Local Development Initiatives and Sustainable Employment Policies
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050).
Viewed by 26527
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Juan Carlos Rodríguez Cohard
Prof. Dr. Juan Carlos Rodríguez Cohard
 Prof. Dr. Juan Carlos Rodríguez Cohard
Prof. Dr. Juan Carlos Rodríguez Cohard
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Department of Economics, University of Jaén, Jaén, Spain
Interests: local development; innovation policies; economic development; institutions; entrepreneurship
 Prof. Dr. Antonio Vázquez Barquero
Prof. Dr. Antonio Vázquez Barquero
 Prof. Dr. Antonio Vázquez Barquero
Prof. Dr. Antonio Vázquez Barquero
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Department of Economic Structure and Development Economics, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
Interests: Endogenous Development; Economic Development; Innovation; Development Policies
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The challenge for territories in the context of new globalization processes, the recent changes in the status quo of international commerce, and, unexpectedly, the irruption of the COVID-19 pandemic are revealing new problems that regions and localities worldwide need to confront. New solutions are needed for territories to face competition in such a confusing scenario.
Sustainable employment policies should be implemented in order to encourage small business and self-employment and to contribute to the recovery of the world economy. Therefore, innovative local development initiatives are appearing in cities and rural areas in developed and developing countries.
This Special Issue of Sustainability is open to contributions covering the range of local development initiatives worldwide, including new business with local participation; small firm systems in global value chains; social innovation processes encouraging local economies; local employment policies; sustainable actions for local development; local governments’ participation in public–private partnerships for stimulating the territorial economic fabric; new institutional initiatives for development; and so on.
Contributions focused on economic development and employment theories and policies from social, economic, and politic sciences are welcomed. Papers presenting case studies are very interesting for a better understanding of how territories are facing the challenging processes of change in these turbulent times.
Prof. Dr. Juan Carlos Rodríguez Cohard
Prof. Dr. Antonio Vázquez Barquero
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- endogenous development
- local development policies
- local initiative
- economic development
- territorial development
- regional development
- territorial innovation policies
- institutional change
- social innovation
- local clusters
Published Papers (8 papers)
Open AccessArticle
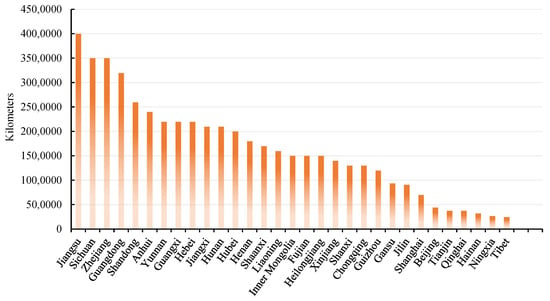
The Impact of Differentiated Development of the Digital Economy on Employment Quality—An Empirical Analysis Based on Provincial Data from China
by
Tongyang Liu, Dong Xue, Yizhuo Fang and Kunpeng Zhang
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1187
Abstract
In the context of the digital age, the digital economy, as a new economic model that the Chinese government is currently committed to developing, has played a positive role in driving consumption and creating employment opportunities. However, the differential development characteristics of the
[...] Read more.
In the context of the digital age, the digital economy, as a new economic model that the Chinese government is currently committed to developing, has played a positive role in driving consumption and creating employment opportunities. However, the differential development characteristics of the digital economy are becoming increasingly evident. The level of digital infrastructure and the application of digital facilities in China’s eastern regions are superior to those in the central and western regions. The increasing level of differential development in the digital economy will further accelerate the cross-regional mobility of labor. For the more developed eastern regions in China, in terms of the digital economy, the ability to empower employment is relatively high, which can create more job opportunities and attract a larger labor force seeking employment opportunities. In contrast, the central and western regions face slower development in the digital economy and relatively insufficient employment-empowering capacity, leading to labor force outflow. Proper cross-regional labor mobility can enhance the efficiency of labor resource allocation. However, excessive labor force mobility can lead to imbalanced labor resource allocation, causing job shortages and reduced employment quality in regions with an excess of labor force, while labor loss regions face labor shortages and talent drain, resulting in a loss of economic vitality in those regions. Therefore, clarifying and addressing the various negative impacts brought about by the differential development of the digital economy are crucial for improving the overall employment quality in the digital economy era. However, there is currently limited research focused on the influence of differential development levels of the digital economy on employment quality. This study delves into the impact of the differential development levels of the digital economy on employment quality and analyzes the underlying mechanisms. Based on panel data from 31 provinces and cities in mainland China from 2011 to 2020, this study uses the entropy method to calculate both the employment quality index and the digital economy index. Building upon the digital economy index, the Gini coefficient of the digital economy development level in various regions in China is calculated using the Gini coefficient formula. Subsequently, a two-way fixed-effects model empirically analyzes the impact of China’s differential development levels in the digital economy on employment quality. The research finds that the improvement in China’s differential development level in the digital economy significantly reduces employment quality. After re-calculating the Gini coefficient and the employment quality index using principal component analysis, it is found that the Gini coefficient of the digital economy still has a significantly negative impact on the employment quality index. After conducting 2SLS regression using instrumental variables, it is confirmed that there is still a significant negative correlation between the Gini coefficient of the digital economy and the employment quality index. According to the regression results, for every 1% increase in the Gini coefficient of the digital economy, the employment quality index will decrease by 0.111% to 0.361%. Through a regression analysis of the mechanism of action, it is found that the industrial structure plays an intermediary role in the impact of the differential development levels of the digital economy on employment quality. The improvement in the differential development levels of the digital economy is unfavorable for the transformation and upgrading of the industrial structure in the central and western regions, as well as the rational development of China’s overall industrial structure, thereby affecting the improvement of employment quality. Based on the above empirical results, the following policy recommendations are proposed: 1. The Chinese government should increase fiscal support for digital infrastructure construction in the central and western regions, continuously narrowing the gap in digital economy development levels between regions. 2. Regional governments in China should actively guide the healthy upgrading of industrial structures based on the actual conditions of each region. 3. In the digital economy era, the government should introduce relevant labor protection and social security policies based on the characteristics of emerging professions to further improve the employment quality of workers in the digital economy era.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
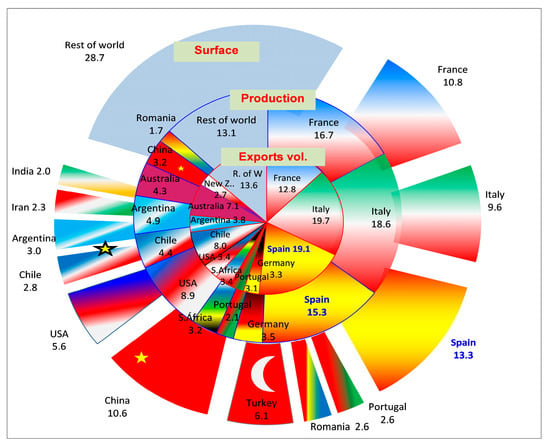
Challenges and Responses of Agri-Food Activities under COVID-19 Pandemic: The Case of the Spanish Territories Producing Wine and Olive Oil
by
Juan Carlos Rodríguez-Cohard, Juan José Juste-Carrión and Antonio Vázquez-Barquero
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2618
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has deeply affected economic activities worldwide. The challenge for territories and companies has been how to cope with mobility restrictions. Even in the case of essential activities such as agri-food industries, the adaptation has been a challenging issue to deal
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has deeply affected economic activities worldwide. The challenge for territories and companies has been how to cope with mobility restrictions. Even in the case of essential activities such as agri-food industries, the adaptation has been a challenging issue to deal with. The paper aims to show how the wine and olive oil industries in Spain have restructured their activities in order to respond to the confinement and the new normalcy, using new technologies as a strategic tool, but also making the most of new actions to keep their presence in the national and international markets. The research was carried out mostly through qualitative analysis, using the in-depth interview as a main tool to gain strategic information from managers of companies and local policymakers. Results show that when local policy makers and managers cooperate, despite the different perceptions they could have, the outcome is positive for facing competitive shocks and carving out new local initiatives, making firms and the territory itself more resilient.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Employment or Development in a Semi-Peripheral Region: The Roadrunner Paradigm
by
María-Luisa Gómez-Moreno
Viewed by 1437
Abstract
This study observes the relationship between employment policies and the evolution of the productive system, applying the theoretical framework of local development to an average-sized town in a semi-peripheral area of the European Union, during the period from 1975 to 2015. To do
[...] Read more.
This study observes the relationship between employment policies and the evolution of the productive system, applying the theoretical framework of local development to an average-sized town in a semi-peripheral area of the European Union, during the period from 1975 to 2015. To do so, a case analysis was made of the outcomes of employment policies via their effects on the variables impacting on the productive fabric. The following data sources were used: grey literature related to public policies; published statistics on demographic variables and economic activity; and local press reports. The following results were obtained: (a) the responses of economic agents owe more to the changes in the international scenario than to employment policies; (b) it is essential to analyse the evolution of demographic factors to properly interpret the relationship between labour supply and demand. We conclude that (a) corporate culture significantly influences the success or otherwise of employment policies, and (b) in the semi-peripheral area discussed, unemployment is an endemic problem that successive cohesion and employment policies have failed to resolve. Therefore, the use of innovation-oriented theoretical and practical approaches should be reconsidered.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Importance of Endogenous Resources for Internationalization: Competitive Advantages in the Olive Groves of Southern Spain
by
Clara Martos-Martínez and Marta Muñoz-Guarasa
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2058
Abstract
The general objective of this paper was to determine how companies in the olive sector could convert the comparative advantages of olive-growing regions (e.g., culture, tradition, raw materials, knowledge, infrastructure, networks, technological centers, etc.) into competitive advantages, to internationalize, in an accelerated way,
[...] Read more.
The general objective of this paper was to determine how companies in the olive sector could convert the comparative advantages of olive-growing regions (e.g., culture, tradition, raw materials, knowledge, infrastructure, networks, technological centers, etc.) into competitive advantages, to internationalize, in an accelerated way, and become born global firms, contributing to economic, social, and sustainable development of regions. Thus, we analyzed four cases of exporting companies in this sector (two born global and two non-born global) in southern Spain (Jaén). We chose this province because it is the world’s leading producer of olive oil and, yet it is only the fourth largest exporter compared to the rest of Spain. For the case study, we conducted (and recorded) personal, semi-structured interviews with the founders/managers or individuals in charge of internationalization. To obtain our results, we used a data sheet that included an action protocol, we analyzed each case individually, and we employed sensemaking and pattern-matching techniques to add validity and reliability to the research. Finally, we proposed the “keys” for these companies to go international in an accelerated way, as it would increase their competitiveness, foster the creation of employment, develop networks between companies, boost investment in innovation, etc. The results indicate that it is necessary to follow market orientation, networking, and international entrepreneurship strategies, and that intellectual capital (human, organizational, relational, and technological) of companies (and, therefore, of regions) will be the means through which competitive capabilities are achieved.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
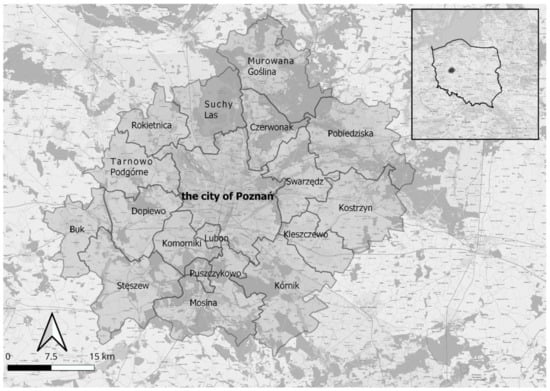
Adaptation Strategies of Migrant Workers from Ukraine during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Paweł Churski, Hanna Kroczak, Marta Łuczak, Olena Shelest-Szumilas and Marcin Woźniak
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2997
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching social and economic consequences. They are visible particularly in the functioning of local labour markets, affecting less privileged groups such as migrant workers, in a specific way. Here, our analysis aims to identify the strategies of adaptation
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching social and economic consequences. They are visible particularly in the functioning of local labour markets, affecting less privileged groups such as migrant workers, in a specific way. Here, our analysis aims to identify the strategies of adaptation of Ukrainian economic migrants to the changing situation in the local labour market in the Poznań agglomeration during the COVID-19 pandemic. The analysis relies on the results from quantitative research on changes in the demand for labour and adjustment of competence of immigrants to the Poznań agglomeration labour market throughout the pandemic and in the perspective of the nearest future, as well as on qualitative research conducted using the IDI (in-depth interviews) technique, carried out via the purposive sampling of 30 economically active Ukrainian migrant workers. The identified adaptation strategies are organised according to the assumptions of Pierre Bourdieu’s concept of capital(s). The capital of the researched group with respect to the labour market is treated as both the potential and resources the immigrants offer, produce, apply, and mutually convert in the implementation of their own adaptation strategies to the changing situation of the labour market. We extracted eight types of migrant adaptation strategies with respect to the labour market. These strategies differ in terms of objectives, resources, time perspectives, and other factors considered to be important from migrants’ perspectives. On the basis of interviews, we were able to assess the robustness of these strategies in view of economic shocks and identify the process of capital conversion and exchange.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
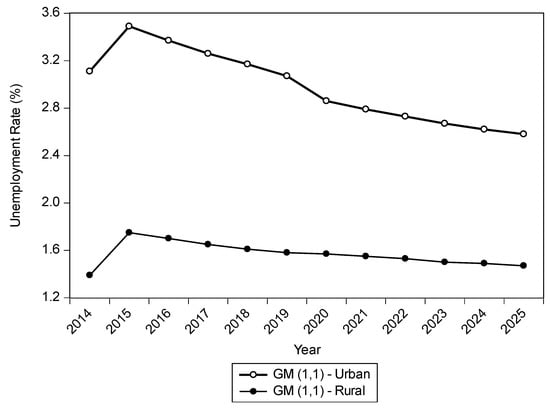
Unemployment Rates Forecasting with Grey-Based Models in the Post-COVID-19 Period: A Case Study from Vietnam
by
Phi-Hung Nguyen, Jung-Fa Tsai, Ihsan Erdem Kayral and Ming-Hua Lin
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 8049
Abstract
The Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has had a significant impact on most countries’ social and economic perspectives worldwide. Unemployment has become a vital challenge for policymakers as a result of COVID-19′s negative impact. Because of the nonstationary and nonlinear nature of the dataset, researchers
[...] Read more.
The Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has had a significant impact on most countries’ social and economic perspectives worldwide. Unemployment has become a vital challenge for policymakers as a result of COVID-19′s negative impact. Because of the nonstationary and nonlinear nature of the dataset, researchers applied various time series models to forecast the unemployment rate. This study aims to ensure a better forecasting approach for predicting the unemployment rates with an uncertainty of insufficient knowledge and tiny data throughout Vietnam. The study proposes the Grey theory system-based GM (1,1), the Grey Verhulst Model (GVM), and the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model that can more precisely predict unemployment rates. The model’s applications are shown using the Vietnamese unemployment rate at six different rural and urban areas with data sets from 2014–2019. The results indicate that the lower Mean Average Percentage Error (MAPE) values obtained with the GM (1,1) model at all regions for rural and urban areas (excluding Highlands Region in urban area) are extremely encouraging in comparison to other traditional methods. The accurate level of the ARIMA and GVM models follows the GM (1,1) model. The findings of this study show that the effects of the modeling assist policymakers in shaping future labor and economic policies. Furthermore, this study can contribute to the unemployment literature, providing future research directions in the unemployment problems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
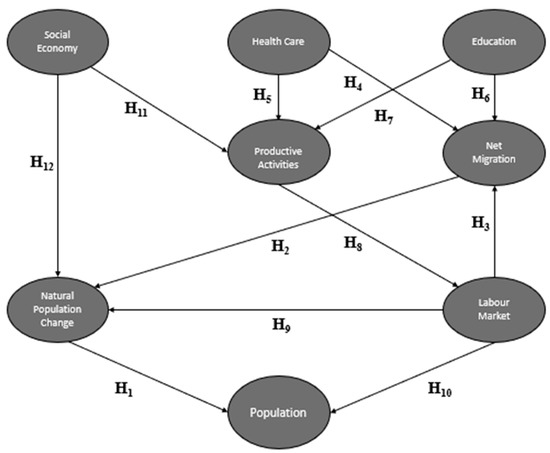
The Social Economy as a Factor of Economic Development and Resilience of Population in Rural Areas. A Study of Mediating Effects in Castilla-La Mancha (Spain)
by
Marcos Carchano, Inmaculada Carrasco, Sebastián Castillo and M. Carmen García-Cortijo
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3272
Abstract
Depopulation is a serious problem facing developed countries, among them Spain. It is especially severe in rural areas, where some vicious circles emerge, nourished by reduced infrastructures and services, deteriorated quality of life, the low inflow of new inhabitants, low local development and
[...] Read more.
Depopulation is a serious problem facing developed countries, among them Spain. It is especially severe in rural areas, where some vicious circles emerge, nourished by reduced infrastructures and services, deteriorated quality of life, the low inflow of new inhabitants, low local development and an aged population. In this context, social economy institutions may be a key factor in the fight against population decline, having a leading role in reactivating economic dynamism through the creation of stable, high-quality jobs, promoting the local endogenous development of rural areas, helping enhance income in those spaces, encouraging the arrival of people and impacting positively on social cohesion, and enabling sustainable growth. This paper focuses on Castilla-La Mancha, an eminently rural region, which is among the areas most severely impacted by the loss of population in Spain. The aim is to analyze the factors that affect the settlement of population, and to demonstrate that social economy institutions may be a resilience factor of rural population. A partial least squares model, composed of 8 constructs related to 21 variables extracted from data for 2017 and 2018 on the 613 municipalities, allows us to demonstrate that the existence of social economy entities helps to anchor population and increase the resilience of this territory.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
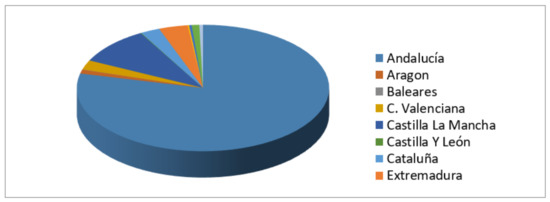
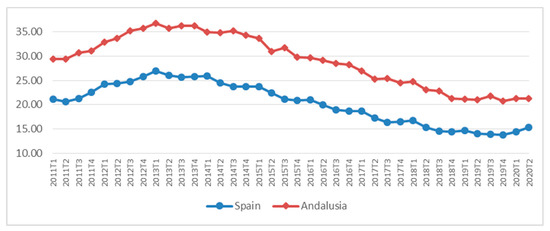
Cooperative Societies and Sustainability: A Spatial Analysis of Andalusia as a Tool for Implementing Territorial Development Policies, Strategies and Initiatives
by
María del Carmen Pérez-González and Lidia Valiente-Palma
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3000
Abstract
Local development strategies, policies and initiatives that contribute to sustainable development are gaining increasing prominence. Cooperative societies—the most relevant organisations within the social economy—are widely present in Andalusia and play a key role in boosting sustainable development through their principles and values. On
[...] Read more.
Local development strategies, policies and initiatives that contribute to sustainable development are gaining increasing prominence. Cooperative societies—the most relevant organisations within the social economy—are widely present in Andalusia and play a key role in boosting sustainable development through their principles and values. On this basis, the article aims to determine whether certain areas in Andalusia are more predisposed to the presence of these enterprises and are more sustainable as a result. The methods used include an adapted shift-share analysis and application of local Moran’s I to obtain spatial clusters allowing the areas most favourable to the presence of this type of organisation to be identified. Therefore, one of the main contributions of the study is that it provides a tool for the application of local development policies, strategies and initiatives involving cooperatives in pursuit of a more sustainable society.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures