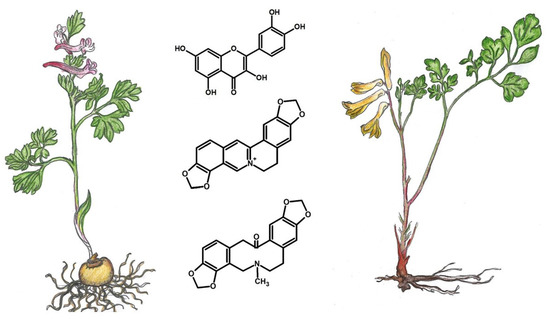
Phytochemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Corydalis solida and Pseudofumaria lutea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Qualitative Analysis
2.2. Quantitative Analysis
2.3. MIC Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
Plant Material Extraction
4.2. Phytochemical Analysis
4.2.1. Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
4.2.2. Identification and Quantification
4.3. Experimental Design for Bioactivity Assays
4.4. Statistical Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, P.F. Angiosperm Phylogeny Website, Version 14. Available online: http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/ (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Lidén, M. Fumariaceae. In Flowering Plants Dicotyledons. The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants; Kubitzki, K., Rohwer, J.G., Bittrich, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Euro + Med PlantBase—The Information Resource for Euro-Mediterranean Plant Diversity. Available online: http://ww2.bgbm.org/EuroPlusMed/PTaxonDetail.asp?NameId=93318&PTRefFk=7500000/ (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- POWO. Plants of the World Online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2019. Available online: http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- USDA, Agricultural Research Service, National Plant Germplasm System. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN-Taxonomy). National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Available online: https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=405102/ (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Lidén, M. Proposal to change the typification of Corydalis, nomen conservandum. Taxon 1981, 30, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salacova, K. Biological Activity of Plant Metabolites XII. Alkaloids of the Genus Corydalis DC. (Fumariaceae) and Their Biological Activity. Ph.D. Thesis, Charles University, Faculty of Pharmacy at Hradec Kralove, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, A.; Imming, P. R(-)-Canadaline as first secoberbine alkaloid from Corydalis cava. Phytochem. Lett. 2008, 1, 168–170. [Google Scholar]
- Preininger, V.; Novak, J.; Simanek, V.; Santavg, F. Isolation and chemistry of the alkaloids from plants of the papaveraceae. LXXIII. Planta Med. 1978, 33, 396–402. [Google Scholar]
- Preininger, V.; Dolejs, L.; Smysl, B.; Simanek, V. Isolation and chemistry of alkaloids from plants of the papaveraceae. LXXV. Planta Med. 1979, 36, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Zarzycki, K.; Trzcińska-Tacik, H.; Różański, W.; Szeląg, Z.; Wołek, J.; Korzeniak, U. Ecological Indicator Values of Vascular Plants of Poland; Polish Academy of Sciences: Kraków, Poland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Greuter, W. Proposal to reject Fumaria bulbosa L. Taxon 1987, 36, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummitt, R.K. Report of the committee for spermatophyta: 28. Taxon 1984, 33, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirek, Z.; Piękoś-Mirkowa, H.; Zając, A.; Zając, M. Flowering Plants and Pteridophytes of Poland. A Checklist; Szafer Institute of Botany, Polish Academy of Sciences: Kraków, Poland, 2002; p. 442. [Google Scholar]
- Tokarska-Guzik, B.; Dajdok, Z.; Zając, M.; Zając, A.; Urbisz, A.; Danielewicz, W.; Hołdyński, C.Z. Rośliny Obcego Pochodzenia w Polsce ze Szczególnym Uwzględnieniem Gatunków Inwazyjnych, Wyd; Generalna Dyrekcja Ochrony Środowiska: Warszawa, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Łuczaj, Ł. Dzikie Rośliny Jadalne Polski; Wydawnictwo Chemigrafia: Krosno, Poland, 2002; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Moszyński, K. Kultura Ludowa Słowian, (cz.1); Polska Akademia Umiejętności: Kraków, Poland, 1929; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, Z.; Smiljanić, M.; Matić, R.; Kostić, R.; Nikić, P.; Bojović, S. Phytotherapeutical plants from the Deliblato Sands (Serbia): Traditional pharmacopoeia and implications for conservation. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2012, 11, 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Boegge, S.; Kesper, S.; Verspohl, E.J.; Nahrstedt, A. Reduction of ACh-induced contraction of rat isolated ileum by coptisine, (+)-caffeoylmalic acid, CheIidonium majus, and Corydalis lutea extracts. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 173–174. [Google Scholar]
- Manske, R.H.F. The alkaloids of Fumariaceous plants XXR. Corydalrs lutea (L.) DC. Can. J. Res. 1939, 17B, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Temizer, H.; Sener, B.; Temizer, A.; Kir, S. Determination of alkaloids by differential pulse polarography. III Corydalis alkaloids. Electroanal 1992, 4, 737–740. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, S.; Seger, C.; Godejohann, M.; Spraul, M.; Stuppner, H. Conventional sample enrichment strategies combined with high-performance liquid chromatography–solid phase extraction–nuclear magnetic resonance analysis allows analyte identification from a single minuscule Corydalis solida plant tuber. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1163, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimizadeh, M.; Miller, R.R.; Onur, M.A.; Gozler, T.; Shamma, M. (+)-corysolidine, a spirobenzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Corydalis solida. Phytochemistry 1986, 25, 2245–2246. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, K.M.; Kaya, E.; Aysal, A.I.; Sener, B. Evaluation of some biological activities of the tubers of Corydalis solida (L.) Clairv. ssp. incisa Lieden growing in Turkey. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 127, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, B.; Temizer, H. Chemical studies on the alkaloids from Corydalis solida subsp. tauricola. Planta. Med. 1990, 56, 510. [Google Scholar]
- Adsersen, A.; Gauguin, B.; Gudiksen, L.; Jager, A.K. Screening of plants used in Danish folk medicine to treat memorydisfunction for acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104, 418–422. [Google Scholar]
- Lidén, M. Notes on Corydalis sect. Corydalis in the Baltic area. Nord. J. Bot. 1991, 11, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Boegge, S.C.; Nahrstedt, A.; Linscheid, M.; Nigge, W. Distribution and stereochemistry of hydroxycinnamoylmalic acids and of free malic acids in Papaveraceae and Fumariaceae. Z. Naturforsch. 1995, 50c, 608–615. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, A.; Anacona, J.R. Metal complexes of the flavonoid quercetin: Antibacterial properties. Transit. Met. Chem. 2001, 26, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Boots, A.W.; Li, H.; Schins, R.P.F.; Duffin, R.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. The quercetin paradox. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2007, 222, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gorlenko, C.L.; Kiselev, H.Y.; Budanova, E.V.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr.; Ikryannikova, L.N. Plant secondary metabolites in the battle of drugs and drug-resistant bacteria: New heroes or worse clones of antibiotics? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Tripathi, A. Demonstration of bactericidal and synergistic activity of quercetin with meropenem among pathogenic carbapenem resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 143, 104120. [Google Scholar]
- Sholkamy, E.N.; Ahmed, M.S.; Yasser, M.M.; Mostafa, A.A. Antimicrobial quercetin 3-O-glucoside derivative isolated from Streptomyces antibioticus strain ess_amA8. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Zhang, L.-F.; Xu, J.-G. Chemical composition, antibacterial activity and action mechanism of diferent extracts from hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifda Bge.). Sci. Rep. UK 2020, 10, 8876. [Google Scholar]
- Zielińska, S.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Dziągwa-Becker, M.; Gleńsk, M.; Sowa, I.; Fijałkowski, K.; Rurańska-Smutnicka, D.; Matkowski, A.; Junka, A. The activity of isoquinoline alkaloids and extracts from Chelidonium majus against pathogenic bacteria and candida sp. Toxins 2019, 11, 406. [Google Scholar]
- Kedzia, B.; Hołderna-Kedzia, E. The effect of alkaloids and other groups of plant compounds on bacteria and fungi. Postep. Fitoter. 2013, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Sheng, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Yao, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, R. Effect of berberine and its derivatives on cancer: A system pharmacology review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Wang, S.B.; Yuan, T.Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Yan, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, X.N.; Gong, L.I.; Qin, H.I.; Fang, L.H.; et al. Coptisine protects rat heart against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing myocardial apoptosis and inflammation. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.A.; Gilani, A.H.; Majoo, R.U.; Shah, B.H. Anti-thrombotic and anti-inflammatory activities of protopine. Pharmacol. Res. 1997, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kikowska, M.; Derda, M.; Thiem, B.; Włodarczyk, A.; Długaszewska, J.; Stochmal, A.; Żuchowski, J.; Hadaś, E. Evaluation of antiamoebic and antimicrobial activities in vitro of Chaenomeles japonica (Thunb.) lindl. ex spach extracts. Acta Biol. Cracs. Bot. 2019, 61, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaoues, S.; Amri, S.; Bensouilah, M. Major phenolic compounds, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Anthemis praecox Link aerial parts. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 131, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, I.; Özcelik, B.; Karaoglu, T.; Sener, B. Antiviral and antimicrobial profiles of selected isoquinoline alkaloids from Fumaria and Corydalis species. Z. Naturforsch. 2007, 62c, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mergaert, P. Role of antimicrobial peptides in controlling symbiotic bacterial populations. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Geddes, B.A.; Paramasivan, P.; Joffrin, A.; Thompson, A.L.; Christensen, K.; Jorrin, B.; Brett, P.; Conway, S.J.; Oldroyd, E.D.; Poole, P.S. Engineering transkingdom signaling in plants to control gene expression in rhizosphere bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3430. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.A.; Zahin, M.; Hasan, S.; Husian, F.M.; Ahmad, I. Inhibition of quorum sensing regulating bacterial functions by plant essential oils with special reference to clove oil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Manefield, M.; de Nys, R.; Naresh, K.; Read, R.; Givskov, M.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Evidence that halogenated furanones from Delisea pulchra inhibit acylated homoserine lactone (AHL)-mediated gene expression by displacing the AHL signal from its receptor protein. Micro. Soc. 1999, 145, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Sowa, I.; Zielinska, S.; Sawicki, J.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Staniak, M.; Bartusiak-Szczesniak, E.; Podolska-Fajks, M.; Kocjan, R.; Wojciak-Kosior, M. Systematic evaluation of chromatographic parameters for isoquinoline alkaloids on XB-C18 core shell column using different mobile phase compositions. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso, F.; Ferreres, Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Valentão, P.; Sampaio, M.; Lima, J.; Andrade, P.B. Box–Behnken factorial design to obtain a phenolic-rich extract from the aerial parts of Chelidonium majus L. Talanta 2014, 130, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the plant material and test extracts are available from the authors. |


| No | Compound | Parent Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Ion Mode | Content Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALKALOIDS | C. solida | P. lutea | ||||
| 1 | protopine derivative | 354 | 320, 260, 196 | + | p | p |
| 2 | allocryptopine | 369 | 352, 188, 290 | + | 328 ± 13.99 * | LOD |
| 3 | coptisine | 320 | 292, 204, 262 | + | 154 ± 7.42 * | 1526 ± 24.12 |
| 4 | berberine | 336 | 320, 292, 321 | + | 128 ± 6.79 * | 197 ± 12.10 |
| 5 | chelidonine derivative | 370 | 356, 339 | + | p | nd |
| 6 | chelidonine | 354 | 275, 189, 247 | + | 58 ± 3.67 * | 3 ± 0.69 |
| 7 | chelerythrine | 348 | 332, 304, 333 | + | 18 ± 1.31 * | 4 ± 0.26 |
| 8 | tetrahydroberberine | 340 | 176, 149 | + | p | p |
| 9 | tetrahydrocoptisine | 324 | 176, 149 | + | p | p |
| 10 | coptisine derivative | 324 | 190 | + | p | p |
| 11 | sanguinarine | 332 | 274, 317, 246 | + | 35 ± 2.78 * | 12 ± 0.89 |
| 12 | protopine | 320 | 303, 107, 124 | + | 440 ± 16.10 * | 1036 ± 30.62 |
| Other Compounds | ||||||
| 13 | malic acid | 133 | 115, 71 | - | LOQ | LOQ |
| 14 | trans-aconitic acid | 173 | 85, 129 | - | LOQ | LOQ |
| 15 | quinic acid | 191 | 85, 93 | - | LOQ | LOQ |
| 16 | trans-caffeic acid | 179 | 135, 134, 89 | - | 21 ± 1.52 * | 32 ± 4.90 |
| 17 | chlorogenic acid | 353 | 191, 85, 93 | - | 1 ± 0.13 * | 32 ± 1.51 |
| 18 | p-coumaric acid | 163 | 119, 93, 117 | - | 28 ± 1.71 * | 16 ± 1.85 |
| 19 | vanillin | 151 | 136, 92, 108 | - | 11 ± 0.93 | 13 ± 1.69 |
| 20 | quercetin | 301 | 151, 65, 121 | - | 177 ± 9.67 * | 3247 ± 66.43 |
| 21 | rutin | 609 | 300 | - | LOQ | LOQ |
| No | Compound | Parent Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Ion Mode | Content Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALKALOIDS | C. solida | P. lutea | ||||
| 1 | protopine derivative | 354 | 320, 260, 196 | + | p | p |
| 2 | allocryptopine | 369 | 352, 188, 290 | + | 516 ± 21.52 * | 6 ± 1.37 |
| 3 | coptisine | 320 | 292, 204, 262 | + | 233 ± 5.13 * | 307 ± 17.36 |
| 4 | berberine | 336 | 320, 292, 321 | + | 78 ± 3.58 * | 326 ± 8.40 |
| 5 | chelidonine derivative | 370 | 356, 339 | + | p | nd |
| 6 | chelidonine | 354 | 275, 189, 247 | + | 1 ± 0.05 * | 5 ± 0.20 |
| 7 | chelerythrine | 348 | 332, 304, 333 | + | 7 ± 0.37 * | 6 ± 0.12 |
| 8 | tetrahydroberberine | 340 | 176, 149 | + | p | p |
| 9 | tetrahydrocoptisine | 324 | 176, 149 | + | p | p |
| 10 | coptisine derivative | 324 | 190 | + | p | p |
| 11 | sanguinarine | 332 | 274, 317, 246 | + | 8 ± 0.28 * | 36 ± 3.53 |
| 12 | protopine | 320 | 303, 107, 124 | + | 1125 ± 32.63 * | 1934 ± 25.98 |
| Other Compounds | ||||||
| 13 | malic acid | 133 | 115, 71 | - | LOQ | LOQ |
| 14 | trans-aconitic acid | 173 | 85, 129 | - | LOQ | LOQ |
| 15 | quinic acid | 191 | 85, 93 | - | LOQ | LOQ |
| 16 | trans-caffeic acid | 179 | 135, 134, 89 | - | nd | nd |
| 17 | chlorogenic acid | 353 | 191, 85, 93 | - | 6 ± 1.26 * | nd |
| 18 | p-coumaric acid | 163 | 119, 93, 117 | - | LOD | nd |
| 19 | vanillin | 151 | 136, 92, 108 | - | nd | nd |
| 20 | quercetin | 301 | 151, 65, 121 | - | 19 ± 2.88 * | 76 ± 4.64 |
| 21 | rutin | 609 | 300 | - | nd | nd |
| Plant Material | S. aureus | P. aeruginosa | C. albicans |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. solida herb | 1.56 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| C. solida corms | 1.56 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| P. lutea herb | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| P.lutea roots | 1.56 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| Octenisept (method suitability control) | 0.0001 | 0.00152 | 0.0001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zielińska, S.; Dziągwa-Becker, M.; Piątczak, E.; Jezierska-Domaradzka, A.; Brożyna, M.; Junka, A.; Kucharski, M.; Çiçek, S.S.; Zidorn, C.; Matkowski, A. Phytochemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Corydalis solida and Pseudofumaria lutea. Molecules 2020, 25, 3591. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/molecules25163591
Zielińska S, Dziągwa-Becker M, Piątczak E, Jezierska-Domaradzka A, Brożyna M, Junka A, Kucharski M, Çiçek SS, Zidorn C, Matkowski A. Phytochemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Corydalis solida and Pseudofumaria lutea. Molecules. 2020; 25(16):3591. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/molecules25163591
Chicago/Turabian StyleZielińska, Sylwia, Magdalena Dziągwa-Becker, Ewelina Piątczak, Anna Jezierska-Domaradzka, Malwina Brożyna, Adam Junka, Mariusz Kucharski, Serhat Sezai Çiçek, Christian Zidorn, and Adam Matkowski. 2020. "Phytochemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Corydalis solida and Pseudofumaria lutea" Molecules 25, no. 16: 3591. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/molecules25163591