound to Solid-Phase Triazine-Scaffolded Biomimetic Ligands
Thermal Stabilization of Lipases Bound to Solid-Phase Triazine-Scaffolded Biomimetic Ligands -
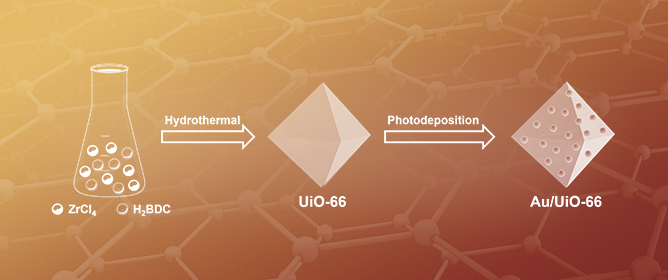 Au Nanoparticle-Loaded UiO-66 Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient Photocatalytic N2 Fixation
Au Nanoparticle-Loaded UiO-66 Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient Photocatalytic N2 Fixation
Journal Description
Processes
Processes
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on processes/systems in chemistry, biology, material, energy, environment, food, pharmaceutical, manufacturing, automation control, catalysis, separation, particle and allied engineering fields published monthly online by MDPI. The Systems and Control Division of the Canadian Society for Chemical Engineering (CSChE S&C Division) and the Brazilian Association of Chemical Engineering (ABEQ) are affiliated with Processes and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges. Please visit Society Collaborations for more details.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, Inspec, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Chemical) / CiteScore - Q2 (Chemical Engineering (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.5 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.4 (2022)
Latest Articles
Correction: Meister et al. Assessing Long-Term Medical Remanufacturing Emissions with Life Cycle Analysis. Processes 2023, 11, 36
Processes 2024, 12(5), 858; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050858 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
In the original publication, ref [...]
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Combining Solution-Blowing and Melt-Blowing Techniques to Produce an Efficient Non-Woven Filter
by
Agata Penconek, Łukasz Werner and Arkadiusz Moskal
Processes 2024, 12(5), 857; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050857 (registering DOI) - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
New substances and particles appearing in the environment following technological development pose new challenges for separation methods. Moreover, the growing amount of waste also forces us to look for environmentally friendly solutions. One way to create filtration structures with the desired properties is
[...] Read more.
New substances and particles appearing in the environment following technological development pose new challenges for separation methods. Moreover, the growing amount of waste also forces us to look for environmentally friendly solutions. One way to create filtration structures with the desired properties is to combine known techniques, thanks to which the advantages of one technique complement the deficiencies and disadvantages of another. Combining the melt-blowing and solution-blowing processes seems to be promising. Fibres created from melt-blowing will provide mechanical strength, while solution-blowing will allow the introduction of nanofibres into the structure with unique filtration and functional properties. Both methods enable working with biodegradable polymers, so the resulting filter can also be environmentally friendly after operation. Our research aimed to check whether combining two fibre production techniques (melt-blown and solution-blowing) is possible and how the joining method will affect the final product. We created a multilayer structure by placing a layer of solution-blowing nanofibres between melt-blown layers, and a mixed structure by simultaneous melt-blowing and solution-blowing. The created multilayer structure was characterised by high filtration efficiency and high-pressure drop. In contrast, the mixed structure achieved a high-quality factor and high mass of deposited droplets per 1 J of energy used for work.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue 10th Anniversary of Processes: Design of the Chemical Industry of the Future)
►▼
Show Figures
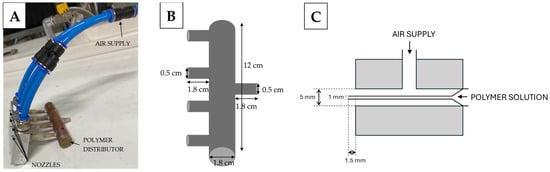
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Ultrasonic Plasticizing and Pressing of High-Aspect Ratio Micropillar Arrays with Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Properties
by
Shiyun Wu, Jianjun Du, Shuqing Xu, Jianguo Lei, Jiang Ma and Likuan Zhu
Processes 2024, 12(5), 856; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050856 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
An ultrasonic plasticizing and pressing method (UPP) that fully utilizes ultrasonic vibration is proposed for fabricating thermoplastic polymer surface microstructures with high aspect ratios (ARs). The characteristics of UPP are elucidated based on the plasticization of the raw material, the melt flow, and
[...] Read more.
An ultrasonic plasticizing and pressing method (UPP) that fully utilizes ultrasonic vibration is proposed for fabricating thermoplastic polymer surface microstructures with high aspect ratios (ARs). The characteristics of UPP are elucidated based on the plasticization of the raw material, the melt flow, and the stress on the template microstructure during the forming process. Initially, the micronscale single-stage micropillar arrays (the highest AR of 4.1) were fabricated by using 304 stainless steel thin sheets with micronscale pore (through-hole) arrays as primary templates. Subsequently, anodic aluminum oxides (AAOs) with ordered nanoscale pore arrays were added as secondary templates, and the micro/nanoscale hierarchical micropillar arrays (the highest AR up to 24.1) were successfully fabricated, which verifies the feasibility and forming capability of UPP. The superiority and achievements of UPP are illustrated by comparing the prepared hierarchical micropillar arrays with those prepared in the previous work in four indexes: microstructure scale, aspect ratio, forming time, and preheating temperature of the raw material. Finally, the water contact angle (WCA) and oil droplet complete immersion time of the surface microstructures were measured by a droplet shape analyzer, and the results indicate that the prepared micropillar arrays are superhydrophobic and superoleophilic.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Micro/Nano Manufacturing Processes: Theories and Optimization Techniques)
Open AccessArticle
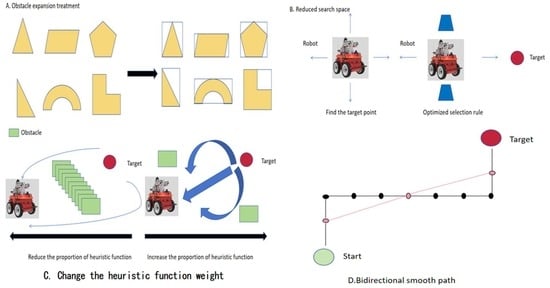
Complex Environment Based on Improved A* Algorithm Research on Path Planning of Inspection Robots
by
Yilin Zhang and Qiang Zhao
Processes 2024, 12(5), 855; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050855 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The proposed research aims to accomplish an improved A* algorithm for mobile robots in complex environments. In this novel algorithm, the guidance of environment information is added to the evaluation function to enhance the adaptability of the algorithm in complex environments. Additionally, to
[...] Read more.
The proposed research aims to accomplish an improved A* algorithm for mobile robots in complex environments. In this novel algorithm, the guidance of environment information is added to the evaluation function to enhance the adaptability of the algorithm in complex environments. Additionally, to solve the problem of path smoothness, the optimal selection rules for child nodes and the bidirectional optimization strategy for path smoothing are introduced to reduce redundant nodes, which effectively makes the search space smaller and the path smoother. The simulation experiments show that, compared with the colony algorithm and Dijkstra algorithms, the proposed algorithm has significantly improved performance. Compared with the A* algorithm, the average planning time is reduced by 17.2%, the average path length is reduced by 2.05%, the average turning point is reduced by 49.4%, and the average turning Angle is reduced by 75.5%. The improved A* algorithm reduces the search space by 61.5% on average. The simulation results show that the effectiveness and adaptability of the improved A* algorithm in complex environments are verified by multi-scale mapping and multi-obstacle environment simulation experiments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Automation Control Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Cs4PMo11VO40-Catalyzed Glycerol Ketalization to Produce Solketal: An Efficient Bioadditives Synthesis Method
by
Márcio José da Silva and Cláudio Júnior Andrade Ribeiro
Processes 2024, 12(5), 854; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050854 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
In this work, a series of vanadium-substituted phosphomolybdic acids were synthesized and tested as the catalysts for the synthesis of solketal, a green fuel bioadditive, from the condensation reaction of glycerol with acetone. The objective was to demonstrate that an easily synthesizable solid
[...] Read more.
In this work, a series of vanadium-substituted phosphomolybdic acids were synthesized and tested as the catalysts for the synthesis of solketal, a green fuel bioadditive, from the condensation reaction of glycerol with acetone. The objective was to demonstrate that an easily synthesizable solid catalyst can efficiently promote glycerol condensation with acetone at room temperature. The activity of pristine heteropolyacid (i.e., H3PMo12O40) and its vanadium-substituted cesium salts (Cs3+nPMo12-nVnO40; n = 0–3) was evaluated in condensation reactions carried out at room temperature. Among the catalysts tested, Cs4PMo11VO40 was the most active and selective towards a five-member ring solketal isomer (dioxolane). A high yield of solketal (i.e., 95% conversion and 95% selectivity to solketal) was achieved in glycerol condensation with acetone at room temperature within a short reaction time (2 h). The influence of the main reaction parameters, such as the acetone–glycerol molar ratio, catalyst load, and reaction temperatures, was investigated. The greatest activity of the Cs4PMo11VO40 catalyst was correlated to its greatest acidity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Continuous Production and Catalysis Optimization of Chemical Industry Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
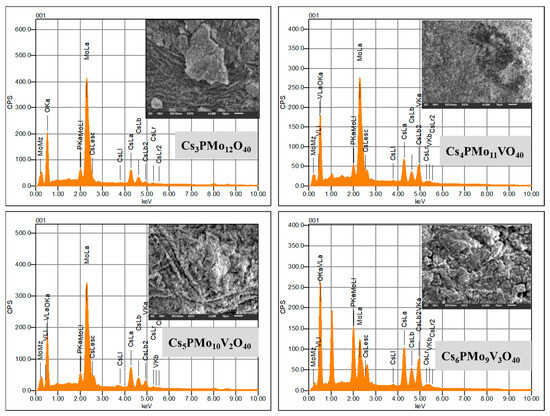
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Editorial for the Special Issue “Wastewater and Waste Treatment: Overview, Challenges and Current Trends”
by
Dimitris P. Zagklis and Georgios Bampos
Processes 2024, 12(5), 853; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050853 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Today’s environmental challenges, marked by escalating pollution levels, climate change and diminishing natural resources, urgently require innovative solutions, particularly in waste and wastewater management [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wastewater and Waste Treatment: Overview, Challenges and Current Trends)
►▼
Show Figures
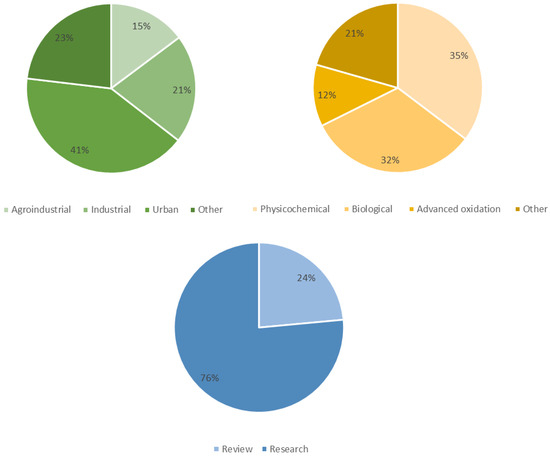
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Boron on Microstructures and Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of Medium-Carbon CrMo Alloy Steels with Different Quenching Temperatures
by
Qiang Wang, Qian Wang, Qingfeng Wang, Chongchong Li and Kefu Li
Processes 2024, 12(5), 852; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050852 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
The effect of boron (B) on the microstructures and low-temperature impact toughness of medium-carbon CrMo steel quenched at 870~1050 °C and tempered at 600 °C was studied via Charpy impact testing and microstructure characterizations. The results showed that with an increasing B content
[...] Read more.
The effect of boron (B) on the microstructures and low-temperature impact toughness of medium-carbon CrMo steel quenched at 870~1050 °C and tempered at 600 °C was studied via Charpy impact testing and microstructure characterizations. The results showed that with an increasing B content from 0 to 50 ppm, the low-temperature impact toughness deteriorated significantly at quenching temperatures (Tq) lower than 950 °C but increased at a higher Tq of 1050 °C. Undissolved M2B particles remained and coarsened during the holding process due to the low Tq, decreasing the critical stress required for crack initiation and deteriorating the impact toughness accordingly. However, this detrimental effect of B could be mitigated by a higher Tq, and the favorable influences on the impact toughness improvement could be attributed to (1) the finer M2B particles formed during quenching effectively pinning the austenite grain boundaries (GBs), leading to a finer block size and a high density of high-angle grain boundaries, which reduced the critical stress for crack initiation; and (2) the fact that the coarsening of M23C6 on the GBs during tempering was slightly suppressed by the segregated B, eventually increasing the energy required for crack propagation. However, the degree of the favorable effect due to B was still lower than the negative effect of a high Tq.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Materials Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
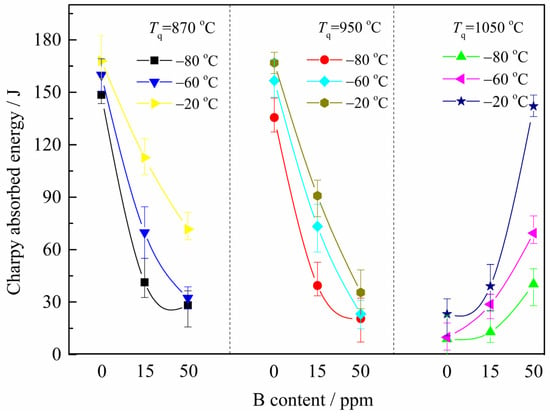
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Functional Improvement of NiOx/CeO2 Model Catalyst Active in Dry Methane Reforming via Optimization of Nickel Content
by
Piotr Legutko, Mateusz M. Marzec, Marcin Kozieł, Krystian Sokołowski, Marek Michalik and Andrzej Adamski
Processes 2024, 12(5), 851; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050851 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
The valorization of greenhouse gases, especially when focused on carbon dioxide, currently belongs to the main challenges of pro-environmental chemical processes. One of the important technologies in this field is dry methane reforming (DMR), leading to the so-called synthesis gas (CO + H
[...] Read more.
The valorization of greenhouse gases, especially when focused on carbon dioxide, currently belongs to the main challenges of pro-environmental chemical processes. One of the important technologies in this field is dry methane reforming (DMR), leading to the so-called synthesis gas (CO + H2). However, to be efficient and economically viable, an active and stable catalyst is required. Ni-based systems can be recommended in this regard. This research aimed to investigate how nickel content can influence the activity of model NiOx/CeO2 catalysts in DMR. A series of NiOx/CeO2 samples of various nickel loadings (0–10 wt.%) were prepared through dry impregnation. The obtained samples were characterized through XRD, RS, N2-BET, DRIFT, SEM, UV/Vis-DR, and XPS. Nonlinear changes in surface properties of the investigated samples with increasing nickel concentration were found. The observed changes are mirrored both in the determined nickel speciation and in the corresponding catalytic activity. The highest activity was found for the catalyst containing 3 wt.%. of nickel.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Synthesis and Applications of Supported Nanocatalysts)
►▼
Show Figures
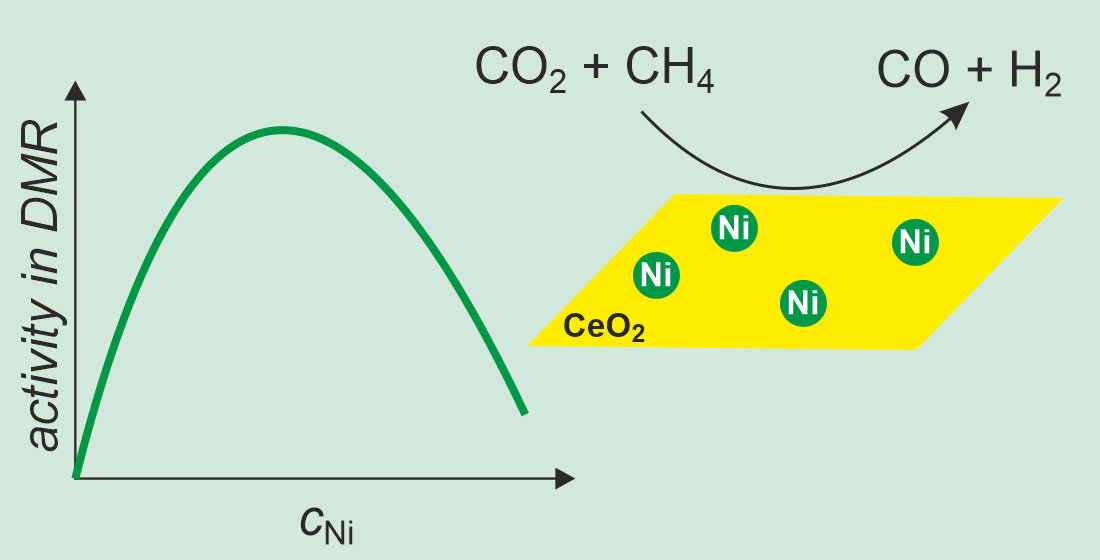
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Measuring Device Detecting Impact Forces on Impact Rollers
by
Leopold Hrabovský, Daniel Kurač, Štěpán Pravda, Eliška Nováková and Tomáš Machálek
Processes 2024, 12(5), 850; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050850 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper presents laboratory devices on which measurements were carried out to prove the validity of the assumption about the reduction in vibrations transmitted to the conveyor belt structure generated by the impact forces of falling material grains in the places of transfer
[...] Read more.
This paper presents laboratory devices on which measurements were carried out to prove the validity of the assumption about the reduction in vibrations transmitted to the conveyor belt structure generated by the impact forces of falling material grains in the places of transfer or on the hoppers of conveyor belts. In order to limit damage to the conveyor belts caused by the impact of the sharp edges of material grains, conveyor belts are supported by impact rollers or impact rubber rods. A special modification of the fixed conveyor idler is presented, which consists of inserting plastic brackets into the structurally modified roller axle holders of the fixed conveyor idler. Measurements showed that the specially modified fixed conveyor idler resulted in a higher damping of up to 15% of the impact forces of the falling weight on the rubberized hoop of the impact roller shell compared to the conventional fixed conveyor idler design. Measurements carried out show that the effective vibration velocity values detected at the points where the impact roller axis fits into the fixed roller table holder are higher than when using plastic brackets, up to 6% for a 108-mm-diameter roller, compared to steel impact roller brackets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Manufacturing Processes and Systems)
Open AccessArticle
A Physics-Based Tweedie Exponential Dispersion Process Model for Metal Fatigue Crack Propagation and Prognostics
by
Lin Yang, Zirong Wang, Zhen Chen and Ershun Pan
Processes 2024, 12(5), 849; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050849 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
Most structural faults in metal parts can be attributed to fatigue crack propagation. The analysis and prognostics of fatigue crack propagation play essential roles in the health management of mechanical systems. Due to the impacts of different uncertainty factors, the crack propagation process
[...] Read more.
Most structural faults in metal parts can be attributed to fatigue crack propagation. The analysis and prognostics of fatigue crack propagation play essential roles in the health management of mechanical systems. Due to the impacts of different uncertainty factors, the crack propagation process exhibits significant randomness, which causes difficulties in fatigue life prediction. To improve prognostic accuracy, a physics-based Tweedie exponential dispersion process (TEDP) model is proposed via integrating Paris Law and the stochastic process. This TEDP model can capture both the crack growth mechanism and uncertainty. Compared with other existing models, the TEDP taking Wiener process, Gamma process, and inverse process as special cases is more general and flexible in modeling complex degradation paths. The probability density function of the model is derived based on saddle-joint approximation. The unknown parameters are calculated via maximum likelihood estimation. Then, the analytic expressions of the distributions of lifetime and product reliability are presented. Significant findings include that the proposed TEDP model substantially enhances predictive accuracy in lifetime estimations of mechanical systems under varying operational conditions, as demonstrated in a practical case study on fatigue crack data. This model not only provides highly accurate lifetime predictions, but also offers deep insights into the reliability assessments of mechanically stressed components.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Intelligent Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Complex Industrial Processes or Equipment)
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Wellbore Cross-Sectional Elongation on the Hydraulic Fracturing Breakdown Pressure and Fracture Initiation Direction
by
Somaie Jolfaei and Ali Lakirouhani
Processes 2024, 12(5), 848; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050848 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
Investigation of breakdown pressure in wellbores in complex conditions is of great importance, both in fracture design and in wellbore log interpretation for in situ stress estimation. In this research, using a two-dimensional numerical model, the breakdown pressure is determined in ellipsoidal and
[...] Read more.
Investigation of breakdown pressure in wellbores in complex conditions is of great importance, both in fracture design and in wellbore log interpretation for in situ stress estimation. In this research, using a two-dimensional numerical model, the breakdown pressure is determined in ellipsoidal and breakout wellbores. To find the breakdown pressure, the mixed criterion is used, in which the toughness and the tensile strength criteria must be satisfied concurrently. In breakout boreholes, the breakdown pressure is lower than the circular wellbores; indeed, the ratio of the breakdown pressure of the breakout wellbore to the breakdown pressure in the circular wellbore is between 1 and 0.04, depending on the deviatoric stress and the width and depth of the breakout zone. In breakout wellbores, the fracture initiation position depends on the deviatoric stress. In small deviatoric stresses, the fracture initiation position is aligned with the minimum in situ stress, unlike circular boreholes; and in large deviatoric stresses, the fracture initiates in the direction of the major principal stress. In large wellbores, the breakdown pressure is controlled by the tensile strength of the rock; and in small wellbores, the breakdown pressure is under the control of the energy spent to create new crack surfaces.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Production of Mannooligosaccharides from Açaí Seed by Immobilized β-Mannanase
by
Sarha Lucia Murillo-Franco, Juan David Galvis-Nieto and Carlos E. Orrego
Processes 2024, 12(5), 847; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050847 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
In this work, an enzyme cocktail with β-mannanase as the main activity was immobilized on epoxy resin foams filled with fibers from annatto capsules. The catalytic system was characterized by SEM, FTIR, and a mechanical crush resistance test. The behavior of the pH
[...] Read more.
In this work, an enzyme cocktail with β-mannanase as the main activity was immobilized on epoxy resin foams filled with fibers from annatto capsules. The catalytic system was characterized by SEM, FTIR, and a mechanical crush resistance test. The behavior of the pH and temperature for the hydrolysis of the locust bean gum were also studied. With the same substrate and with respect to the free enzyme, the immobilized enzyme showed an activity retention of 79.61%. Its operational stability in ten reuse cycles did not show any statistically significant loss of activity. This catalytic system was used to study the preferential release of MOS of two to five degrees of polymerization from mannan present in dried and ground açaí seeds, which were not subjected to any other pretreatment. Using an experimental response surface design, the predicted quadratic models for the M2–M5 MOS content were obtained and they fit well with the experimental data, predicting a production range between 0.435 and 20 g/L of MOS (M2–M5). In addition, the production reached about 12 g/L under the optimized conditions. These results indicate that the used foamed epoxy resin supports and immobilization methodology are suitable for catalyzing the hydrolysis of mannan from açaí seeds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Separation and Extraction Techniques in Food Processing and Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
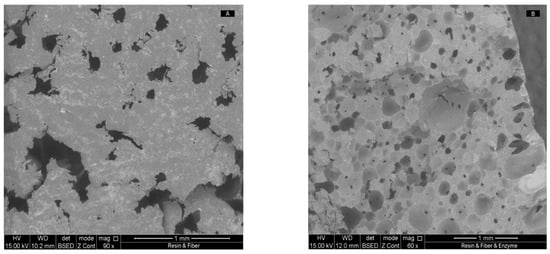
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Sustainable Development Processes for Renewable Energy Technology II: An Overview
by
Sergey Zhironkin and Radim Rybar
Processes 2024, 12(5), 846; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12050846 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
This Special Issue, titled “Sustainable Development Processes for Renewable Energy Technology II: An Overview”, presents a collection of papers in the field of sustainable development in the mineral resource sector, detailing the “seamless” process of transforming energy production into the use of renewable
[...] Read more.
This Special Issue, titled “Sustainable Development Processes for Renewable Energy Technology II: An Overview”, presents a collection of papers in the field of sustainable development in the mineral resource sector, detailing the “seamless” process of transforming energy production into the use of renewable sources [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Development Processes for Renewable Energy Technology II)
Open AccessArticle
Low-Carbon Optimal Configuration of Integrated Electricity and Natural Gas Energy System with Life-Cycle Carbon Emission
by
Jianpei Han, Ershun Du, Xunyan Lv and Jinming Hou
Processes 2024, 12(4), 845; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12040845 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
In response to the challenges of global warming and the development of A low-carbon economy, the integrated electricity and natural gas energy system (IEGES) is known as an important structure for future energy supply; thus, its planning and design must take low-carbon and
[...] Read more.
In response to the challenges of global warming and the development of A low-carbon economy, the integrated electricity and natural gas energy system (IEGES) is known as an important structure for future energy supply; thus, its planning and design must take low-carbon and environmental protection factors into account. Regarding carbon emissions as an optimization criterion, this paper built life-cycle carbon emission models of IEGES components. Then, taking the capacities of the energy resources, storage and conversion units of IEGES as the optimization variables, a multi-objective optimization configuration model was established considering the annual investment operation cost and the life-cycle carbon emissions. The multi-objective model was transformed into a single-objective one by an ε-constraint approach and the polynomial fitting method was employed to obtain the value of ε for obtaining uniformly distributed Pareto sets. Based on the fuzzy entropy weight method and the fuzzy affiliation degree approach, the obtained Pareto sets were ranked and the solution with the highest ranking value was selected as the optimal solution for the original problem. Finally, the configuration schemes were analyzed from the perspectives of economy, carbon emission and renewable energy utilization, and the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed optimization method were verified through MATLAB simulation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Process and Modelling of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Sources)
►▼
Show Figures
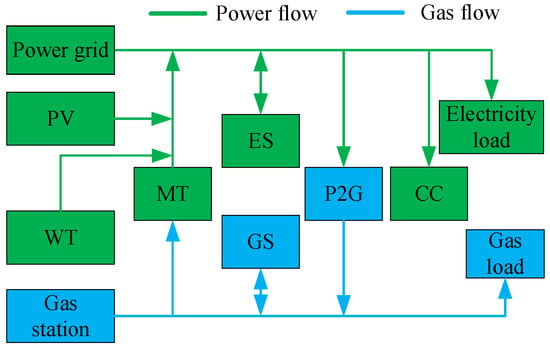
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pristine and UV-Weathered PET Microplastics as Water Contaminants: Appraising the Potential of the Fenton Process for Effective Remediation
by
Marin Kovačić, Antonija Tomić, Stefani Tonković, Anamarija Pulitika, Josipa Papac Zjačić, Zvonimir Katančić, Boštjan Genorio, Hrvoje Kušić and Ana Lončarić Božić
Processes 2024, 12(4), 844; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12040844 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics constitute a significant portion of plastic pollution in the environment and pose substantial environmental challenges. In this study, the effectiveness of the Fenton process and post-oxidation coagulation for the removal of non-weathered and UV-weathered PET microplastics (PET MPs) were
[...] Read more.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics constitute a significant portion of plastic pollution in the environment and pose substantial environmental challenges. In this study, the effectiveness of the Fenton process and post-oxidation coagulation for the removal of non-weathered and UV-weathered PET microplastics (PET MPs) were investigated. A response surface methodology was used to investigate the interplay between PET concentration and ferrous ion (Fe2+) concentration. The models revealed an intricate interplay between these variables, highlighting the need for a balanced system for optimal PET MP removal. For non-weathered PET, the simultaneous increase in the concentrations of both PET microplastics and Fe2+ was found to enhance the removal efficiency. However, this synergistic effect was not observed in UV-weathered PET, which also demonstrated a more pronounced effect from the Fe2+ concentration. The statistical analysis provided a strong basis for the validity of the models. X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) further elucidated the mechanisms behind these findings, revealing that UV weathering results in surface changes, which facilitate hydroxyl radical oxidation. These findings underline the complexity of the Fenton process in PET microplastic removal and the different behavior of non-weathered and UV-weathered microplastics. This has significant implications for tailoring remediation strategies and underscores the importance of considering environmental weathering in these strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Treatment and Remediation of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants)
►▼
Show Figures
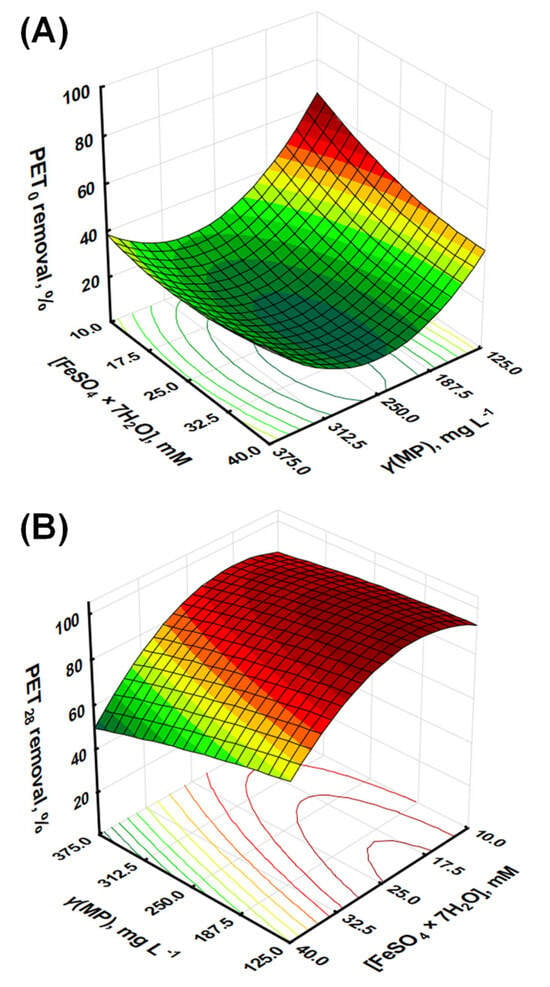
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
A Linear Fit for Atomic Force Microscopy Nanoindentation Experiments on Soft Samples
by
Stylianos Vasileios Kontomaris, Anna Malamou, Andreas Zachariades and Andreas Stylianou
Processes 2024, 12(4), 843; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12040843 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) nanoindentation is a powerful technique for determining the mechanical properties of soft samples at the nanoscale. The Hertz model is typically used for data processing when employing spherical indenters for small indentation depths (h) compared to the
[...] Read more.
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) nanoindentation is a powerful technique for determining the mechanical properties of soft samples at the nanoscale. The Hertz model is typically used for data processing when employing spherical indenters for small indentation depths (h) compared to the radius of the tip (R). When dealing with larger indentation depths, Sneddon’s equations can be used instead. In such cases, the fitting procedure becomes more intricate. Nevertheless, as the h/R ratio increases, the force–indentation curves tend to become linear. In this paper the potential of using the linear segment of the curve (for h > R) to determine Young’s modulus is explored. Force–indentation data from mouse and human lung tissues were utilized, and Young’s modulus was calculated using both conventional and linear approximation methods. The linear approximation proved to be accurate in all cases. Gaussian functions were applied to the results obtained from both classic Sneddon’s equations and the simplified approach, resulting in identical distribution means. Moreover, the simplified approach was notably unaffected by contact point determination. The linear segment of the force–indentation curve in deep spherical indentations can accurately determine the Young’s modulus of soft materials at the nanoscale.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multiscale Modeling and Control of Biomedical Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
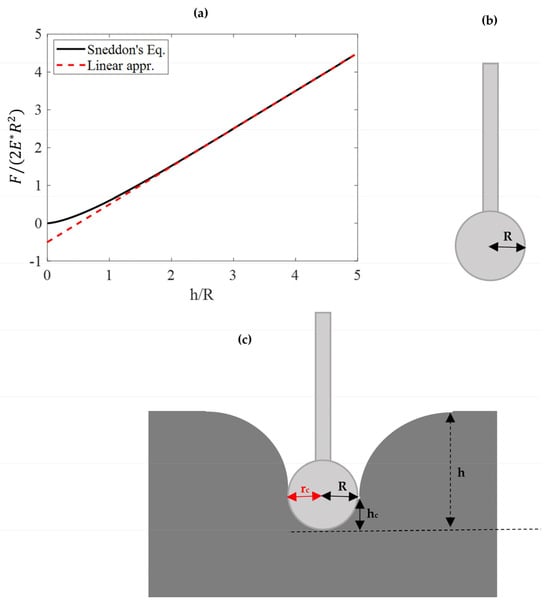
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Slow-Release Urea Fertilizer with Water Retention and Photosensitivity Properties Based on Sodium Alginate/Carboxymethyl Starch Sodium/Polydopamine
by
Yan Li, Yu Ma, Fan Chang, Haiyun Zhu, Chengshan Tian, Fengan Jia, Yang Ke and Jiakun Dai
Processes 2024, 12(4), 842; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12040842 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
Using slow-release fertilizer is one of the sustainable strategies to improve the effectiveness of fertilizers and mitigate the environmental pollution caused by excess usage of fertilizer. In this study, a slow-release urea fertilizer with water retention and photosensitivity properties was prepared by a
[...] Read more.
Using slow-release fertilizer is one of the sustainable strategies to improve the effectiveness of fertilizers and mitigate the environmental pollution caused by excess usage of fertilizer. In this study, a slow-release urea fertilizer with water retention and photosensitivity properties was prepared by a two-step method. It was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy and an infrared camera. This fertilizer can prolong the release period of urea, improve water-retention capacity of soil, and carry out photothermal conversion under illumination. Comparing four release kinetics models, the Ritger–Peppas model was the best fitting model for releasing behavior in soil, and diffusion followed the Fickian mechanism. The application of fertilizer on winter wheat was carried out to intuitively evaluate the fertilizer’s effects on promoting plant growth and resisting water stress. Thus, this study provides a new strategy for improving fertilizer utilization rate and maintaining soil moisture, which will be beneficial for sustainable agriculture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Chemical Processes and Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
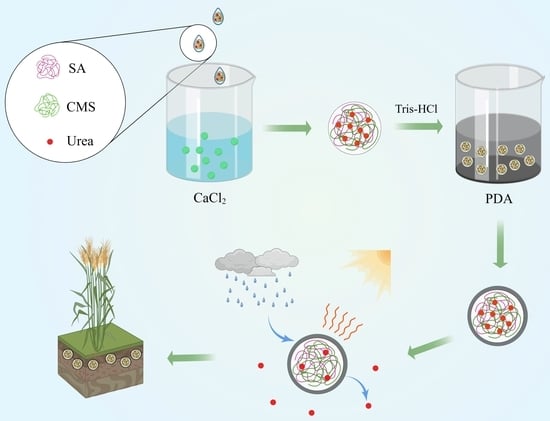
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Critical Failure Characteristics of a Straight-Walled Arched Tunnel Constructed in Sandstone under Biaxial Loading
by
Jian Gao, Xiaoshan Wang, Yu Cong, Qiqi Li, Yequan Pan and Xianglin Ding
Processes 2024, 12(4), 841; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12040841 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
To characterize the failure of rock mass surrounding underground tunnels, biaxial compression tests were conducted on a real sandstone model with a straight-walled arched hole. The acoustic emission (AE) system and digital image correlation (DIC) optical inspection equipment were used to investigate the
[...] Read more.
To characterize the failure of rock mass surrounding underground tunnels, biaxial compression tests were conducted on a real sandstone model with a straight-walled arched hole. The acoustic emission (AE) system and digital image correlation (DIC) optical inspection equipment were used to investigate the crack evolution process and failure precursors of the tunnel. A two-dimensional particle flow code (PFC2D) was used to conduct numerical simulations on the sample, so as to investigate the mesoscopic failure mechanism of rock mass. The results show that the failure of the single tunnel constructed in sandstone occurs mainly in the walls on both sides (between the spandrels and arch feet), showing slabbing failure characteristics and a certain abruptness. The crack initiation in sandstone in early stage is not obvious, and the crack propagation in rock mass is rapid when acoustic emissions are enhanced. The small increments in the AE count and amplitude and the continuous reduction in the b-value can be used as precursors for the failure of rock mass. When the height–span ratio is 0.8 and 1.0, the stress distribution around the chamber is more uniform, and when the height–span ratio is greater than 1.0, the stress is mainly concentrated in the vault and arch bottom. In the PFC simulations, tensile fractures firstly initiate in the middle of walls and at the arch feet, arcuate fracture concentration zones are then formed, in which shear fractures appear and a few particles spall from the surfaces. When approaching the ultimate bearing capacity, rock masses on both sides of the tunnel are fractured over large areas, and the slender coalesced fractured zone develops to the deep part of rock mass, causing failure of the sample.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Process Safety and Monitoring of Intelligent and Green Mining Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
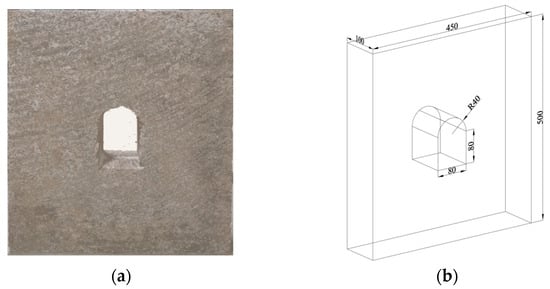
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Event-Driven Day-Ahead and Intra-Day Optimal Dispatch Strategy for Sustainable Operation of Power Systems Considering Major Weather Events
by
Zhifeng Liang, Dayan Sun, Ershun Du and Yuchen Fang
Processes 2024, 12(4), 840; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12040840 - 21 Apr 2024
Abstract
As the proportion of renewable energy installations in modern power systems increases, major weather events can easily trigger significant fluctuations in new energy generation and electricity load, presenting the system with the dual challenges of ensuring power supply and renewable energy consumption. Traditional
[...] Read more.
As the proportion of renewable energy installations in modern power systems increases, major weather events can easily trigger significant fluctuations in new energy generation and electricity load, presenting the system with the dual challenges of ensuring power supply and renewable energy consumption. Traditional dispatch models need more coordination and optimization of flexible resources under major weather events and risk management of system operations. This study focuses on provincial-level transmission systems, aiming to achieve the coordinated and optimized dispatch of flexible resources across multiple time scales in response to the complex and variable environments faced by the system. Firstly, by profoundly analyzing the response mechanisms of power systems during major weather events, this study innovatively proposes an event-driven day-ahead and intra-day optimal dispatch strategy for power systems. This strategy can sense and respond to major weather events in the day-ahead phase and adjust dispatch decisions in real time during the intra-day phase, thereby comprehensively enhancing the adaptability of power systems to sudden weather changes. Secondly, by considering the variability of renewable energy sources and electricity demand in the day-ahead and intra-day dispatch plans, the strategy ensures efficient and reliable power system operation under normal and major weather event scenarios. Finally, the method’s effectiveness is validated using actual data from a provincial-level power grid in China. The proposed dispatch strategy enhances the resilience and adaptability of power systems to major weather events, which are becoming increasingly frequent and severe due to climate change. The research demonstrates that an event-driven day-ahead and intra-day optimal dispatch strategy can enhance the economic efficiency and robustness of power system operations through the coordinated dispatch of flexible resources during major weather events, thereby supporting the transition toward sustainable energy systems that are resilient against the challenges of a changing climate.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Energy Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
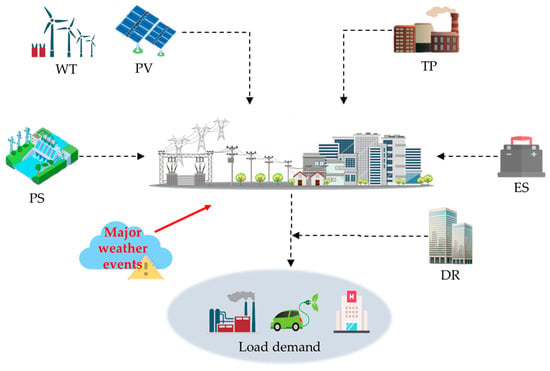
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on the Influence of Perforating Parameters on the Flow Rate and Stress Distribution of Multi-Fracture Competitive Propagation
by
Xing Zhao, Jin Zhao, Hehua Wang and Yuandong Liu
Processes 2024, 12(4), 839; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/pr12040839 - 21 Apr 2024
Abstract
It is of great significance to investigate the flow rate and stress distribution of multi-fracture propagation for the optimization of perforation parameters and fracture parameters. Considering the coupling of rock deformation, fracture direction and fluid flow in multi-fracture scenarios, a mathematical model and
[...] Read more.
It is of great significance to investigate the flow rate and stress distribution of multi-fracture propagation for the optimization of perforation parameters and fracture parameters. Considering the coupling of rock deformation, fracture direction and fluid flow in multi-fracture scenarios, a mathematical model and solution program for the flow and stress distribution of multiple fractures are established, and the analytical model is used for comparison and verification. The effects of perforation cluster number, cluster spacing, perforation diameter on fracture extension trajectory, fracture width, flow rate of each fracture and stress field are studied by the model. The results show that, as the number of perforating clusters increases, the inner fracture is inhibited more severely with less width, length and flow distribution, as well as lower bottom hole pressure. With the increase in cluster spacing, the stress interference between whole fractures is weakened and the flow distribution of the inner fracture is increased with lower bottom hole pressure. With the decrease in perforation diameter, the inhibition effect of inside fractures is weakened, while the inhibition effect of outside fractures, the flow distribution of inside fractures and the bottom hole pressure are increased. The uniform propagation of multiple fractures can be promoted by decreasing the perforation clusters’ number and perforation diameter or increasing fracture spacing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Hydraulic Fracturing Technology for Unconventional Reservoirs)
►▼
Show Figures
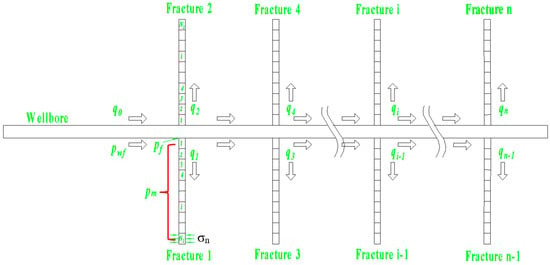
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Processes Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Analytica, Foods, Molecules, Processes, Separations
New Trends on Separation and Extraction of Bioactive Compounds and Respective Applications
Topic Editors: Isabel Maria Duque Martins, Madalena M. DiasDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Materials, Minerals, Processes, Sustainability, Toxics, Water
Removal of Hazardous Substances from Water Resources
Topic Editors: Gujie Qian, Yan Zhou, Weifeng ChenDeadline: 20 May 2024
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Processes, Solar, Sustainability
Solar Thermal Energy and Photovoltaic Systems, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Pedro Dinis Gaspar, Pedro Dinho da Silva, Luís C. PiresDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Clean Technol., Energies, Environments, Processes, Sustainability
Sustainable Energy: Efficient Technological Solutions Combining Environmental, Economic, Political and Social Aspects
Topic Editors: Fabio Orecchini, Adriano Santiangeli, Fabrizio ZuccariDeadline: 15 June 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Processes
New Trends and Perspectives on In Vitro Digestion Processes and Applications
Guest Editors: Krzysztof Dziedzic, Anabela Raymundo, Kristian PastorDeadline: 25 April 2024
Special Issue in
Processes
Chemical Process Modelling and Simulation
Guest Editor: Tamás VargaDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Processes
Design Processes via Manipulation of Nanoparticles and Their Suitability for Gas Sensors
Guest Editors: Gugu Hlengiwe Mhlongo, Dimitra PapadakiDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Processes
Advances in Sol-Gel Processes
Guest Editors: Stéphanie Lambert, Julien MahyDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Processes
Modeling, Simulation and Computation on Dynamics of Complex Fluids
Collection Editors: Gabriella Bognár, Krisztian Hriczo
Topical Collection in
Processes
Multi-Objective Optimization of Processes
Collection Editors: Gade Pandu Rangaiah, Andrew Hoadley
Topical Collection in
Processes
Principles of Modular Design and Control in Complex Systems
Collection Editor: Cong T. Trinh
Topical Collection in
Processes
Sustainable Food Processing Processes
Collection Editors: Dariusz Dziki, Renata Różyło, Urszula Gawlik-Dziki







