1. Introduction
Embedded systems have become omnipresent, with the number of just mobile devices now nearly reaching the world population. Embedded systems implementations embrace, for example, home applications, pacemakers, cell phones, satellites, energy generation and distribution, industrial automation, and many other kinds of systems. The process of managing their energy consumption has become extremely challenging. Embedded systems extremely affect the layout and development restrictions of their respective surrounding systems and inversely. Some embedded systems communicate with the physical surrounding and must ensure that a certain action is carried out successfully and that it is terminated within a determined time frame. Some eminent examples of these devices are airbags in cars, medical pacemakers, and autopilots in airplanes, and they are called real-time embedded systems.
Multi-core processors are now the current architecture for recent real-time embedded systems. To achieve both efficiency and speed, CPU architectures have evolved multi-core processor units in which two or more processors have been used to perform a task. Multi-core technology provided better response times when running massive applications, improved power management, and provided faster execution times. Multi-core processors are specially designed to run tasks in parallel. Parallelism can be at two levels in multi-core processors—one at the hardware level and another one at the software level. The proposed software has been designed to take benefit of available parallelism.
Now, several multi-core processors are used with a dynamic voltage/frequency scaling (DVFS) mechanism to save extra energy, where the voltage or frequency for every core can be set by the CPU. As a consequence, each core in the processor may have a different processing power and energy exhaustion. Numerous strategies were suggested, recently, for energy-aware real-time task scheduling on multi-core processors that enable DVFS mechanisms [
1,
2].
Despite dependent tasks being widespread in many real-life applications, there are few studies that have been carried out on them. When considering dependent real-time tasks, shared resources must be accessed through a mutually exclusive approach that guarantees that a task must accomplish its critical section execution before the next task tries to access the same resource. The allocating of tasks and the scheduling in multi-core embedded real-time systems have become vital problems in curtailment of energy consumption while still satisfying the needed performance. There are several scheduling algorithms suggested to completely utilize the computing resources from multiple cores to attain high efficiency. Traditionally, multi-core real-time task scheduling can be divided into global scheduling, Global Earliest-Deadline-First (G-EDF), and partitioned scheduling, Partitioned-EDF (P-EDF) [
3,
4,
5]. Tasks are scheduled by one scheduler in the global scheme, and every task is permitted to move from one processor to another during the execution. The jobs are arranged in a single global queue and an individual job of a task can be preempted on a processor and continued on a different processor. Conversely, within the partitioning scheme, task migration is prohibited and all the task instances are performed on the same processor. Every processor will have a different queue prepared to schedule task jobs. Therefore, run-time performance is enhanced and tasks can only intervene on the local processor.
Partitioned scheduling protocols are widely used and extensively endorsed in their performance and usability through commercial real-time operating systems [
6]. Besides, excellently studied single-processor scheduling and synchronization mechanisms could be adapted for multiprocessors with little adjustment (or without alters). Nonetheless, partitioning tasks to the processors is believed to be a bin-packing problem that is an NP-hard problem in the strong sense; finding the optimal mechanism in polynomial time is, therefore, not likely in the generic state. So, scheduling protocols should be configured with suitable partitioning algorithms to utilize the efficiency provided by multi-cores. Heuristic techniques and adequate practicability studies have been developed to discover a near-optimal partitioning for bin-packing algorithms [
3,
7]. Nonetheless, scheduling protocols and existing multiprocessors (multi-cores) partitioning algorithms primarily presume independent tasks while tasks typically share resources in real applications. The classic bin-packing algorithm does not consider the blocking time, and therefore, the tasks can suffer much blocking. When tasks access shared resources such as Input/Output ports and shared memories, locking protocols are used to avoid uncontrolled priority inversions [
8,
9] and to preserve data coherence. To comprehend the full capabilities of embedded multi-core systems, resource-aware partitioning techniques are needed.
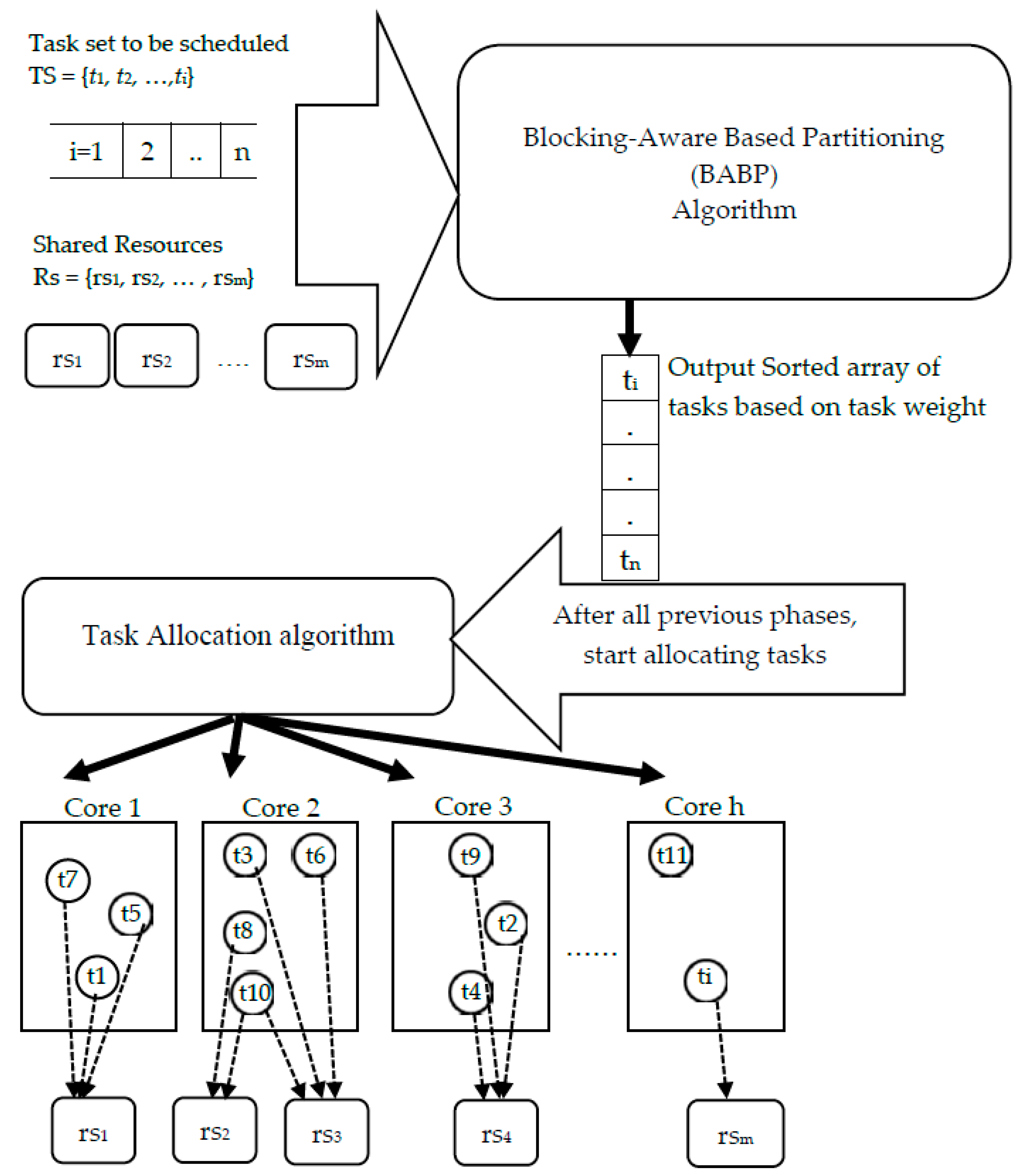
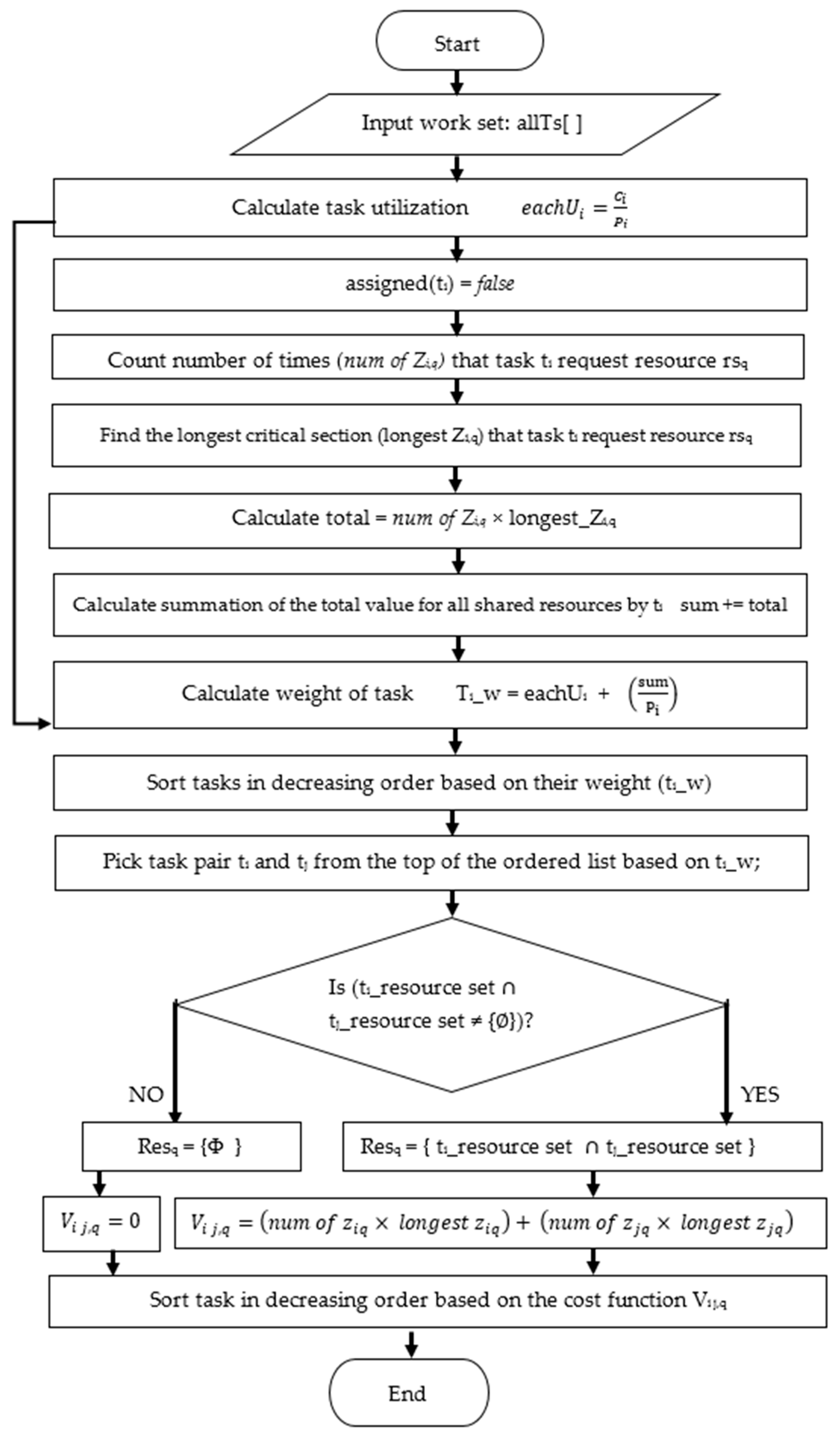
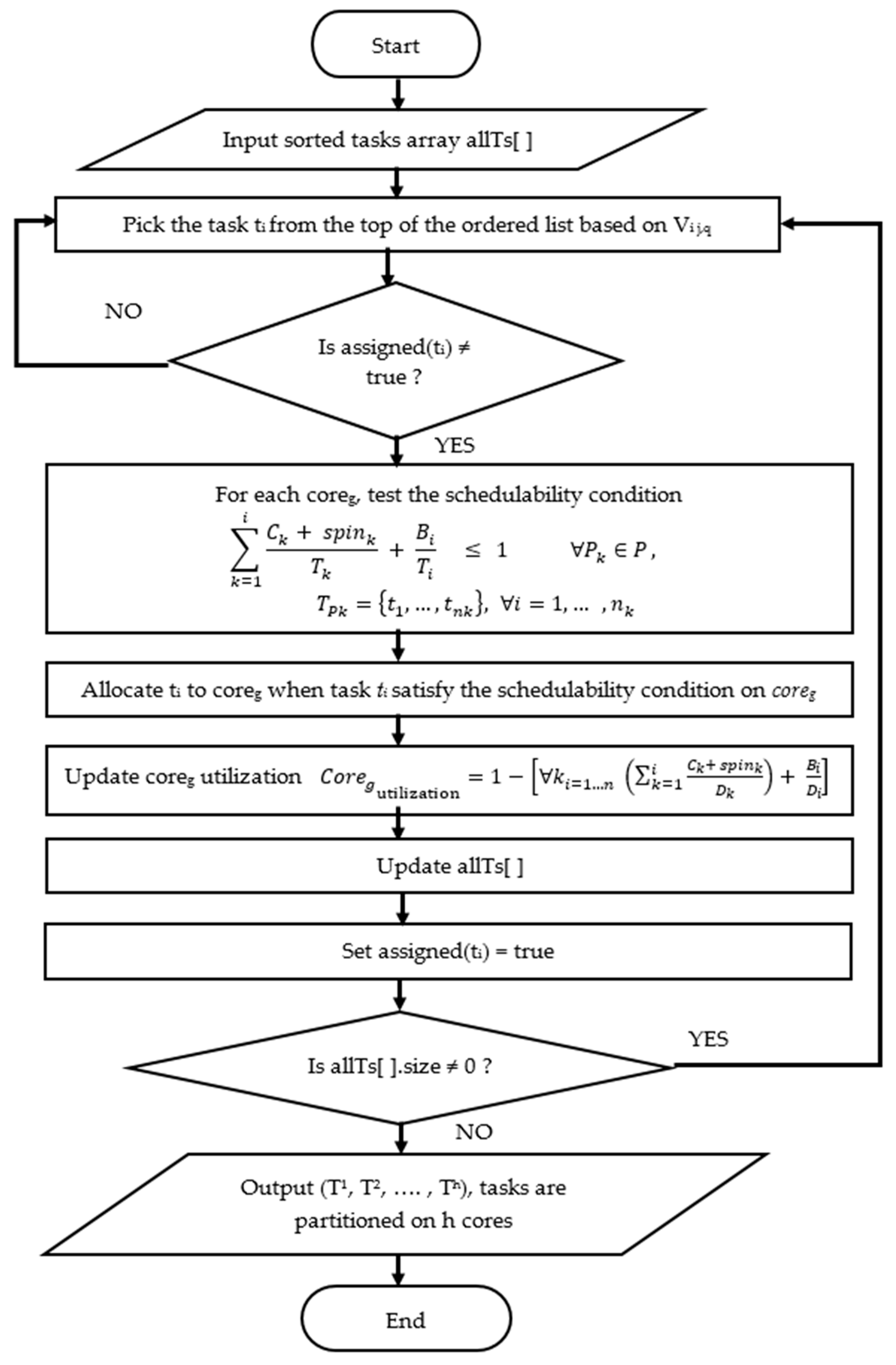
This study presents a heuristic partitioning algorithm, the blocking-aware-based partitioning (BABP) algorithm, to assign tasks that may access the same shared resources to the same core (beginning with the task that has the longest blocking time). Therefore, the BABP algorithm makes the best of the available parallelism in these multi-core systems, as much as possible, because it guarantees that the parallel tasks—not having shared resources—are dispatched to different cores so as to execute then in parallel.
The proposed algorithm partitions a collection of real-time tasks on a non-ideal DVS processor of a multi-core architecture. According to DVFS methods, the BABP uses a Two-Speed Strategy (TSS)-based approach known as the Dual-Speed (DS) algorithm [
10], which is initially used to carry out tasks at a low level of speed and then shifts to a high-level speed immediately when the tasks are blocked.
Partitioned Earliest-Deadline-First (P-EDF) [
3] is used as the dynamic priority task-scheduling strategy for each processing core of a multicore system. Upon considering dependent real-time tasks, the BABP algorithm uses the Multiprocessor Stack Resource Policy (MSRP) [
11] to synchronize the access of tasks to shared resources. By using MSRP, a limited blocking time is ensured for tasks when accessing the global resources, and local resources are synchronized using SRP. When using the P-EDF algorithm to schedule tasks [
3], the DS algorithm computes the low level of speed and the high level of speed based on the EDF-sufficient condition of schedulability. Therefore, while energy consumption is decreased, the timing restrictions of tasks can be guaranteed. Particularly, when tasks arrive, the DS algorithm allocates the low-speed level for executing them, while at the moment the tasks are blocked, the processor speed will shift to the high-speed level. With the DS algorithm, a high-speed interval begins when the blocking starts and terminates at the blocking task deadline. The capabilities of the proposed approach were appraised by using a simulation platform named the multi-core real-time scheduling simulator (MCRTsim) [
12].
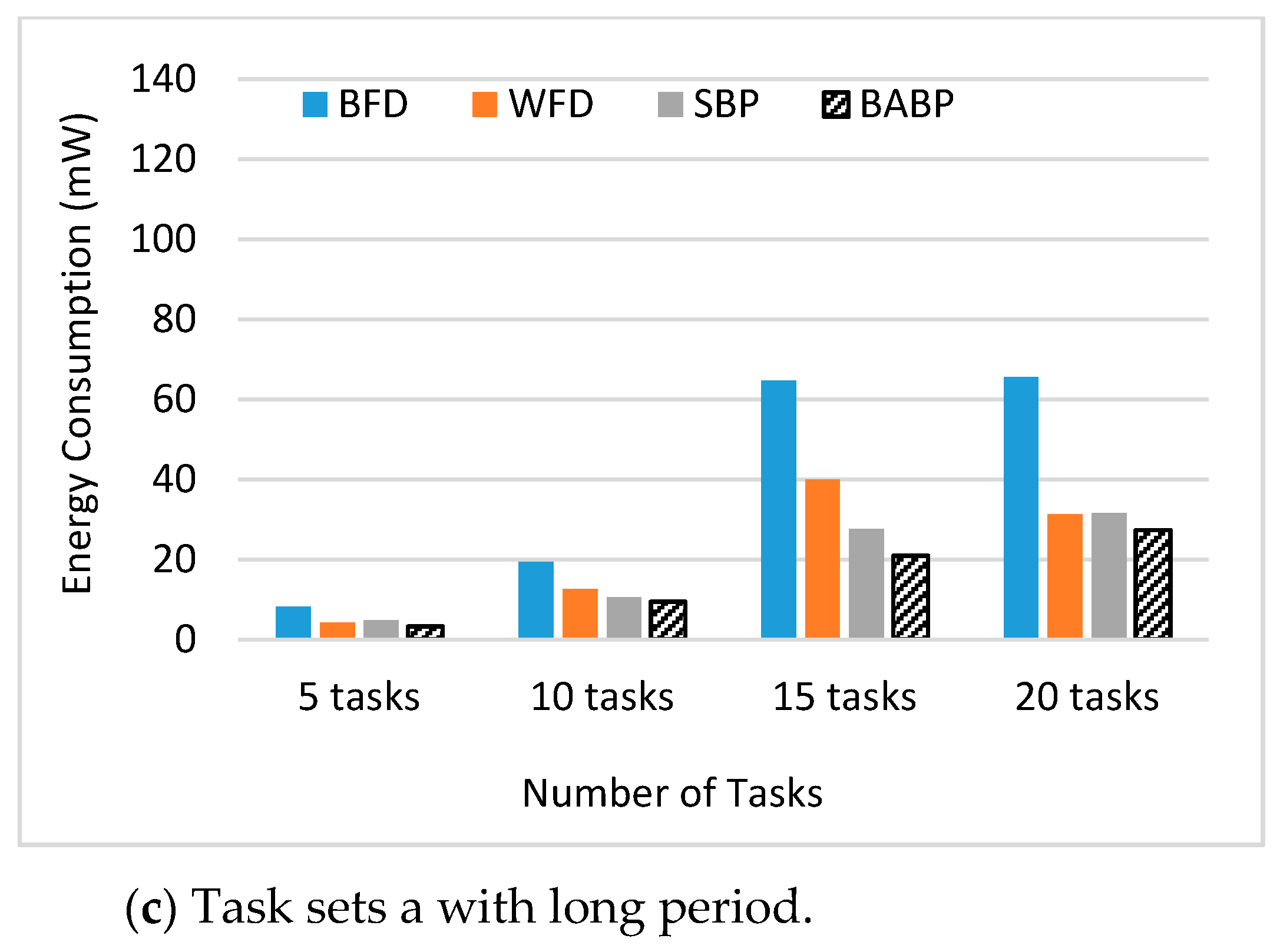
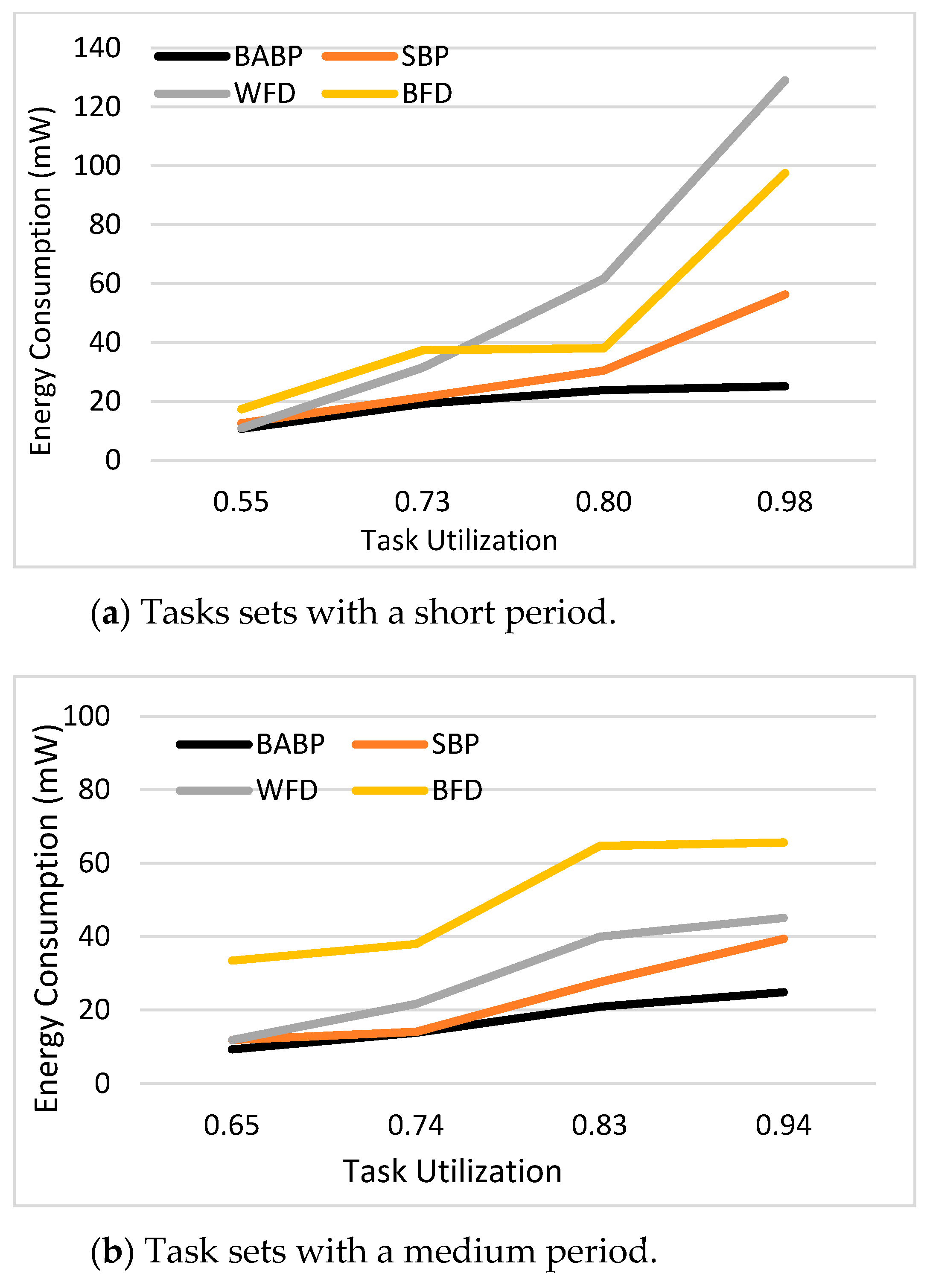
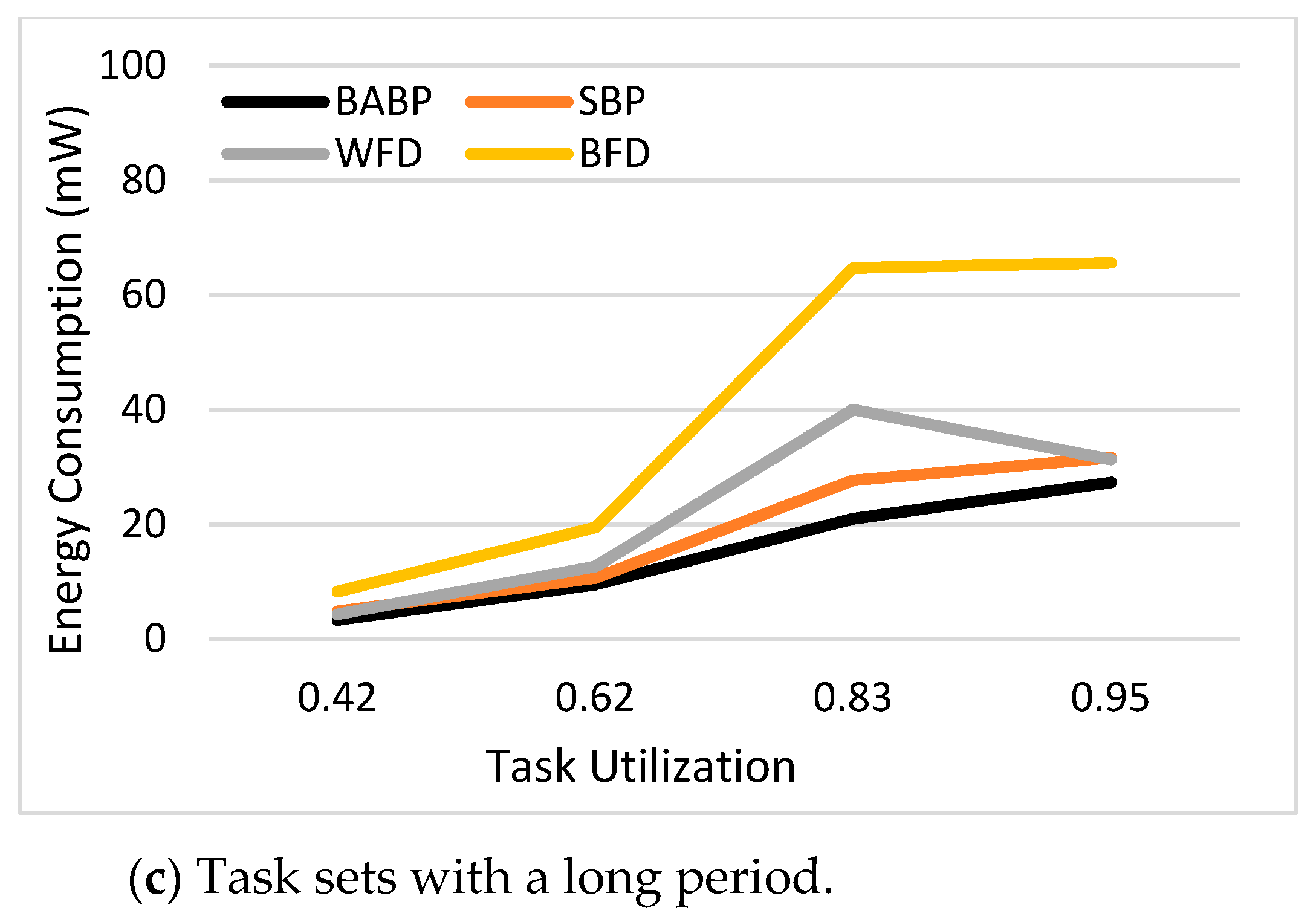
The key contributions of this study are: (1) A BABP heuristic algorithm is proposed to effectively exploit the available parallelism, balance the workload in these multi-core systems, and assign tasks which can run in parallel to different cores as much as possible. For example, as shown in
Figure 1, the tasks τ1, τ5, and τ7 can be dispatched to one core and the others to another core. (2) The suggested algorithm is implemented with a simulation platform called MCRTsim. (3) An assessment of the suggested algorithm in conjunction with the blocking-agnostic bin-backing partitioning algorithm and the (SBP) algorithm, as a reference, is done. Within the framework of this study, the blocking-agnostic algorithm points to a bin-packing algorithm that does not include blocking parameters to improve the efficiency of partitioning while the schedulability check comprises blocking times. In particular, this research presumes that tasks are periodic, preemptive (only of non-critical sections), and dependent because of the synchronous access to shared resources. By using the BABP algorithm as a partitioning strategy and P-EDF as a scheduling algorithm, the simulation results indicate that the BABP algorithm achieves more energy savings than other partitioning techniques.
The remainder of this paper is arranged as set out below.
Section 2 sums up the previous research on real-time systems scheduling and synchronization with a uniprocessor or a multi-core processor.
Section 3 depicts the system model and problem formulation.
Section 4 discusses the proposed BABP algorithm and its implementation, with the schedulability analysis.
Section 5 reports on the simulation assessment and outcomes analysis. The conclusion is reported in
Section 6.
2. Related Work
Many studies have focused, within recent years, on energy-aware scheduling of embedded systems in real time. In uniprocessor environments, there are several research papers in the domain of energy-aware scheduling of independent real-time tasks, and an extensive survey can be found in [
1]. Very little research has discussed the problem of dependent real-time tasks within the context of task synchronization [
13,
14]. The DVFS mechanism that works to slow the processing speed is a widely used energy-saving technique due to the convexity of the power consumption function [
15,
16,
17].
The interest in multiprocessor techniques has increased as a result of the growth in multi-core architectures. The article [
18] tackled the problem of energy-aware static partitioning of periodic real-time tasks on asymmetric multiprocessor (multi-core) embedded systems. It formulated the problem according to the platform-supported DVFS model and outlined optimal methods of reference partitioning for each case of the DVFS model.
The authors of [
19], from the perspective of allocating workloads to cores, suggested a method for energy administration of applications in a multi-core partitioned architecture. They introduced the Energy Efficient Allocator (EEA) algorithm as an allocation method for assigning partitions to cores founded on bin-packing algorithms that consider the various frequencies at which a core can work. They also presented a variety of solutions to the problem of energy minimization. Every solution will provide an appropriate allocation of workload to cores with various levels of energy and system utilization. The EEA algorithm picks out the type of allocator (First Fit Decreasing Utilization (FFDU) WFDU, and BFDU) and the criteria (decreasing utilization (DU), increasing utilization (IU), or randomly (R)) under which partitions are chosen to minimize their frequency.
For hard real-time systems, the authors of the article [
20] presented a study of energy-aware multi-core scheduling algorithms. They summed up several algorithms listed in the literature and grouped them by both homogeneous and heterogeneous multi-core processors, depending on Partitioned, Semi-Partitioned, and Global scheduling strategies. An Inter-task Affinity-aware Task Allocation (IATA) algorithm was proposed in [
21] to nullify overheads in the WCET due to cache evictions. IATA collects the tasks considering their constraints, dependencies, preferences (shared resources, inter-core communication, and cache evictions) and assigns these groups to multiple cores to decrease the additive overheads in WCET.
A static mixed task scheduling (SMTS) algorithm has been proposed in [
22] to solve the problem of scheduling mixed tasks that comprise of n hard real-time periodic tasks with shared resources and soft aperiodic tasks. They take into account two opposing objectives: decreasing the energy consumption and reducing aperiodic task response time. The SMTS algorithm schedules aperiodic tasks with the maximum processor speed and periodic tasks with the best speed. They have also introduced a dynamic mixed task scheduling algorithm (DMTS) capable of reclaiming dynamic slack time produced from periodic tasks and the constant bandwidth server to minimize energy consumption. Their results display that the DMTS technique outperforms the SMTS algorithm and the baseline algorithm, where DMTS decreases an average of 7.18% of energy consumption and 53.66% of response time compared with the other algorithms.
The authors of [
23] suggested research on the maximum gains for volunteer computing platforms (VCPs). VCPs can be considered asymmetric multiprocessing systems (AMSs). The authors needed to pick tasks from users and assign the tasks to appropriate workers to solve the maximum benefit problem. They proposed a list-based task assignment (LTA) strategy and showed that the LTA strategy could complete the task with a deadline restriction as soon as possible. Then, based on the LTA technique, they proposed a maximum benefit scheduling (MBS) algorithm, a new task assignment algorithm aimed at optimizing VCP gains.
The authors of [
24] implemented a comparison of 11 heuristics for mapping independent tasks on heterogeneous distributed computing systems. It has been shown that the relatively simple Min-min heuristic achieves minimum energy in comparison with the other strategies for the cases studied. The article [
25] showed that the proposed Resource-Oriented Partitioned (ROP) scheduling with a distributed resource sharing strategy would achieve a significant speed-up factor guarantee. The authors of [
26] aimed to reduce energy consumption under real-time and reliability constraints. They suggested that a formulation of an Integer Non-Linear Programming (INLP) performs task mapping by jointly addressing task allocation, assignment of task frequency, and duplication of tasks. The original INLP problem was safely converted to an analogous Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) problem to provide an optimal solution. Appointing a real-time task group to the multi-core platform is a bin-packing problem that is understood to be an NP-hard problem in the powerful sense; therefore, finding the best solution in polynomial time is not pragmatic in the generic state. Given the unfavorable nature of the problem, numerous heuristics and their performance analyses were subject to various research papers, such as the First-Fit, Best-Fit, Next-Fit, and Worst-Fit methods [
27,
28]. A comparison was made for homogeneous multi-core systems and periodic independent tasks between these four well-known heuristics behaviors [
29].
Indeed, when the Earliest-Deadline-First scheduling technique was used, the problem had a near resemblance to bin-packing [
30,
31], and the results/heuristics that can be acquired in this vastly studied field show insights into partitioning-based scheduling. The suggested algorithm in [
32] uses the Worst-First strategy to partition the collection of frame-based tasks (with the same period and deadline) and then scales the speed in accordance with the task characteristics in a certain instant. Although the method is represented by a rational approximation factor for optimum scheduling, some unrealistic assumptions were made by the author such as a continuous and infinitive frequency range (s
[0, ∞]) and negligible in idle-state consumption. The problem of appointing a series of periodic real-time tasks in multi-core systems characterized by a single voltage island (where all processors share the same voltage and frequency) was considered in [
33]. First, they examined the approximation upper bound for the classical Worst-First heuristic, and then they introduced their technique that overcomes many state-of-the-art limitations.
Resource control policies for single-processor systems are well recognized. The Priority Ceiling Protocol (PCP) [
34], in particular, is one of the most attractive suggested protocols for synchronization of resource accesses. It avoids both deadlock and transitive blocking. Stack Resource Policy (SRP) [
35,
36] was defined as a refinement to PCP for EDF systems that strictly binds priority inversion and permits simple schedulability tests. Each task under SRP is assigned a preemption level that reflects the relative deadlines of the tasks. The shorter the deadline, the higher the preemption level. The authors of [
37,
38] subsequently developed multiprocessor and distributed versions of PCP. Hence, the protocol was targeted at distributed shared memory systems. There have been some versions of the Multiprocessor Priority Ceiling Protocol (MPCP) that extend PCP to multiprocessor systems and reduce the remote blocking. The authors of [
39] extend the research for dynamic PCP. A dynamic priority multiprocessor version of the Priority Ceiling Protocol based upon EDF scheduling (MDPCP) was introduced in [
40]. The authors of [
11,
41] extend SRP to the Multiprocessor Stack Resource Policy (MSRP), the first spin-lock protocol in multiprocessor real-time systems.
Partitioning-based real-time scheduling of multiprocessors finds feasibility as the primary aim. The problem occurs in two different patterns: to decrease the number of processors necessary to assure the feasibility of the task set, or, instead, to find sufficient schedulability (usually, utilization) limits given a fixed multiprocessor platform. In this research, the researchers also take into consideration the energy factor to this problem. Because generic bin-packing heuristics do not regard the blocking time caused by resource requests, they may not be efficient for task sets that have shared resources. To regard this extra blocking, the two well-known multi-core synchronization protocols, MPCP and MSRP, were presented. A partitioning heuristic adapted to the MPCP was introduced [
6], a semaphore-based multiprocessor real-time locking protocol. The MSRP, spin-lock protocol [
11], was proposed where tasks are busy waiting for shared resources once blocked.
The Similarity-Based Partitioning (SBP) algorithm [
42] was presented. It is another partitioning heuristic for MSRP using the same methodology, which uses modern cost heuristics to more precisely classify group splits with low energy consumption. It appoints the tasks which can access the same collection of shared resources to the same core to avoid a number of blockings.
3. Research Model and Problem Formulation
3.1. Multi-Core DVFS Processor and Energy Model
Most recent processors allow variable levels for voltage and frequency, and this processor can perform dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) and its speed is proportional to the supply voltage. In the literature, DVS processors are classified as ideal and non-ideal. The ideal DVS processor will run at any speed, ranging from the lowest to the highest possible speed, whereas a non-ideal DVS processor possesses only separate speeds. Recently, multiple DVS processors are non-ideal, whereas ideal DVS processors are for theoretical research purposes only. This study regards a multi-core platform P consisting of a set of z cores, i.e., P = {core1, core2, …, corez}, and it supports h discrete speeds S = {s1, s2, …, sh}, where s1 < s2 < … < sh. The researchers presume that the platform P supports per-core DVFS capabilities where cores may run at different speeds at the run time.
The processor power model [
43] used in this study has been greatly used in the literature [
13,
44]. The researchers suppose a DVFS-enabled multi-core processor is capable of operating at a variety of separate voltage levels. Commonly, the power exhaustion of a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) system is known as dynamic and static power consumption [
14]. The dynamic power dominates the total energy consumed by the processor core and the dynamic power dissipation is the most costly and time-consuming part. Therefore, this study is aiming only to detract dynamic power consumption during this study and the static power consumption is neglected [
26].
The static power consumption is foremost caused by leakage currents (
Ileak), and the static (leakage) power (
Pleak) will be defined by:
The dynamic power consumption will be displayed as a convex function of the processor speed. The dynamic power consumption for CMOS circuits [
45] depends on the processor operating voltage and frequency at speed
S and it can be presented by:
where
Ceff is the effective switching capacitance,
Vdd is the supply voltage, and
f is the clock frequency of the processor (speed) that will be declared as:
where
k is a constant,
Vdd is the supply voltage, and the threshold voltage
Vth. To express the power consumption of a specified core
i of processor P, the researchers use a function
PCi(
s) of the selected speed
s. If a task keeps a processor throughout the implementation duration of [
t1,
t2], then the energy exhausted by the processor throughout this period is given by:
where
si(
t) is the speed of the processor at time t.
3.2. Task and Resource Models
This study focuses on real-time systems consisting of a periodic task set with n tasks, TS = {t1, t2, …, tn}. Each task ti is presented by a tuple (Ai, Pi, Di, Ci, and Zi), where:
The arrival time (Ai): the timing when the task is first issued.
The period (Pi): the fixed time duration among jobs.
The relative deadline (Di): the maximum appropriate delay for task processing.
The computation time (Ci): the worst-case execution time (WCET).
The list of critical sections (Zi) of task i.
This research regards well-formed tasks that meet the requirement 0 ≤ Ci ≤ Di ≤ Ti. Each task ti is a prototype of its instances and every instance can reach for every period Ti regularly. Let ti,j represent the jth instance of task ti. Within this research, researchers are concerned about scheduling and synchronizing the dependent real-time tasks. The researchers presume these tasks are periodic, dependent (because of their access to shared resources), and preemptible (only in non-critical sections). Furthermore, they presume that a set of m shared resources (software objects, e.g., data structure, files, data objects, or shared variables) RS = {rs1, rs2, …, rsm} may be accessed in a mutually exclusive method (simultaneous access is not allowable).
Researchers presume that a semaphore provides access control of shared resources to ensure mutual exclusion amongst competitive tasks. Task requests for shared resource access will happen at any moment during its implementation; a portion of code accessing a shared resource is classified as a critical section under mutual exclusion restrictions. A list that describes the critical sections of a task ti is Zi = < zi,1, zi,2, …, zi,n>, where zi,j is the jth critical section of ti. This study presumes that the shared resource requests are not nested. Locks are freed in the opposite order in which they were acquired. A task ti may request a shared resource rs ∈ RS several times during its execution but just one job at a time will access a shared resource, i.e., binary semaphore. Real-time locking protocols assist to ensure mutual exclusion. For instance, if a task ti asks for a shared resource rs already locked by another task, it must wait until rs is available. Besides, each shared resource rs can have a ceiling priority Ω, indicating the highest possible priority that it can have. Researchers declare ui as the task utilization and it can be described by . The system utilization Utot is equal to and the periodic task set is scheduled by the P-EDF policy. According to P-EDF policy, priorities are appointed dynamically and are inversely proportional to the absolute deadlines of the active tasks, and the higher priority tasks are executed first.
3.3. Problem Description
Consider a workload set
TS of
n dependent periodic real-time tasks (dependency because of simultaneous access to shared resources) and a set
RS of m shared resources. The idea is how to optimally schedule the
TS and synchronize their access of
RS on a multi-core processor
P that supports the DVFS technique and allows
h discrete speeds. The research aimed to find the optimum method of task-to-processor assignment (task partitioning) to minimize the total energy exhaustion of a real-time system. In this case, the tasks allocated to each processor can be feasibly scheduled, and the overall energy consumption of
P is minimized (among all feasible task allocations). The problem of optimizing dynamic energy consumption using DVFS on a multi-core platform is an optimization problem, that is, to find feasible scheduling with minimal energy consumption [
15,
17]. Notice that scheduling is considered feasible if all scheduled task instances can be finished within their deadlines at the latest [
33].
4. Task Scheduling and Synchronization in a Multi-Core Platform
In particular, this study uses P-EDF [
3] as the scheduling algorithm and multiprocessor stack resource policy (MSRP) [
11] as the synchronization protocol. By using the P-EDF scheduling algorithm, the priority-driven scheduling algorithm, tasks are partitioned offline at first among cores and are then scheduled on the allocated cores. Under MSRP, the resources are divided into two groups: local and global. Local resources are accessed only by tasks that execute on the same processor. Global resources are those which can be accessed by tasks running on different processors. There are two types of blocking: local blocking, which occurs when a task running on one core is blocked by another task running on the same core, and remote blocking, which occurs when this task is blocked by a task that is running on another core. Unlike SRP, global resources have different ceilings—one for each processor. Moreover, every processor has its own system ceiling. On processor P, tasks can only use global resources at the processor ceiling priority, that is, the highest preemption level of all the tasks on processor P. Global resources are shared across processors in a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) manner. To acquire a global resource, a task must be running at the processor ceiling which makes it non-preemptive. Whenever a task tries to access a shared resource that is already locked in the system by another task, the task performs a busy wait (called a spin-lock), and the task resumes when the shared resource is unlocked from the previously locked task.
This study use MSRP to ensure a mutual exclusion among the competing tasks from multiple cores and to maintain the data consistency of shared resources. Under the MSRP, every task has a fixed value, named preemption level
of task
ti, to estimate the possible blocking in the presence of dynamic priority scheduling. Tasks with a shorter deadline will have a higher preemption level so the levels of preemption will represent the relative deadlines of the tasks. Resources are given a ceiling value during the run-time according to the maximum preemption level of the tasks accessing the resource. Whenever a task is issued, it can only preempt the currently performed task if its absolute deadline is lesser and its degree of preemption is greater than the highest ceiling of currently locked resources. The effect of this protocol is nearly identical to PCP; tasks experience only one blocking, deadlocks are avoided, and a simple formula can be obtained to compute the blocking time. The MSRP lets tasks use the local critical resources under the SRP policy. As a result, SRP saves redundant context switches by blocking earlier [
11].
Schedulability Analysis of the MSRP
For a multi-core platform, researchers propose a partitioning algorithm for appointing tasks onto processors; then, the tasks will be scheduled by EDF as a scheduling algorithm and will use MSRP as a synchronization algorithm. When tasks are scheduled to be carried out on a uniprocessor [
37], a group of
n real-time tasks are schedulable by EDF and SRP if:
where
Bi is the worst-case blocking time of
ti. Tasks can access resources in a mutually exclusive technique, and therefore, the overheads due to blocking time must be considered whilst checking the schedulability of tasks assigned to the core. Under MSRP, if a task
ti tries to request a global resource
rs, it becomes non-preemptive. If the resource
rs is free. it locks the resource, but if
rs is already locked by another task
tj running on a different processor,
ti performs busy wait (spinning state). The worst-case blocking time
can be calculated by considering busy wait time as follows:
where
spin(Pc, rs) is the upper bound of busy wait time that any task can wait on processor
Pc to access a global resource
rs, which can be expressed as follows:
where
refers to the length of any critical section of task
tj requesting to access the resource rs.
is considered to be the worst-case blocking time of task
ti when accessing a local resource. By using the synchronization protocol MSRP,
can be calculated as follows:
where
is preemption level of task
, and ceil(rs) is the ceiling of local resource
rs which is the highest preemption level of all the tasks that may access
rs in core
Pc.
The worst-case blocking time
Bi of task
ti executing on processor
Pc is calculated as follows:
Based on the schedulability analysis of multiprocessor environments [
11], a set of n real-time tasks on processor
Pk, ordered by decreasing preemption level, is schedulable under EDF and MSRP if:
The proposed algorithm aims to reduce the overall blocking overhead in the system that may excess the schedulability of a task set.