Journal Description
Axioms
Axioms
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of mathematics, mathematical logic and mathematical physics, published monthly online by MDPI. The European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology (EUSFLAT), International Fuzzy Systems Association (IFSA) and Union of Slovak Mathematicians and Physicists (JSMF) are affiliated with Axioms and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High visibility: indexed within SCIE (Web of Science), dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Mathematics, Applied)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Logics.
Impact Factor:
2.0 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
Ideals and Filters on Neutrosophic Topologies Generated by Neutrosophic Relations
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 292; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050292 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Recently, Milles and Hammami presented and studied the concept of a neutrosophic topology generated by a neutrosophic relation. As a continuation in the same direction, this paper studies the concepts of neutrosophic ideals and neutrosophic filters on that topology. More precisely, we offer
[...] Read more.
Recently, Milles and Hammami presented and studied the concept of a neutrosophic topology generated by a neutrosophic relation. As a continuation in the same direction, this paper studies the concepts of neutrosophic ideals and neutrosophic filters on that topology. More precisely, we offer the lattice structure of neutrosophic open sets of a neutrosophic topology generated via a neutrosophic relation and examine its different characteristics. Furthermore, we enlarge to this lattice structure the notions of ideals (respectively, filters) and characterize them with regard to the lattice operations. We end this work by studying the prime neutrosophic ideal and prime neutrosophic filter as interesting types of neutrosophic ideals and neutrosophic filters.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Classical and Applied Mathematics)
Open AccessArticle
Hyperholomorphicity by Proposing the Corresponding Cauchy–Riemann Equation in the Extended Quaternion Field
by
Ji-Eun Kim
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 291; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050291 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
In algebra, the sedenions, an extension of the octonion system, form a 16-dimensional noncommutative and nonassociative algebra over the real numbers. It can be expressed as two octonions, and a function and differential operator can be defined to treat the sedenion, expressed as
[...] Read more.
In algebra, the sedenions, an extension of the octonion system, form a 16-dimensional noncommutative and nonassociative algebra over the real numbers. It can be expressed as two octonions, and a function and differential operator can be defined to treat the sedenion, expressed as two octonions, as a variable. By configuring elements using the structure of complex numbers, the characteristics of octonions, the stage before expansion, can be utilized. The basis of a sedenion can be simplified and used for calculations. We propose a corresponding Cauchy–Riemann equation by defining a regular function for two octonions with a complex structure. Based on this, the integration theorem of regular functions with a sedenion of the complex structure is given. The relationship between regular functions and holomorphy is presented, presenting the basis of function theory for a sedenion of the complex structure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Functional Analysis and Its Applications)
Open AccessArticle
Full Classification of Finite Singleton Local Rings
by
Sami Alabiad and Yousef Alkhamees
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 290; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050290 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
The main objective of this article is to classify all finite singleton local rings, which are associative rings characterized by a unique maximal ideal and a distinguished basis consisting of a single element. These rings are associated with four positive integer invariants
[...] Read more.
The main objective of this article is to classify all finite singleton local rings, which are associative rings characterized by a unique maximal ideal and a distinguished basis consisting of a single element. These rings are associated with four positive integer invariants
Open AccessArticle
Photon-Added Deformed Peremolov Coherent States and Quantum Entanglement
by
Kamal Berrada
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 289; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050289 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
In the present article, we build the excitedcoherent states associated with deformed
In the present article, we build the excitedcoherent states associated with deformed
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Advancement in Mathematical and Quantum Physics)
►▼
Show Figures
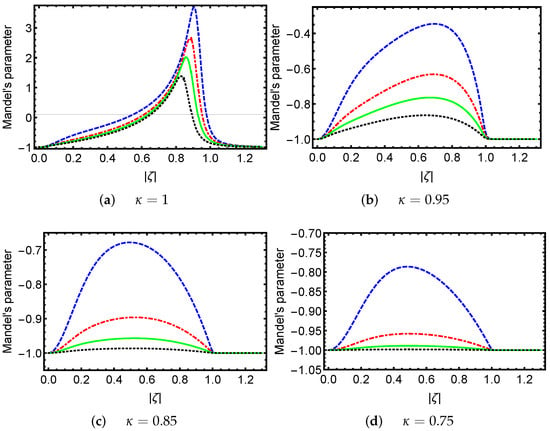
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sparse Signal Recovery via Rescaled Matching Pursuit
by
Wan Li and Peixin Ye
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 288; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050288 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
We propose the Rescaled Matching Pursuit (RMP) algorithm to recover sparse signals in high-dimensional Euclidean spaces. The RMP algorithm has less computational complexity than other greedy-type algorithms, such as Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP). We show that if the restricted isometry property is satisfied,
[...] Read more.
We propose the Rescaled Matching Pursuit (RMP) algorithm to recover sparse signals in high-dimensional Euclidean spaces. The RMP algorithm has less computational complexity than other greedy-type algorithms, such as Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP). We show that if the restricted isometry property is satisfied, then the upper bound of the error between the original signal and its approximation can be derived. Furthermore, we prove that the RMP algorithm can find the correct support of sparse signals from random measurements with a high probability. Our numerical experiments also verify this conclusion and show that RMP is stable with the noise. So, the RMP algorithm is a suitable method for recovering sparse signals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Numerical Computation, Approximation of Functions and Applied Mathematics II)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Display Conventions for Octagons of Opposition
by
David Makinson
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 287; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050287 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
As usually presented, octagons of opposition are rather complex objects and can be difficult to assimilate at a glance. We show how, under suitable conditions that are satisfied by most historical examples, different display conventions can simplify the diagrams, making them easier for
[...] Read more.
As usually presented, octagons of opposition are rather complex objects and can be difficult to assimilate at a glance. We show how, under suitable conditions that are satisfied by most historical examples, different display conventions can simplify the diagrams, making them easier for readers to grasp without the loss of information. Moreover, those conditions help reveal the conceptual structure behind the visual display.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Modal Logic and Logical Geometry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
On the Convergence of an Approximation Scheme of Fractional-Step Type, Associated to a Nonlinear Second-Order System with Coupled In-Homogeneous Dynamic Boundary Conditions
by
Constantin Fetecău, Costică Moroşanu and Silviu-Dumitru Pavăl
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 286; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050286 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
The paper concerns a nonlinear second-order system of coupled PDEs, having the principal part in divergence form and subject to in-homogeneous dynamic boundary conditions, for both
The paper concerns a nonlinear second-order system of coupled PDEs, having the principal part in divergence form and subject to in-homogeneous dynamic boundary conditions, for both
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Numerical Computation, Approximation of Functions and Applied Mathematics II)
Open AccessArticle
Combined Observer-Based State Feedback and Optimized P/PI Control for a Robust Operation of Quadrotors
by
Oussama Benzinane and Andreas Rauh
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 285; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050285 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper deals with a discrete-time observer-based state feedback control design by taking into consideration bounded parameter uncertainty, actuator faults, and stochastic noise in an inner control loop which is extended in a cascaded manner by outer PI- and P-control loops for velocity
[...] Read more.
This paper deals with a discrete-time observer-based state feedback control design by taking into consideration bounded parameter uncertainty, actuator faults, and stochastic noise in an inner control loop which is extended in a cascaded manner by outer PI- and P-control loops for velocity and position regulation. The aim of the corresponding subdivision of the quadrotor model is the treatment of the control design in a systematic manner. In the inner loop, linear matrix inequality techniques are employed for the placement of poles into a desired area within the complex z-plane. A robustification of the design towards noise is achieved by optimizing both control and observer gains simultaneously guaranteeing stability in a predefined bounded state domain. This procedure helps to reduce the sensitivity of the inner control loop towards changes induced by the outer one. Finally, a model-based optimization process is employed to tune the parameters of the outer P/PI controllers. To allow for the validation of accurate trajectory tracking, a comparison of the novel approach with the use of a standard extended Kalman filter-based linear-quadratic regulator synthesis is presented to demonstrate the superiority of the new design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Mathematical Methods in Optimal Control and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
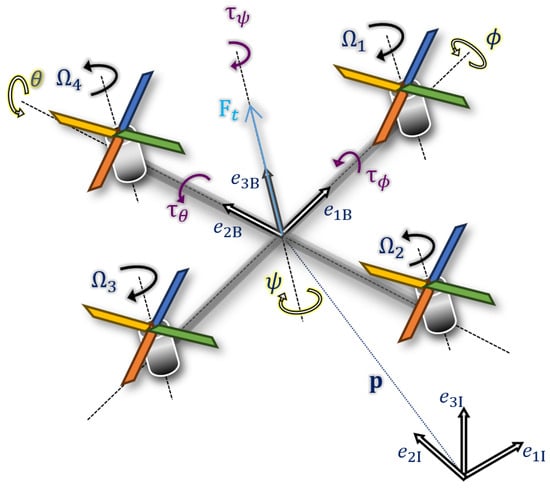
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analytic Solutions for Hilfer Type Fractional Langevin Equations with Variable Coefficients in a Weighted Space
by
Fang Li, Ling Yang and Huiwen Wang
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 284; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050284 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
In this work, analytic solutions of initial value problems for fractional Langevin equations involving Hilfer fractional derivatives and variable coefficients are studied. Firstly, the equivalence of an initial value problem to an integral equation is proved. Secondly, the existence and uniqueness of solutions
[...] Read more.
In this work, analytic solutions of initial value problems for fractional Langevin equations involving Hilfer fractional derivatives and variable coefficients are studied. Firstly, the equivalence of an initial value problem to an integral equation is proved. Secondly, the existence and uniqueness of solutions for the above initial value problem are obtained without a contractive assumption. Finally, a formula of explicit solutions for the proposed problem is derived. By using similar arguments, corresponding conclusions for the case involving Riemann–Liouville fractional derivatives and variable coefficients are obtained. Moreover, the nonlinear case is discussed. Two examples are provided to illustrate theoretical results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Fractional Differential Equations and Inequalities)
►▼
Show Figures
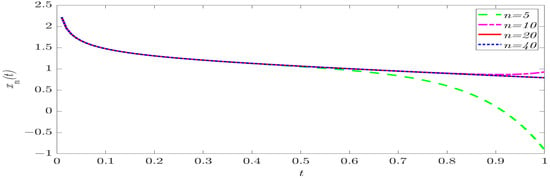
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Study of Generalized Lambert, Generalized Stieltjes, and Stieltjes–Poisson Transforms
by
Jeetendrasingh Maan and E. R. Negrín
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 283; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050283 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
In this paper, we explore the properties of the generalized Lambert transform, the L-transform, the generalized Stieltjes transform, and the Stieltjes–Poisson transform within the framework of Lebesgue spaces. We establish Parseval-type relations for each transform, providing a comprehensive analysis of their behaviour and
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we explore the properties of the generalized Lambert transform, the L-transform, the generalized Stieltjes transform, and the Stieltjes–Poisson transform within the framework of Lebesgue spaces. We establish Parseval-type relations for each transform, providing a comprehensive analysis of their behaviour and mathematical characteristics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Special Functions and Applications)
Open AccessArticle
A Class of Multi-Component Non-Isospectral TD Hierarchies and Their Bi-Hamiltonian Structures
by
Jianduo Yu and Haifeng Wang
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 282; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050282 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
By using the classical Lie algebra, the stationary zero curvature equation, and the Lenard recursion equations, we obtain the non-isospectral TD hierarchy. Two kinds of expanding higher-dimensional Lie algebras are presented by extending the classical Lie algebra. By solving the expanded non-isospectral zero
[...] Read more.
By using the classical Lie algebra, the stationary zero curvature equation, and the Lenard recursion equations, we obtain the non-isospectral TD hierarchy. Two kinds of expanding higher-dimensional Lie algebras are presented by extending the classical Lie algebra. By solving the expanded non-isospectral zero curvature equations, the multi-component non-isospectral TD hierarchies are derived. The Hamiltonian structure for one of them is obtained by using the trace identity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Physics)
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Investigation of Some Reductions for the Gatenby–Gawlinski Model
by
Corrado Mascia, Pierfrancesco Moschetta and Chiara Simeoni
Axioms 2024, 13(5), 281; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13050281 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
Two (consecutive) reductions of the complete Gatenby–Gawlinski model for cancer invasion are proposed in order to investigate the mathematical framework, mainly from a computational perspective. After a brief overview of the full model, we proceed by examining the case of a two-equations-based and
[...] Read more.
Two (consecutive) reductions of the complete Gatenby–Gawlinski model for cancer invasion are proposed in order to investigate the mathematical framework, mainly from a computational perspective. After a brief overview of the full model, we proceed by examining the case of a two-equations-based and one-equation-based reduction, both obtained by means of a quasi-steady-state assumption. We focus on invasion fronts, exploiting a numerical strategy based on a finite volume approximation, and perform corresponding computational simulations to study the sharpness/smoothness of the traveling waves. Then, we employ a space-averaged wave speed estimate—referred to as the LeVeque–Yee formula—to quantitatively approach the propagation phenomenon. Concerning the one-equation-based model, we propose a scalar degenerate reaction-diffusion equation, which proves to be effective in order to qualitatively recover the typical trends arising from the Gatenby–Gawlinski model. Finally, we carry out some numerical tests in a specific case where the analytical solution is available.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
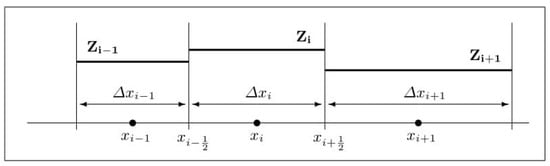
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Existence of Li–Yorke Chaos in a Discrete-Time Glycolytic Oscillator Model
by
Mirela Garić-Demirović, Mustafa R. S. Kulenović, Mehmed Nurkanović and Zehra Nurkanović
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 280; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040280 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper investigates an autonomous discrete-time glycolytic oscillator model with a unique positive equilibrium point which exhibits chaos in the sense of Li–Yorke in a certain region of the parameters. We use Marotto’s theorem to prove the existence of chaos by finding a
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates an autonomous discrete-time glycolytic oscillator model with a unique positive equilibrium point which exhibits chaos in the sense of Li–Yorke in a certain region of the parameters. We use Marotto’s theorem to prove the existence of chaos by finding a snap-back repeller. The illustration of the results is presented by using numerical simulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Dynamical Systems and Control)
►▼
Show Figures
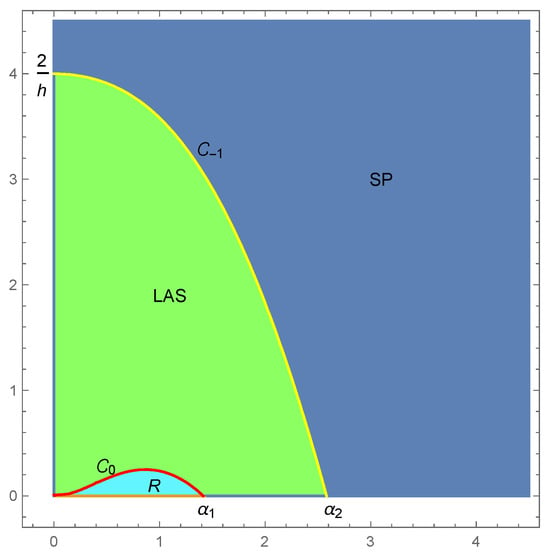
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Estimation of Gumbel Distribution Based on Ordered Maximum Ranked Set Sampling with Unequal Samples
by
Nuran Medhat Hassan and Osama Abdulaziz Alamri
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 279; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040279 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sample selection is one of the most important factors in estimating the unknown parameters of distributions, as it saves time, saves effort, and gives the best results. One of the challenges is deciding on a suitable distribution estimate technique and adequate sample selection
[...] Read more.
Sample selection is one of the most important factors in estimating the unknown parameters of distributions, as it saves time, saves effort, and gives the best results. One of the challenges is deciding on a suitable distribution estimate technique and adequate sample selection to provide the best results in comparison with earlier research. The method of moments (MOM) was decided on to estimate the unknown parameters of the Gumbel distribution, but with four changes in the sample selection, which were simple random sample (SRS), ranked set sampling (RSS), maximum ranked set sampling (MRSS), and ordered maximum ranked set sampling (OMRSS) techniques, due to small sample sizes. The MOM is a traditional method for estimation, but it is difficult to use when dealing with RSS modification. RSS modification techniques were used to improve the efficiency of the estimators based on a small sample size compared with the usual SRS estimator. A Monte Carlo simulation study was carried out to compare the estimates based on different sampling. Finally, two datasets were used to demonstrate the adaptability of the Gumbel distribution based on the different sampling techniques.
Full article
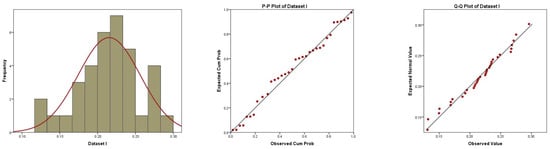
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Unified Representation of q- and h-Integrals and Consequences in Inequalities
by
Da Shi, Ghulam Farid, Bakri Adam Ibrahim Younis, Hanaa Abu-Zinadah and Matloob Anwar
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 278; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040278 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
This paper aims to unify q-derivative/q-integrals and h-derivative/h-integrals into a single definition, called
This paper aims to unify q-derivative/q-integrals and h-derivative/h-integrals into a single definition, called
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Theory of Functions and Applications II)
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Study of the Langevin Boundary Value Problems with Variable Order Fractional Derivatives
by
John R. Graef, Kadda Maazouz and Moussa Daif Allah Zaak
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 277; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040277 - 21 Apr 2024
Abstract
The authors investigate Langevin boundary value problems containing a variable order Caputo fractional derivative. After presenting the background for the study, the authors provide the definitions, theorems, and lemmas that are required for comprehending the manuscript. The existence of solutions is proved using
[...] Read more.
The authors investigate Langevin boundary value problems containing a variable order Caputo fractional derivative. After presenting the background for the study, the authors provide the definitions, theorems, and lemmas that are required for comprehending the manuscript. The existence of solutions is proved using Schauder’s fixed point theorem; the uniqueness of solutions is obtained by adding an additional hypothesis and applying Banach’s contraction principle. An example is provided to demonstrate the results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fractional Calculus and Its Applications: Historical and Recent Developments)
Open AccessArticle
Evidential-Reasoning-Type Multi-Attribute Large Group Decision-Making Method Based on Public Satisfaction
by
Chenguang Cai, Yuejiao Wang, Pei Wang and Hao Zou
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 276; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040276 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
To address public participation-oriented, large group decision-making problems with uncertain attribute weights, we propose a multi-attribute decision-making method considering public satisfaction. Firstly, a large group is organized to provide their opinions in the form of linguistic variables. Public opinions can be categorized into
[...] Read more.
To address public participation-oriented, large group decision-making problems with uncertain attribute weights, we propose a multi-attribute decision-making method considering public satisfaction. Firstly, a large group is organized to provide their opinions in the form of linguistic variables. Public opinions can be categorized into two types based on their content: one reflects the effectiveness of an alternative implementation and the other reflects the public expectations. Secondly, the two types of public opinions are sorted separately by linguistic variables. The evaluation of alternatives and the evaluation of expectations in different attributes are determined, both of which are expressed in the form of linguistic distributions. These two evaluations are then compared to determine the public satisfaction of the attributes in different alternatives. Thirdly, based on the deviation of public satisfaction in different attributes, a weight optimization model is constructed to determine the attribute weights. Fourthly, leveraging the interval credibility of attribute satisfaction for various alternatives, an evidential reasoning non-linear optimization model is established to obtain the comprehensive utility evaluation value for each alternative, which is used for ranking. Finally, a numerical example is employed to validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed approach. According to the results of the numerical example, it can be concluded that the proposed approach can be effectively applied to large group decision-making problems that consider public satisfaction. Based on the comparison of methods, the proposed approach has certain advantages in reflecting public opinions and setting reference points, which can ensure the reliability of the decision results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Decision-Making Modeling and Optimization)
►▼
Show Figures
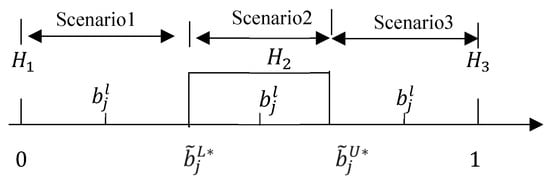
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Monotonic Random Variables According to a Direction
by
José Juan Quesada-Molina and Manuel Úbeda-Flores
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 275; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040275 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
In this paper, we introduce the concept of monotonicity according to a direction for a set of random variables. This concept extends well-known multivariate dependence notions, such as corner set monotonicity, and can be used to detect dependence in multivariate distributions not detected
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we introduce the concept of monotonicity according to a direction for a set of random variables. This concept extends well-known multivariate dependence notions, such as corner set monotonicity, and can be used to detect dependence in multivariate distributions not detected by other known concepts of dependence. Additionally, we establish relationships with other known multivariate dependence concepts, outline some of their salient properties, and provide several examples.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Classical and Applied Mathematics)
Open AccessArticle
Spectral Curves for Third-Order ODOs
by
Sonia L. Rueda and Maria-Angeles Zurro
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 274; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040274 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
Spectral curves are algebraic curves associated to commutative subalgebras of rings of ordinary differential operators (ODOs). Their origin is linked to the Korteweg–de Vries equation and to seminal works on commuting ODOs by I. Schur and Burchnall and Chaundy. They allow the solvability
[...] Read more.
Spectral curves are algebraic curves associated to commutative subalgebras of rings of ordinary differential operators (ODOs). Their origin is linked to the Korteweg–de Vries equation and to seminal works on commuting ODOs by I. Schur and Burchnall and Chaundy. They allow the solvability of the spectral problem
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Theory of Curves and Knots with Applications)
Open AccessArticle
Double-Step Shape Invariance of Radial Jacobi-Reference Potential and Breakdown of Conventional Rules of Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics
by
Gregory Natanson
Axioms 2024, 13(4), 273; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/axioms13040273 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The paper reveals some remarkable form-invariance features of the ‘Jacobi-reference’ canonical Sturm–Liouville equation (CSLE) in the particular case of the density function with the simple pole at the origin. It is proven that the CSLE under consideration preserves its form under the two
[...] Read more.
The paper reveals some remarkable form-invariance features of the ‘Jacobi-reference’ canonical Sturm–Liouville equation (CSLE) in the particular case of the density function with the simple pole at the origin. It is proven that the CSLE under consideration preserves its form under the two second-order Darboux–Crum transformations (DCTs) with the seed functions represented by specially chosen pairs of ‘basic’ quasi-rational solutions (q-RSs), i.e., such that their analytical continuations do not have zeros in the complex plane. It is proven that both transformations generally either increase or decrease by 2 the exponent difference (ExpDiff) for the mentioned pole while keeping two other parameters unchanged. The change is more complicated in the latter case if the ExpDiff for the pole of the original CSLE at the origin is smaller than 2. It was observed that the DCTs in question do not preserve bound energy levels according to the conventional supersymmetry (SUSY) rules. To understand this anomaly, we split the DCT in question into the two sequential Darboux deformations of the Liouville potentials associated with the CSLEs of our interest. We found that the first Darboux transformation turns the initial CSLE into the Heun equation written in the canonical form while the second transformation brings us back to the canonical form of the hypergeometric equation. It is shown that the first of these transformations necessarily places the mentioned ExpDiff into the limit-circle (LC) range and then the second transformation keeps the pole within the LC region, violating the conventional prescriptions of SUSY quantum mechanics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Differential Geometry and Mathematical Physics)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Axioms Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Axioms, Computation, MCA, Mathematics, Symmetry
Mathematical Modeling
Topic Editors: Babak Shiri, Zahra AlijaniDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Algorithms, Axioms, Fractal Fract, Mathematics, Symmetry
Fractal and Design of Multipoint Iterative Methods for Nonlinear Problems
Topic Editors: Xiaofeng Wang, Fazlollah SoleymaniDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Crystals, Mathematics, Symmetry, Fractal Fract, Axioms
Mathematical Applications of Nonlinear Wave Properties in Crystalline and Dispersive Media
Topic Editors: Mahmoud A.E. Abdelrahman, Emad El-ShewyDeadline: 31 August 2024
Topic in
Entropy, Fractal Fract, Dynamics, Mathematics, Computation, Axioms
Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics: Methods and Applications
Topic Editors: Ravi P. Agarwal, Maria Alessandra RagusaDeadline: 20 October 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Axioms
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Techniques for Mathematical Problem Solving
Guest Editors: Minhyeok Lee, Yoojoong Kim, Gustavo OlagueDeadline: 26 April 2024
Special Issue in
Axioms
Computational and Experimental Fluid Dynamics
Guest Editors: Yuli Chashechkin, Sergey E. YakushDeadline: 29 April 2024
Special Issue in
Axioms
Advances in Mathematical Methods and Applications for High-Performance Computing
Guest Editor: Jin SunDeadline: 20 May 2024
Special Issue in
Axioms
Discrete Curvatures and Laplacians
Guest Editors: Emil Saucan, David Xianfeng GuDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Axioms
Mathematical Analysis and Applications
Collection Editor: Hari Mohan Srivastava
Topical Collection in
Axioms
Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems
Collection Editor: Feliz Manuel Minhós






