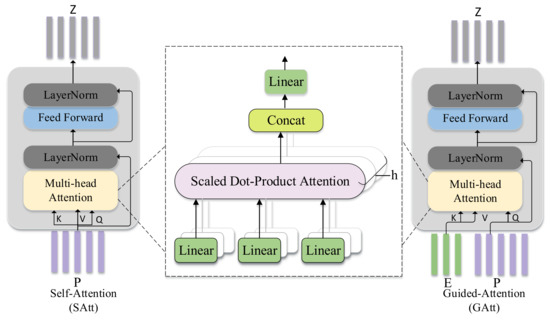
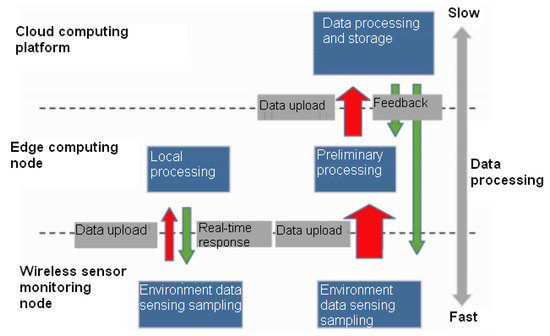
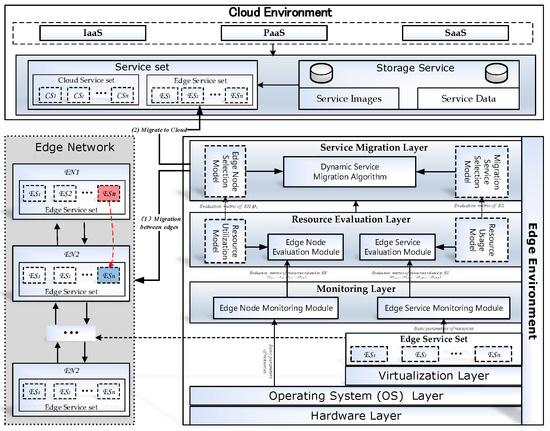
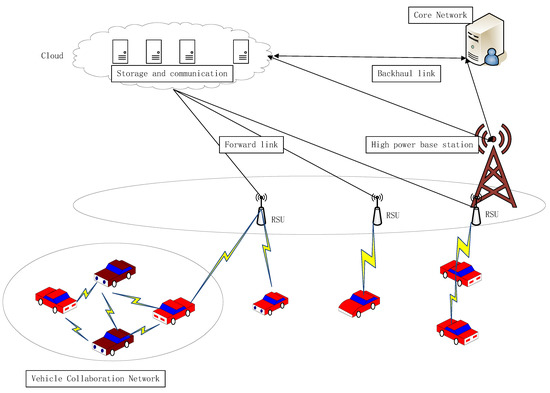
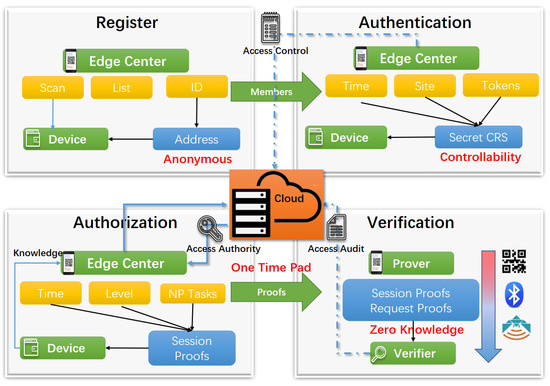
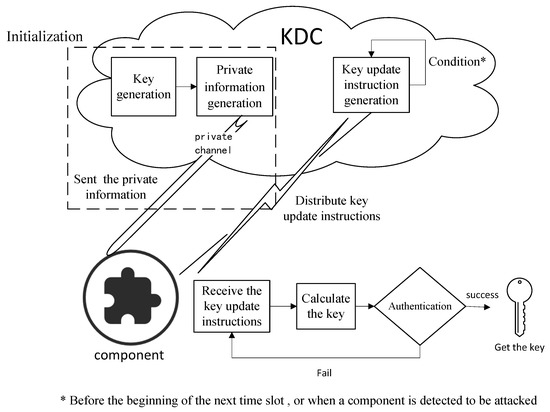
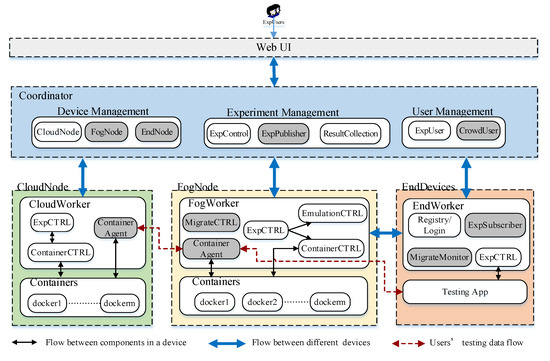
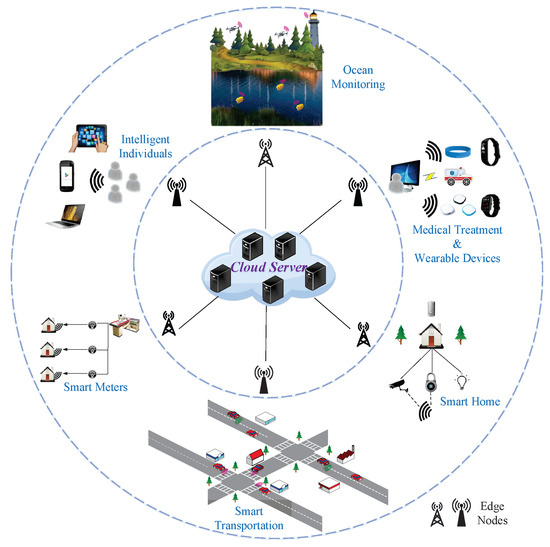
Fog/Edge Computing based Smart Sensing System (Closed)
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Sensor Networks".
Viewed by 89859Editors
Interests: sensor networks; cyber physical system
Interests: computer networks; wireless communications; parallel and distributed computing; ubiquitous computing; multimedia systems; modeling and performance engineering
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The Fourth International Symposium on Sensor-Cloud Systems (SCS 2020, http://www.spaccs.org/SCS2020/) will be held in Nanjing, China, Oct. 23-25, 2020. Moreover, the 18th IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing (IEEE EUC 2020) and the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (CSE 2020) will be held in Guangzhou, China, November 10-13, 2020.
This Topical Collection is cooperating with SCS 2020, EUC 2020 and CSE 2020. Authors of outstanding papers related to sensors presented at these conferences are invited to submit extended versions of their work to the Topical Collection for publication.
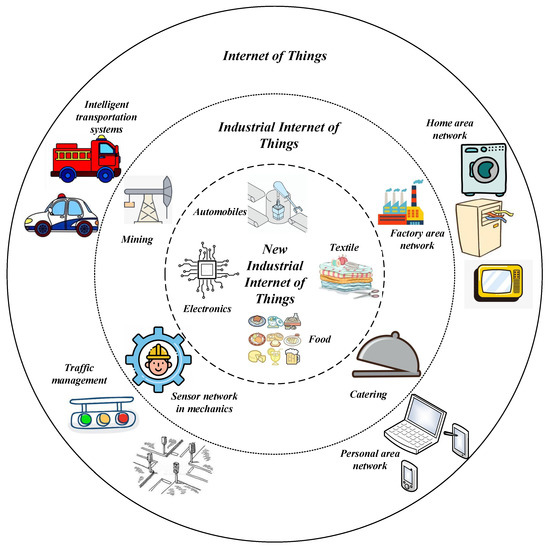
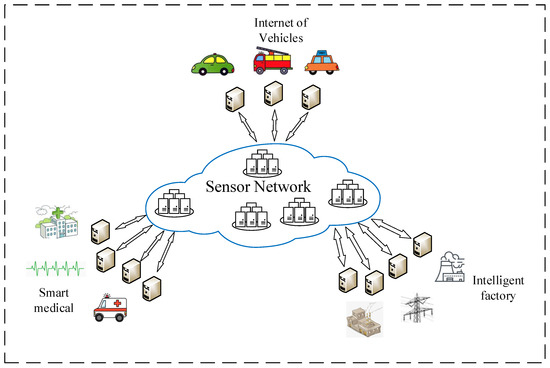
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) and Cloud Computing have received tremendous attentions from both academia and industry, as they are emerging to own numerous exciting applications in Internet of Things and smart cities, which can fundamentally change the way people interacting with the physical world.
However, there are still challenges need to be addressed in order to accelerate the development of these integrated systems. First of all, current techniques of Cloud Computing cannot satisfy the real-time requirement. The cloud cannot respond to sensors’ emergency requests. Second, the communication from sensors to cloud is a big problem, because sensors are with low bandwidth and low energy supplies. Third, as sensors are weak in processing and communication abilities, it is difficult for the cloud to guarantee the stability of the connection or even tolerate errors in that data. Finally, when sensors upload data to cloud for storage, how to ensure the data security and privacy in the cloud environment is a big problem.
Compared with Cloud Computing, Fog/Edge Computing is a promising technique for Sensor-Cloud systems. Fog/Edge Computing is proposed to enable computing directly at the edge of networks, delivering applications and services especially for IoT or smart cities. These fog devices, called fog nodes, have some local computation and storage capacity, wide geo-distribution like sensors and support for mobility. They can be industrial controllers, switches, routers, embedded servers and video surveillance cameras, and can be deployed anywhere with network connections. Serving as a link between sensor networks and the cloud, the fog can process and store data near where they are produced, and then manage and control sensors in a short distance. In this way, Fog/Edge Computing can extend Cloud Computing and cover its shortage in smart sensing system.
Prof. Md Zakirul Alam Bhuiyan
Prof. Dr. Geyong Min
Prof. Tian Wang
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Smart Sensing and Ubiquitous Computing in IoT
- Trustworthy Data Collection in IoT
- Smart Grids and Energy
- Smart and Intelligent Transport Systems
- Smart sensor-cloud system
- Applications for smart sensing and communication
- Fog/Edge computing framework for Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for real-time computing of Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for communications of Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for reliabilities of Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for data security of Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for privacy of Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for energy efficiency of Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for trust and reputation evaluation of Smart City
- Fog/Edge computing for data Integrity of Smart City
- Fog/Edge based applications for Smart City
- Mobile fog/edge computing for Smart City
- Mobile fog/edge elements for Smart City
- AI technologies for Smart City
- Edge intelligent for Smart City and IoT