Targeting Immune Cell Checkpoints during Sepsis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Sepsis-Induced Immunosuppression
1.2. Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) and Its Ligands PD-L1/PD-L2
1.2.1. PD-1
1.2.2. PD-L1 and PD-L2
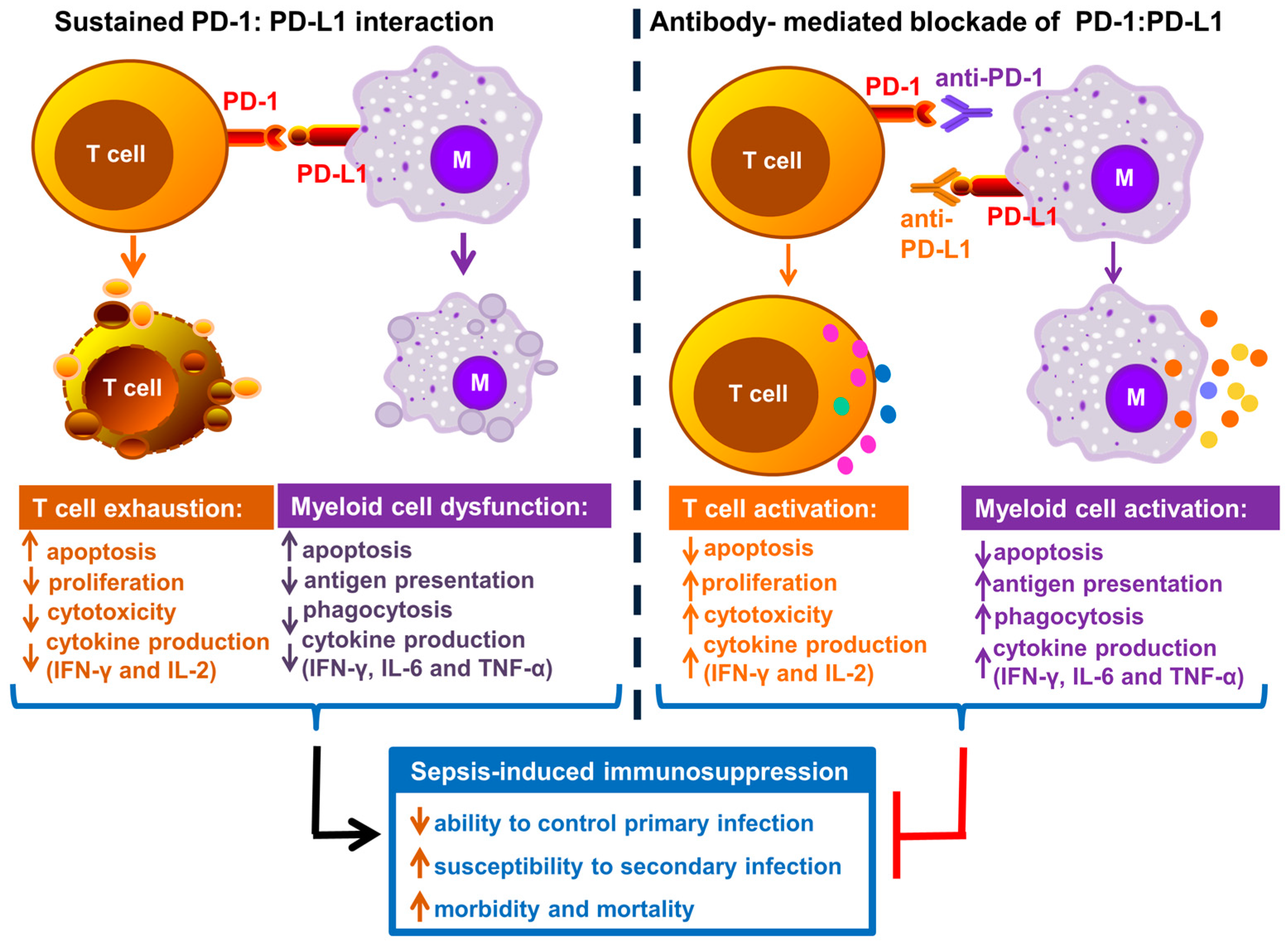
1.3. Role of PD-1 and Its Ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 in Immune Cell Dysfunction during Sepsis
1.4. Does PD-L1 Play a Role in Organ Injury during Sepsis?
1.5. Targeting PD-1 and PD-L1 during Sepsis
1.5.1. Targeting PD-L1 during Sepsis
1.5.2. Targeting PD-1 during Sepsis
2. Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen-4 (CTLA-4)
3. B and T Lymphocyte Attenuator (BTLA)
4. T Cell Membrane Protein-3 (TIM-3), Lymphocyte Activation-Gene-3 (LAG-3) and 2B4
5. Blockade of Immune Checkpoints during Sepsis: Is it always Appropriate?
Potential Side Effects of Blocking Immune Checkpoints
6. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand-1 |
| PD-L2 | Programmed death ligand-2 |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antign-4 |
| BTLA | B and T lymphocyte attenuator |
| HVEM | Herpes virus entry mediator |
| TIM-3 | T cell membrane protein-3 |
| CEACM | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| sTIM-3-Ig | Soluble TIM-3 Immunoglobulin |
| NK cell | Natural Killer Cell |
| CLP | Cecal ligation and puncture |
References
- Mayr, F.B.; Yende, S.; Angus, D.C. Epidemiology of severe sepsis. Virulence 2014, 5, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K. International Forum of Acute Care Team. Assessment of Global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delano, M.J.; Ward, P.A. Sepsis-induced immune dysfunction: Can immune therapies reduce mortality? J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Sherwood, E.R. Immunology. Getting sepsis therapy right. Science 2015, 347, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomer, J.S.; Green, J.M.; Hotchkiss, R.S. The changing immune system in sepsis: Is individualized immuno-modulatory therapy the answer? Virulence 2014, 5, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.M.; Huang, S.J.; McLean, A.S. Genome-wide transcription profiling of human sepsis: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, L.F.; Cuenca, A.G.; Efron, P.A.; Ang, D.; Bihorac, A.; McKinley, B.A.; Moldawer, L.L.; Moore, F.A. Persistent inflammation and immunosuppression: A common syndrome and new horizon for surgical intensive care. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monneret, G.; Venet, F.; Kullberg, B.J.; Netea, M.G. ICU-acquired immunosuppression and the risk for secondary fungal infections. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49 (Suppl. S1), S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, G.P.; Sossdorf, M.; Claus, R.A.; Rodel, J.; Menge, K.; Reinhart, K.; Bauer, M.; Riedemann, N.C. The late phase of sepsis is characterized by an increased microbiological burden and death rate. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, N.K.; Parajuli, N.; MacMillan-Crow, L.A.; Mayeux, P.R. Inactivation of renal mitochondrial respiratory complexes and manganese superoxide dismutase during sepsis: Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant mitigates injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, F734–F743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, E.; Singer, M. Mechanisms of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Luan, L.; Patil, N.K.; Wang, J.; Bohannon, J.K.; Rabacal, W.; Fensterheim, B.A.; Hernandez, A.; Sherwood, E.R. IL-15 Enables Septic Shock by Maintaining NK Cell Integrity and Function. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Karl, I.E. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Coopersmith, C.M.; McDunn, J.E.; Ferguson, T.A. The sepsis seesaw: Tilting toward immunosuppression. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Opal, S. Immunotherapy for sepsis—A new approach against an ancient foe. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, N.K.; Bohannon, J.K.; Sherwood, E.R. Immunotherapy: A promising approach to reverse sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schorr, C.A.; Dellinger, R.P. The surviving sepsis campaign: Past, present and future. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyt, C.E.; Kaiser, L. Virus detection in patients with severe pneumonia: Still more questions than answers? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, A.H.; Muenzer, J.T.; Rasche, D.; Boomer, J.S.; Sato, B.; Brownstein, B.H.; Pachot, A.; Brooks, T.L.; Deych, E.; Shannon, W.D.; et al. Reactivation of multiple viruses in patients with sepsis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Immunosuppression in sepsis: A novel understanding of the disorder and a new therapeutic approach. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudick, C.P.; Cornell, D.L.; Agrawal, D.K. Single versus combined immunoregulatory approach using PD-1 and CTLA-4 modulators in controlling sepsis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomer, J.S.; To, K.; Chang, K.C.; Takasu, O.; Osborne, D.F.; Walton, A.H.; Bricker, T.L.; Jarman, S.D., 2nd; Kreisel, D.; Krupnick, A.S.; et al. Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis and multiple organ failure. JAMA 2011, 306, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patera, A.C.; Drewry, A.M.; Chang, K.; Beiter, E.R.; Osborne, D.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Frontline Science: Defects in immune function in patients with sepsis are associated with PD-1 or PD-L1 expression and can be restored by antibodies targeting PD-1 or PD-L1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 1239–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Schwartz, J.C.; Guo, X.; Bhatia, S.; Cao, E.; Lorenz, M.; Cammer, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Edidin, M.A.; et al. Structural and functional analysis of the costimulatory receptor programmed death-1. Immunity 2004, 20, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, T.; Maeda, A.; Nishimura, H.; Kurosaki, T.; Honjo, T. PD-1 immunoreceptor inhibits B cell receptor-mediated signaling by recruiting src homology 2-domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2 to phosphotyrosine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13866–13871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, T.; Taniwaki, M.; Ishida, Y.; Kawaichi, M.; Honjo, T. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human PD-1 gene (PDCD1). Genomics 1994, 23, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; Chen, L. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Latchman, Y.; Wood, C.R.; Chernova, T.; Chaudhary, D.; Borde, M.; Chernova, I.; Iwai, Y.; Long, A.J.; Brown, J.A.; Nunes, R.; et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.; Ling, V.; Carreno, B.M. The B7 family of immune-regulatory ligands. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crawford, A.; Wherry, E.J. The diversity of costimulatory and inhibitory receptor pathways and the regulation of antiviral T cell responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmamdam, P.; Inoue, S.; Unsinger, J.; Chang, K.C.; McDunn, J.E.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Delayed administration of anti-PD-1 antibody reverses immune dysfunction and improves survival during sepsis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lou, J.; Li, J.; Bo, L.; Zhu, K.; Wan, X.; Deng, X.; Cai, Z. PD-L1 blockade improves survival in experimental sepsis by inhibiting lymphocyte apoptosis and reversing monocyte dysfunction. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Venet, F.; Wang, Y.L.; Lepape, A.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Swan, R.; Kherouf, H.; Monneret, G.; Chung, C.S.; et al. PD-1 expression by macrophages plays a pathologic role in altering microbial clearance and the innate inflammatory response to sepsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6303–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chung, C.S.; Yuan, Z.; Monaghan, S.F.; Wang, F.; Ayala, A. Identification of B7-H1 as a novel mediator of the innate immune/proinflammatory response as well as a possible myeloid cell prognostic biomarker in sepsis. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNab, F.W.; Berry, M.P.; Graham, C.M.; Bloch, S.A.; Oni, T.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Kon, O.M.; Banchereau, J.; Chaussabel, D.; et al. Programmed death ligand 1 is over-expressed by neutrophils in the blood of patients with active tuberculosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Huang, X.; Chung, C.S.; Chen, Y.; Hutchins, N.A.; Ayala, A. Contribution of programmed cell death receptor (PD)-1 to Kupffer cell dysfunction in murine polymicrobial sepsis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G237–G245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, N.K.; Bohannon, J.K.; Luan, L.; Guo, Y.; Fensterheim, B.; Hernandez, A.; Wang, J.; Sherwood, E.R. Flt3 Ligand treatment attenuates T cell dysfunction and improves survival in a murine model of burn wound sepsis. Shock 2017, 47, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, W.A.; Fallon, E.A.; Heffernan, D.S.; Efron, P.A.; Cioffi, W.G.; Ayala, A. Improved survival after induction of sepsis by cecal slurry in PD-1 knockout murine neonates. Surgery 2017, 161, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guignant, C.; Lepape, A.; Huang, X.; Kherouf, H.; Denis, L.; Poitevin, F.; Malcus, C.; Cheron, A.; Allaouchiche, B.; Gueyffier, F.; et al. Programmed death-1 levels correlate with increased mortality, nosocomial infection and immune dysfunctions in septic shock patients. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bo, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, K.; Wan, X.; Cai, Z.; Deng, X. Upregulation of programmed death-1 on T cells and programmed death ligand-1 on monocytes in septic shock patients. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.; Svabek, C.; Vazquez-Guillamet, C.; Sato, B.; Rasche, D.; Wilson, S.; Robbins, P.; Ulbrandt, N.; Suzich, J.; Green, J.; et al. Targeting the programmed cell death 1: Programmed cell death ligand 1 pathway reverses T cell exhaustion in patients with sepsis. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spec, A.; Shindo, Y.; Burnham, C.A.; Wilson, S.; Ablordeppey, E.A.; Beiter, E.R.; Chang, K.; Drewry, A.M.; Hotchkiss, R.S. T cells from patients with Candida sepsis display a suppressive immunophenotype. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, R.; Fang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C.S. Monocyte programmed death ligand-1 expression after 3–4 days of sepsis is associated with risk stratification and mortality in septic patients: A prospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, S.; Bo, L.; Bian, J.; Unsinger, J.; Chang, K.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Dose-dependent effect of anti-CTLA-4 on survival in sepsis. Shock 2011, 36, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubin, N.J.; Chung, C.S.; Heffernan, D.S.; Irwin, L.R.; Monaghan, S.F.; Ayala, A. BTLA expression contributes to septic morbidity and mortality by inducing innate inflammatory cell dysfunction. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Bao, R.; Fan, X.; Tao, T.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Bo, L.; Deng, X. PD-L1 blockade attenuated sepsis-induced liver injury in a mouse cecal ligation and puncture model. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 361501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.C.; Burnham, C.A.; Compton, S.M.; Rasche, D.P.; Mazuski, R.J.; McDonough, J.S.; Unsinger, J.; Korman, A.J.; Green, J.M.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Blockade of the negative co-stimulatory molecules PD-1 and CTLA-4 improves survival in primary and secondary fungal sepsis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchins, N.A.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Chung, C.S.; Ayala, A. Kupffer cells potentiate liver sinusoidal endothelial cell injury in sepsis by ligating programmed cell death ligand-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chung, C.S.; Chen, Y.; Monaghan, S.F.; Patel, S.; Huang, X.; Heffernan, D.S.; Ayala, A. A novel role for programmed cell death receptor ligand-1 (PD-L1) in Sepsis-induced intestinal dysfunction. Mol. Med. 2016, 41, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.; Bai, J.; Chung, C.S.; Chen, Y.; Biron, B.M.; Ayala, A. Enhanced innate inflammation induced by anti-BTLA antibody in dual insult model of hemorrhagic shock/sepsis. Shock 2016, 45, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, Y.; McDonough, J.S.; Chang, K.C.; Ramachandra, M.; Sasikumar, P.G.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Anti-PD-L1 peptide improves survival in sepsis. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 208, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Mittal, R.; Klingensmith, N.J.; Burd, E.M.; Terhorst, C.; Martin, G.S.; Coopersmith, C.M.; Ford, M.L. Cutting Edge: 2B4-Mediated Coinhibition of CD4+ T Cells Underlies Mortality in Experimental Sepsis. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomer, J.S.; Shuherk-Shaffer, J.; Hotchkiss, R.S.; Green, J.M. A prospective analysis of lymphocyte phenotype and function over the course of acute sepsis. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubin, N.J.; Monaghan, S.F.; Heffernan, D.S.; Chung, C.S.; Ayala, A. B and T lymphocyte attenuator expression on CD4+ T-cells associates with sepsis and subsequent infections in ICU patients. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, G.; Xiao, Y.; Geng, S.; Kang, C.; Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, H.; et al. T cell Ig mucin-3 promotes homeostasis of sepsis by negatively regulating the TLR response. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Ai, J.; Hou, C.; Jia, Y.; Han, G.; et al. Plasma soluble Tim-3 emerges as an inhibitor in sepsis: Sepsis contrary to membrane Tim-3 on monocytes. Tissue Antigens 2015, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, A.; Sunden-Cullberg, J.; Magnuson, A.; Hultgren, O. Soluble B and T lymphocyte attenuator correlates to disease severity in sepsis and high levels are associated with an increased risk of mortality. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Han, X. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy of human cancer: Past, present, and future. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Kang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Hou, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, R.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, T.; Wen, Z.; et al. Blockade of the T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain protein 3 pathway exacerbates sepsis-induced immune deviation and immunosuppression. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 178, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, Y.; Unsinger, J.; Burnham, C.A.; Green, J.M.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Interleukin-7 and anti-programmed cell death 1 antibody have differing effects to reverse sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Shock 2015, 43, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.S.; Sansom, D.M. The emerging role of CTLA4 as a cell-extrinsic regulator of T cell responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krummel, M.F.; Allison, J.P. CD28 and CTLA-4 have opposing effects on the response of T cells to stimulation. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walunas, T.L.; Lenschow, D.J.; Bakker, C.Y.; Linsley, P.S.; Freeman, G.J.; Green, J.M.; Thompson, C.B.; Bluestone, J.A. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity 1994, 1, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Wolchok, J.D. Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M. Slow down and survive: Enigmatic immunoregulation by BTLA and HVEM. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepenies, B.; Pfeffer, K.; Hurchla, M.A.; Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M.; Oetzel, J.; Fleischer, B.; Jacobs, T. Ligation of B and T lymphocyte attenuator prevents the genesis of experimental cerebral malaria. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4093–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, A.; Wherry, E.J. Editorial: Therapeutic potential of targeting BTLA. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Anderson, A.C.; Schubart, A.; Xiong, H.; Imitola, J.; Khoury, S.J.; Zheng, X.X.; Strom, T.B.; Kuchroo, V.K. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leentjens, J.; Kox, M.; van der Hoeven, J.G.; Netea, M.G.; Pickkers, P. Immunotherapy for the adjunctive treatment of sepsis: From immunosuppression to immunostimulation. Time for a paradigm change? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshadri, A.; Brat, G.A.; Yorkgitis, B.K.; Keegan, J.; Dolan, J.; Salim, A.; Askari, R.; Lederer, J.A. Phenotyping the Immune Response to Trauma: A Multiparametric Systems Immunology Approach. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opal, S.M.; Fisher, C.J., Jr.; Dhainaut, J.F.; Vincent, J.L.; Brase, R.; Lowry, S.F.; Sadoff, J.C.; Slotman, G.J.; Levy, H.; Balk, R.A.; et al. Confirmatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. The Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Sepsis Investigator Group. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 25, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoory, B.; Carcillo, J.A.; Chatham, W.W.; Amdur, R.L.; Zhao, H.; Dinarello, C.A.; Cron, R.Q.; Opal, S.M. Interleukin-1 Receptor Blockade Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in Sepsis Patients With Features of Macrophage Activation Syndrome: Reanalysis of a Prior Phase III Trial. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, J.K.; Luan, L.; Hernandez, A.; Afzal, A.; Guo, Y.; Patil, N.K.; Fensterheim, B.; Sherwood, E.R. Role of G-CSF in monophosphoryl lipid A-mediated augmentation of neutrophil functions after burn injury. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, S.; Unsinger, J.; Davis, C.G.; Muenzer, J.T.; Ferguson, T.A.; Chang, K.; Osborne, D.F.; Clark, A.T.; Coopersmith, C.M.; McDunn, J.E.; et al. IL-15 prevents apoptosis, reverses innate and adaptive immune dysfunction, and improves survival in sepsis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsinger, J.; McGlynn, M.; Kasten, K.R.; Hoekzema, A.S.; Watanabe, E.; Muenzer, J.T.; McDonough, J.S.; Tschoep, J.; Ferguson, T.A.; McDunn, J.E.; et al. IL-7 promotes T cell viability, trafficking, and functionality and improves survival in sepsis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3768–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.; Bohannon, J.K.; Luan, L.; Fensterheim, B.A.; Guo, Y.; Patil, N.K.; McAdams, C.; Wang, J.; Sherwood, E.R. The role of MyD88- and TRIF-dependent signaling in monophosphoryl lipid A-induced expansion and recruitment of innate immunocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutros, C.; Tarhini, A.; Routier, E.; Lambotte, O.; Ladurie, F.L.; Carbonnel, F.; Izzeddine, H.; Marabelle, A.; Champiat, S.; Berdelou, A.; et al. Safety profiles of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 antibodies alone and in combination. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michot, J.M.; Bigenwald, C.; Champiat, S.; Collins, M.; Carbonnel, F.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Berdelou, A.; Varga, A.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 54, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, H.; Nose, M.; Hiai, H.; Minato, N.; Honjo, T. Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 1999, 11, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T. PD-1 and PD-1 ligands: From discovery to clinical application. Int. Immunol. 2007, 19, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaillon, J.M.; Eisen, D.; Annane, D. Is boosting the immune system in sepsis appropriate? Crit. Care 2014, 18, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reference | Sepsis Model | Alterations in Expression of Immune Checkpoints | Other Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al., 2009 [37] | Cecal Ligation and Puncture (CLP) | Increased PD-1 on peritoneal macrophages |
|
| Brahmamdam et al., 2010 [35] | CLP | Increased PD-1 on CD4+ and CD8+ splenic T cells |
|
| Zhang et al., 2010 [36] | CLP |
|
|
| Inoue et al., 2011 [48] | CLP | Increased CTLA-4 on splenic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells | Increased splenic T cell apoptosis and decreased survival rate |
| Shubin et al., 2012 [49] | CLP | Increased BTLA and HVEM on macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells and neutrophils in peritoneum |
|
| Zhu et al., 2013 [50] | CLP | Increased PD-L1 in liver tissue |
|
| Chang et al., 2013 [51] |
| Increased PD-1 on splenic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells |
|
| Hutchins et al., 2013 [52] | CLP |
|
|
| Huang et al., 2014 [38] | CLP | Increased PD-L1 on macrophages, monocytes, T and Natural Killer T (NKT) cells and neutrophils |
|
| Wang et al., 2016 [40] | CLP | Increased PD-1 on liver Kupffer cells |
|
| Patil et al., 2016 [41] | Burn wound sepsis (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
|
|
| Wu et al., 2016 [53] | CLP | Increased PD-L1 intestinal epithelial cells |
|
| Cheng et al., 2016 [54] | Two hit model (hemorrhage + CLP) | Increased BTLA on peritoneal macrophages and dendritic cells; and in tissues—ileum, kidney, lung, liver and spleen |
|
| Shindo et al., 2017 [55] | Two hit model (CLP + fungal sepsis) | Increased PD-1 on splenic CD4+, NKT and NK cells Increased PD-L1 on CD4+, NKT and Natural Killer (NK) cells | Significantly decreased survival rate |
| Chen et al., 2017 [56] | CLP | Increased 2B4 on splenic CD4+ and CD8+ Increased PD-1 and BTLA on splenic CD4+ and CD8+ |
|
| Reference | Sample Size | Alterations in Expression of Immune Checkpoints | Any Other Major Clinical Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guignant et al., 2011 [43] | 64 Patients, prospective study | Increased PD-1 and PD-L1 on CD4+ T cells, and higher PD-L1/PD-L2 on monocytes |
|
| Zhang et al., 2011 [44] | 19 Patients, prospective study | Increased PD-1 and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and higher PD-L1 on monocytes |
|
| Boomer et al., 2011 [23] | Postmortem study, 40 patients |
|
|
| Boomer et al., 2012 [57] | 24 Patients, prospective study |
| Impaired splenic T cell function (as measured by decreased IFN-γ production upon ex vivo stimulation of cells) |
| Shubin et al., 2013 [58] | 24 Patients, prospective study | Increased BTLA on circulating CD4+ T cells | Increased BTLA correlated with increased mortality |
| Yang et al., 2013 [59] | 26 Patients (12-sepsis,14-severe sepsis) | Increased TIM-3 mRNA in PBMC’s in sepsis patients as compared to severe sepsis patients | None |
| Chang et al., 2014 [45] | 43 Patients, Prospective study |
|
|
| Ren et al., 2015 [60] | Prospective study; 40-sepsis and42-severe sepsis patients18-septic shock pateints |
| Decreased soluble TIM-3 levels correlated with increased mortality |
| Patera et al., 2016 [24] | 17 Pateints, prospective study |
|
|
| Spec et al., 2016 [46] | 27 Candida fungal sepsis pateints, prospective study |
|
|
| Shao et al., 2016 [47] | 59 Patients, prospective study |
|
|
| Wu et al., 2016 [53] | Retrospective analysis | Increased PD-L1 on epithelial cells of colon | None |
| Lange et al., 2017 [61] | 101 Patients, prospective study | Increased plasma soluble BTLA levels (sBTLA) |
|
| Chen et al., 2017 [56] | 14 Patients, prospective study | Increased 2B4, PD-1 and CTLA-4 on CD4+ T cells | Decreased co-stimulatory ICOS and CD28 on CD4+ T cells |
| Reference | Sepsis Model | Antibody | Observed Therapeutic Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al., 2010 [36] | CLP | anti-PD-L1, 200 µg, i.p. route, 24 h before and 2 h after CLP |
|
| Brahmamdam et al., 2010 [35] | CLP | anti-PD-1, 200 µg, i.v. route, 24 h after CLP |
|
| Inoue et al., 2011 [48] | CLP | anti-CTLA-4, 50 µg, i.p. route, 6 and 24 h after CLP; and 33 µg, i.p. after fungal sepsis |
|
| Zhu et al., 2013 [50] | CLP | anti-PD-L1, 50 µg, i.p. route, 1 h after CLP | Attenuation of liver injury (improved histology, and decreased ALT, AST) |
| Chang et al., 2013 [51] | Candida fungal sepsis, and two hit model (CLP + fungal sepsis) |
|
|
| Yang et al., 2013 [59] | CLP | anti-TIM-3, 200 µg, i.p. route, 1 day before and 1, 3, 5 and 7 days after CLP |
|
| Zhao et al., 2014 [63] | CLP | sTIM3-Ig to block TIM-3 signaling, 200 µg, i.p. route, 12 h before, and 48 and 96 h after CLP |
|
| Shindo et al., 2015 [64] | Two hit model (CLP + fungal sepsis) | anti-PD-1, 200 µg, i.p. route, on day 4 and 8 post CLP |
|
| Cheng et al., 2016 [54] | Two hit model (hemorrhage + CLP) | anti-BTLA-4, 25 µg/g administered just after CLP |
|
| Chen et al., 2017 [56] | CLP | anti-2B4, 250 µg, i.p. route, on days—0, 2, 4 and 6, after CLP |
|
| Shindo et al., 2017 [55] | Two hit model (CLP + fungal sepsis) | anti-PD-L1 peptide (compound 8), 3 mg/kg, s.c route, three times daily from days 5 to 13 after CLP | Significantly improved survival |
| Reference | Sepsis Model | Animal Model | Observed Therapeutic Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al., 2009 [37] | CLP | PD-1 knockout |
|
| Shubin et al., 2012 [49] | CLP | BTLA knockout |
|
| Hutchins et al., 2013 [52] | CLP | PD-L1 knockout |
|
| Huang et al., 2014 [38] | CLP | PD-1 knockout |
|
| Zhao et al., 2014 [63] | CLP | TIM-3 overexpression |
|
| Wang et al., 2016 [40] | CLP | PD-1 knockout |
|
| Young et al., 2016 [42] | Neonatal sepsis model using cecal slurry | PD-1 knockout |
|
| Wu et al., 2016 [53] | CLP | PD-L1 knockout |
|
| Reference | Patient Population | Antibody Used | Observed Therapeutic Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al., 2011 [44] | Prospective clinical study with 19 septic patients | anti-PD-L1 antibody |
|
| Chang et al., 2014 [45] | Prospective study with 43 septic patients | anti-PD-L1 antibody and anti-PD-1 antibody |
|
| Patera et al., 2013 [24] | Prospective study with 17 septic patients | anti-PD-L1 antibody and anti-PD-1 antibody |
|
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, N.K.; Guo, Y.; Luan, L.; Sherwood, E.R. Targeting Immune Cell Checkpoints during Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2413. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijms18112413
Patil NK, Guo Y, Luan L, Sherwood ER. Targeting Immune Cell Checkpoints during Sepsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2413. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijms18112413
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Naeem K., Yin Guo, Liming Luan, and Edward R. Sherwood. 2017. "Targeting Immune Cell Checkpoints during Sepsis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2413. https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/ijms18112413





