Journal Description
Knowledge
Knowledge
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on knowledge and knowledge-related technologies published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
subject
Imprint Information
Open Access
ISSN: 2673-9585
Latest Articles
Reflections on Knowledge Production in Humanities from an Academic Exchange Experience
Knowledge 2024, 4(2), 213-232; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4020011 - 11 Apr 2024
Abstract
Over the last two decades, the knowledge production, research, and reconfiguration of universities have been understood as ways of giving new meanings to the university–society binomial. In this regard, humanities are the subject of multiple debates in the face of ideas about their
[...] Read more.
Over the last two decades, the knowledge production, research, and reconfiguration of universities have been understood as ways of giving new meanings to the university–society binomial. In this regard, humanities are the subject of multiple debates in the face of ideas about their impact in relation to the “other sciences”. Based on these premises, this article sets out to explore possible meanings attributed by researchers to the concepts of commitment, mobilization, and transfer of research in humanities in view of the debates on the university–society interaction and the third mission of the university. The methodology used will address bibliographical analysis, theoretical background, and statements from different institutions, as well as the analysis of material from four interviews. As a first instance, the preliminary results show that strengthening critical thinking as forms of commitment emerge as central senses, focusing on Hungarian characteristics and productions in order to unravel the ways of understanding and imagining Eastern European reality. In this respect, the discussion of certain aspects of Western knowledge is seen as a task associated with social commitment with public universities as a focus of resistance.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
An Active Approach for Teaching and Learning Electrical Technology
by
Carla Terron-Santiago, Jordi Burriel-Valencia, Javier Martinez-Roman and Angel Sapena-Bano
Knowledge 2024, 4(2), 194-212; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4020010 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
This contribution describes the change in methodology introduced in the subject of electrical technology within the industrial technologies engineering degree at Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingeniería Industrial, Universitat Politècnica de València. The main purpose of the methodology change was to improve the attainment
[...] Read more.
This contribution describes the change in methodology introduced in the subject of electrical technology within the industrial technologies engineering degree at Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingeniería Industrial, Universitat Politècnica de València. The main purpose of the methodology change was to improve the attainment of student outcomes by the introduction of project-based learning supported by flipped teaching. Moreover, a software tool was developed that generates standard exercise statements for the design of electrical installations. Using this tool, students can practice with different problem exercises, enter their solution, and receive immediate feedback on their results, improving the teaching–learning experience. The level of student outcomes attained was improved, and other positive aspects arose from the experience, such as boosting students’ responsibility in their own learning (learn to learn), their ability to solve problems, and students’ motivation. Furthermore, the instructors’ opinions on the methodology change were highly positive.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Decision-Making: Processes and Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures
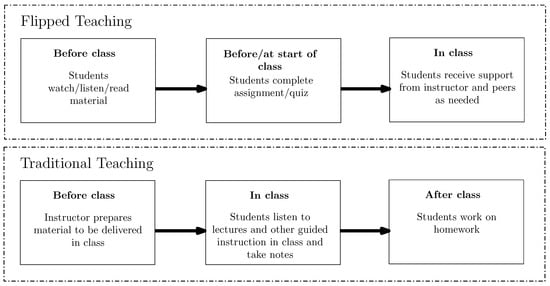
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Value Perception Analysis in the Brazilian Company of Research and Industrial Innovation
by
Isabela Evora Moreira, Diego de Castro Fettermann and Viviane Vasconcellos Ferreira Grubisic
Knowledge 2024, 4(2), 171-193; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4020009 - 04 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study aims to analyze the perceived value of services provided by the Brazilian Company of Research and Industrial Innovation (EMBRAPII) to its contracting ministries and institutional partners. It utilizes the theory of value perception analysis and Constructivist Multi-criteria Decision Analysis to identify
[...] Read more.
This study aims to analyze the perceived value of services provided by the Brazilian Company of Research and Industrial Innovation (EMBRAPII) to its contracting ministries and institutional partners. It utilizes the theory of value perception analysis and Constructivist Multi-criteria Decision Analysis to identify critical elements for evaluating EMBRAPII’s contracting organizations. Brainstorming sessions with experts led to the identification of five criteria and 14 sub-criteria. These criteria include a relationship with EMBRAPII, a signed agreement, EMBRAPII’s reputation, technical capacity, and the ability to adapt to changes. Data were entered into the second version of the MyMCDA-C software for value perception analysis. The findings showed a positive perceived value, with the best-performing sub-criteria relating to the organization’s reputation and the agreement signed. The study concludes that EMBRAPII needs to improve in areas such as adapting to change, the adequacy of its proposals for distinct types of partnership, and social media positioning. However, the contracting organizations generally support EMBRAPII’s direction and proposed solutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Decision-Making: Processes and Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures
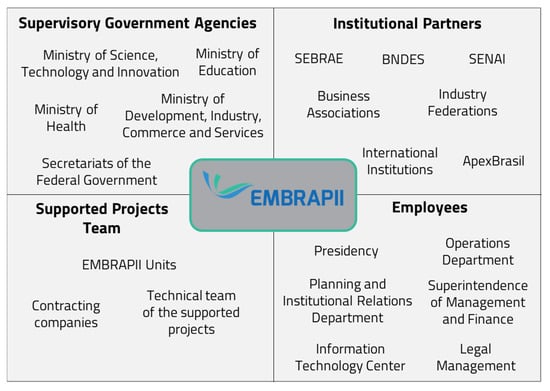
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Omni-Secure Firewall System in a Private Cloud Environment
by
Salman Mahmood, Raza Hasan, Nor Adnan Yahaya, Saqib Hussain and Muzammil Hussain
Knowledge 2024, 4(2), 141-170; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4020008 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
This research explores the optimization of firewall systems within private cloud environments, specifically focusing on a 30-day evaluation of the Omni-Secure Firewall. Employing a multi-metric approach, the study introduces an innovative effectiveness metric (E) that amalgamates precision, recall, and redundancy considerations. The evaluation
[...] Read more.
This research explores the optimization of firewall systems within private cloud environments, specifically focusing on a 30-day evaluation of the Omni-Secure Firewall. Employing a multi-metric approach, the study introduces an innovative effectiveness metric (E) that amalgamates precision, recall, and redundancy considerations. The evaluation spans various machine learning models, including random forest, support vector machines, neural networks, k-nearest neighbors, decision tree, stochastic gradient descent, naive Bayes, logistic regression, gradient boosting, and AdaBoost. Benchmarking against service level agreement (SLA) metrics showcases the Omni-Secure Firewall’s commendable performance in meeting predefined targets. Noteworthy metrics include acceptable availability, target response time, efficient incident resolution, robust event detection, a low false-positive rate, and zero data-loss incidents, enhancing the system’s reliability and security, as well as user satisfaction. Performance metrics such as prediction latency, CPU usage, and memory consumption further highlight the system’s functionality, efficiency, and scalability within private cloud environments. The introduction of the effectiveness metric (E) provides a holistic assessment based on organizational priorities, considering precision, recall, F1 score, throughput, mitigation time, rule latency, and redundancy. Evaluation across machine learning models reveals variations, with random forest and support vector machines exhibiting notably high accuracy and balanced precision and recall. In conclusion, while the Omni-Secure Firewall System demonstrates potential, inconsistencies across machine learning models underscore the need for optimization. The dynamic nature of private cloud environments necessitates continuous monitoring and adjustment of security systems to fully realize benefits while safeguarding sensitive data and applications. The significance of this study lies in providing insights into optimizing firewall systems for private cloud environments, offering a framework for holistic security assessment and emphasizing the need for robust, reliable firewall systems in the dynamic landscape of private clouds. Study limitations, including the need for real-world validation and exploration of advanced machine learning models, set the stage for future research directions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trends in Knowledge Creation and Retention)
►▼
Show Figures
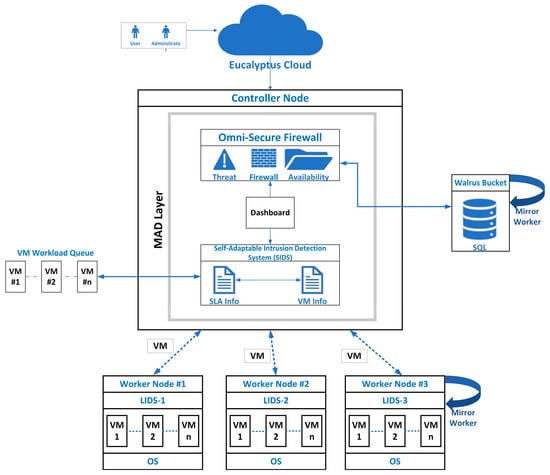
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
DIKW as a General and Digital Twin Action Framework: Data, Information, Knowledge, and Wisdom
by
Michael Grieves
Knowledge 2024, 4(2), 120-140; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4020007 - 25 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper will discuss Data, Information, Knowledge, and Wisdom, which is commonly referred to as DIKW. The DIKW Pyramid Model is a hierarchical model that is often referenced in both academic and practitioner circles. This model will be discussed and shown to be
[...] Read more.
This paper will discuss Data, Information, Knowledge, and Wisdom, which is commonly referred to as DIKW. The DIKW Pyramid Model is a hierarchical model that is often referenced in both academic and practitioner circles. This model will be discussed and shown to be faulty on several levels, including a lack of definitional agreement. A new DIKW framework with systems orientation will be proposed that focuses on what the DIKW elements do in the way humans think, not what they are by definition. Information as a replacement for wasted physical resources in goal-oriented tasks will be a central organizing point. The paper will move the DIKW discussion to the computer-based concept of Digital Twins (DTs) and its augmentation of how we can use DIKW to be more effective and efficient. This will especially be the case as we move toward Intelligent Digital Twins (IDTs) with Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Full article
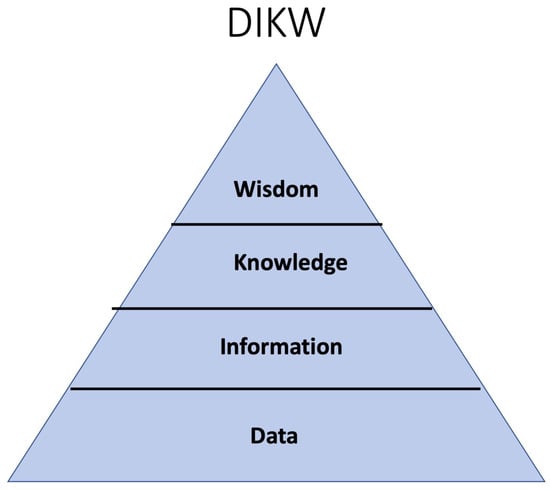
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Resampling to Classify Rare Attack Tactics in UWF-ZeekData22
by
Sikha S. Bagui, Dustin Mink, Subhash C. Bagui and Sakthivel Subramaniam
Knowledge 2024, 4(1), 96-119; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4010006 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
One of the major problems in classifying network attack tactics is the imbalanced nature of data. Typical network datasets have an extremely high percentage of normal or benign traffic and machine learners are skewed toward classes with more data; hence, attack data remain
[...] Read more.
One of the major problems in classifying network attack tactics is the imbalanced nature of data. Typical network datasets have an extremely high percentage of normal or benign traffic and machine learners are skewed toward classes with more data; hence, attack data remain incorrectly classified. This paper addresses the class imbalance problem using resampling techniques on a newly created dataset, UWF-ZeekData22. This is the first dataset with tactic labels, labeled as per the MITRE ATT&CK framework. This dataset contains about half benign data and half attack tactic data, but specific tactics have a meager number of occurrences within the attack tactics. Our objective in this paper was to use resampling techniques to classify two rare tactics, privilege escalation and credential access, never before classified. The study also looks at the order of oversampling and undersampling. Varying resampling ratios were used with oversampling techniques such as BSMOTE and SVM-SMOTE and random undersampling without replacement was used. Based on the results, it can be observed that the order of oversampling and undersampling matters and, in many cases, even an oversampling ratio of 10% of the majority data is enough to obtain the best results.
Full article
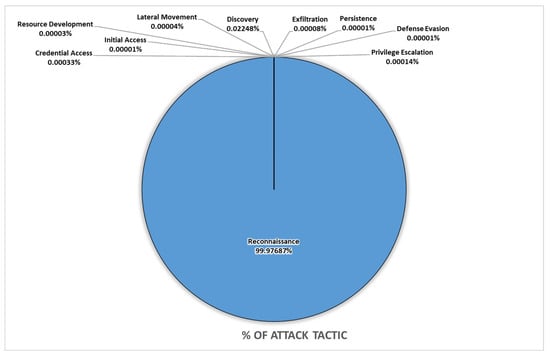
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of a Computing Curriculum Accessible to Students with ASD on the Development of Computing Artifacts
by
Abdu Arslanyilmaz, Margaret L. Briley, Gregory V. Boerio, Katie Petridis, Ramlah Ilyas and Feng Yu
Knowledge 2024, 4(1), 85-95; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4010005 - 05 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
There has been no study examining the effectiveness of an accessible computing curriculum for students with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) on their learning of computational thinking concepts (CTCs), flow control, data representation, abstraction, user interactivity, synchronization, parallelism, and logic. This study aims to
[...] Read more.
There has been no study examining the effectiveness of an accessible computing curriculum for students with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) on their learning of computational thinking concepts (CTCs), flow control, data representation, abstraction, user interactivity, synchronization, parallelism, and logic. This study aims to investigate the effects of an accessible computing curriculum for students with ASD on their learning of CTCs as measured by the scores of 312 computing artifacts developed by two groups of students with ASD. Conducted among 21 seventh-grade students with ASD (10 in the experimental group and 11 in the control), this study involved collecting data on the computing projects of these students over 24 instructional sessions. Group classification was considered the independent variable, and computing project scores were set as the dependent variables. The results showed that the original curriculum was statistically significantly more effective for students in learning logic than the accessible one when all seven CTCs were examined as a single construct. Both curriculums were statistically significantly effective in progressively improving students’ learning of data representation, abstraction, synchronization, parallelism, and all CTCs as a single construct when examining the gradual increase in their computing artifact scores over the 24 sessions. Both curriculums were statistically significantly effective in increasing the scores of synchronization and all CTCs as a single construct when the correlations between CTCs and sessions for individual groups were analyzed. The findings underscore that students with ASD can effectively learn computing skills through accessible or standard curriculums, provided that adjustments are made during delivery.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Curriculum in IDD Healthcare (CIDDH) eLearn Course: Evidence of Continued Effectiveness Using the Streamlined Evaluation and Analysis Method (SEAM)
by
John P. Bartkowski, Xiaohe Xu and Katherine Klee
Knowledge 2024, 4(1), 68-84; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4010004 - 21 Feb 2024
Abstract
Medical professionals are rarely trained to treat the unique healthcare needs and health disparities of people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDD). The Curriculum in IDD Healthcare (CIDDH) eLearn course aims to redress gaps in the delivery of medical care to people with
[...] Read more.
Medical professionals are rarely trained to treat the unique healthcare needs and health disparities of people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDD). The Curriculum in IDD Healthcare (CIDDH) eLearn course aims to redress gaps in the delivery of medical care to people with IDD. An initial comprehensive evaluation of CIDDH in-person training content had previously underscored its knowledge and skill transfer efficacy for Mississippi healthcare providers. Training content has recently become available to medical professionals nationwide through an online self-paced modality to address physicians’ IDD education needs. This study introduces and applies a new evaluation framework called SEAM (Streamlined Evaluation and Analysis Method) that offers a promising avenue for rendering a follow-up appraisal after rigorous evidence of program effectiveness has been previously established. SEAM reduces the data-reporting burden on trainees and maximizes instructor–trainee contact time by relying on an abbreviated post-only questionnaire focused on subjective trainee appraisals. It further reduces methodological and analytical complexity to enhance programmatic self-assessment and facilitate sound data interpretation when an external evaluator is unavailable. Ratings from a small sample of early-cohort trainees provide an important test of effectiveness during CIDDH’s transition to online learning for clinicians nationwide. Using SEAM, CIDDH achieved high ratings from this initial wave of trainees across various evaluative domains. The study concludes by highlighting several promising implications for CIDDH and SEAM.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Web Mining of Online Resources for German Labor Market Research and Education: Finding the Ground Truth?
by
Andreas Fischer and Jens Dörpinghaus
Knowledge 2024, 4(1), 51-67; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4010003 - 19 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The labor market is highly dependent on vocational and academic education, training, retraining, and further education in order to master challenges such as advancing digitalization and sustainability. Further training is a key factor in ensuring a qualified workforce, the employability of all employees,
[...] Read more.
The labor market is highly dependent on vocational and academic education, training, retraining, and further education in order to master challenges such as advancing digitalization and sustainability. Further training is a key factor in ensuring a qualified workforce, the employability of all employees, and, thus, national competitiveness and innovation. In the contribution at hand, we explore an innovative way to derive knowledge about learning pathways by connecting the dots from different data sources of the German labor market. In particular, we focus on the web mining of online resources for German labor market research and education, such as online advertisements, information portals, and official government websites. A key question for working with different data sources is how to find the ground truth and common data structures that can be used to make the data interoperable. We discuss how to classify and summarize web data from different platforms and which methods can be used for extracting data, entities and relationships from online resources on the German labor market to build a network of educational pathways. Our proposed solution is based on the classification of occupations (KldB) and related document codes (DKZ), and combines natural language processing and knowledge graph technologies. Our research provides the foundation for further investigation into educational pathways and linked data for labor market research. While our work focuses on German data, it is also useful for other German-speaking countries and could easily be extended to other languages such as English.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Uncovering Challenges and Pitfalls in Identifying Threshold Concepts: A Comprehensive Review
by
Paulo R. M. Correia, Ivan A. I. Soida, Izabela de Souza and Manolita C. Lima
Knowledge 2024, 4(1), 27-50; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4010002 - 30 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The exploration of threshold concepts, which represent a transformed way of understanding, interpreting, or viewing something necessary for a learner’s progress, has significantly influenced teaching and learning in higher education, gaining broad acceptance in academic circles. Despite widespread enthusiasm, the scientific development of
[...] Read more.
The exploration of threshold concepts, which represent a transformed way of understanding, interpreting, or viewing something necessary for a learner’s progress, has significantly influenced teaching and learning in higher education, gaining broad acceptance in academic circles. Despite widespread enthusiasm, the scientific development of the field faces obstacles, especially epistemological and ontological uncertainties, directly implying the reliability of identification techniques and, by extension, raising questions about the validity of previous findings. This comprehensive review delves into 60 articles sourced from the Web of Science database to scrutinize the literature on threshold concept identification. The findings confirm the adaptability of threshold concepts across diverse disciplines. However, the fluid definition inherent in these concepts introduces ontological challenges, influencing biases in the identification process. The review highlights the diverse identification methods influenced by knowledge area specificities, community affinities, and research practice traditions. A diagram depicting the methods employed to identify threshold concepts is offered to highlight five central decisions to be considered. Acknowledging professors as pivotal mediators adept at navigating the epistemological and ontological dimensions of threshold concepts while integrating theoretical and applied knowledge, this study enhances our nuanced understanding of threshold concept identification. Emphasizing methodological validity and reliability, it acknowledges the crucial role of experienced educators in this issue and presents future perspectives for advancing current research, fostering the maturation of the field.
Full article
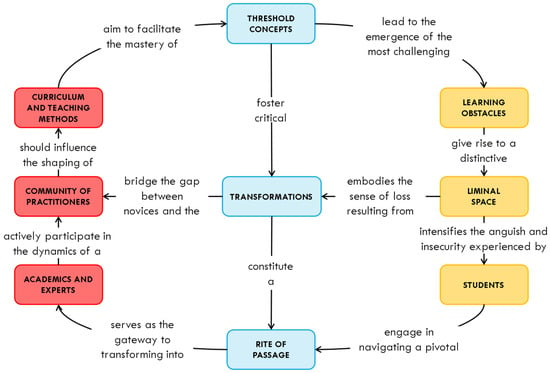
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Agriculture Named Entity Recognition—Towards FAIR, Reusable Scholarly Contributions in Agriculture
by
Jennifer D’Souza
Knowledge 2024, 4(1), 1-26; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge4010001 - 19 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We introduce the Open Research Knowledge Graph Agriculture Named Entity Recognition (the ORKG Agri-NER) corpus and service for contribution-centric scientific entity extraction and classification. The ORKG Agri-NER corpus is a seminal benchmark for the evaluation of contribution-centric scientific entity extraction and classification in
[...] Read more.
We introduce the Open Research Knowledge Graph Agriculture Named Entity Recognition (the ORKG Agri-NER) corpus and service for contribution-centric scientific entity extraction and classification. The ORKG Agri-NER corpus is a seminal benchmark for the evaluation of contribution-centric scientific entity extraction and classification in the agricultural domain. It comprises titles of scholarly papers that are available as Open Access articles on a major publishing platform. We describe the creation of this corpus and highlight the obtained findings in terms of the following features: (1) a generic conceptual formalism focused on capturing scientific entities in agriculture that reflect the direct contribution of a work; (2) a performance benchmark for named entity recognition of scientific entities in the agricultural domain by empirically evaluating various state-of-the-art sequence labeling neural architectures and transformer models; and (3) a delineated 3-step automatic entity resolution procedure for the resolution of the scientific entities to an authoritative ontology, specifically AGROVOC that is released in the Linked Open Vocabularies cloud. With this work we aim to provide a strong foundation for future work on the automatic discovery of scientific entities in the scholarly literature of the agricultural domain.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Digital Transformation of Health Professionals: Using the Context Optimisation Model for Person-Centred Analysis and Systematic Solutions (COMPASS) Implementation Model Use Case
by
Carey Ann Mather, Joshua Fraser Bailey and Helen Mary Almond
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 679-687; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040042 - 14 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In today’s demanding healthcare landscape, the use of theoretical frameworks is paramount for navigating the complexities of digital health challenges. The Context Optimisation Model for Person-centred Analysis and Systematic Solutions (COMPASS) theoretical framework and implementation model serves as an invaluable direction tool in
[...] Read more.
In today’s demanding healthcare landscape, the use of theoretical frameworks is paramount for navigating the complexities of digital health challenges. The Context Optimisation Model for Person-centred Analysis and Systematic Solutions (COMPASS) theoretical framework and implementation model serves as an invaluable direction tool in planning, implementing, and evaluating digital healthcare initiatives. This paper showcases the tangible value of the COMPASS implementation model through a use case scenario involving an accredited exercise physiologist and a healthcare user with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus who seeks credible information via a mobile digital device. Within this example, the COMPASS model demonstrates the ability to enhance systematic processes, streamline the workflow of health professionals and develop their capabilities to actively contribute to the transformative realm of digital health. Through exploration of the use case and the significance of the systematic processes as a research direction, the empowerment of health professionals to play pivotal roles in ongoing digital health transformation is emphasised. The COMPASS model emerges as a powerful tool, guiding health professionals and organisations towards innovative and sustainable solutions in the dynamic landscape of digital healthcare.
Full article
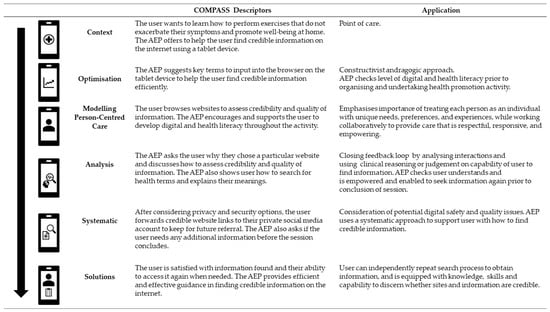
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Process Mining Organization (PMO) Modeling and Healthcare Processes
by
Angelo Rosa and Alessandro Massaro
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 662-678; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040041 - 22 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Process mining organizatioQn (PMO) is an innovative approach based on artificial intelligence (AI) decision making suitable for designing healthcare processes for human resource (HR) organizations. The proposed work suggests some examples of PMO-based Business Process Modeling and Notation (BPMN) workflows by highlighting the
[...] Read more.
Process mining organizatioQn (PMO) is an innovative approach based on artificial intelligence (AI) decision making suitable for designing healthcare processes for human resource (HR) organizations. The proposed work suggests some examples of PMO-based Business Process Modeling and Notation (BPMN) workflows by highlighting the advances in HR management and in risk decrease according to healthcare scenarios. Specifically proposed are different examples of “TO BE” process pipelines related to an upgrade of the organizational healthcare framework, including digital technologies and telemedicine. Important elements are provided to formulate HR management guidelines supporting PMO design. The proposed BPMN workflows are the result of different consulting actions in healthcare institutions based on the preliminary mapping of “AS IS” processes highlighting bottlenecks and needs in HR organization. A pilot experimental dataset is used to show how it is possible to apply AI algorithms providing organization corrective actions. The paper is mainly focused on discussing some validated BPMN models managing HR in the healthcare sector. The methodology is based on the application of the BPMN approach to deploy human resource organizational processes. The results show AI data-driven workflows adopted in healthcare and examples of AI fuzzy c-means outputs addressing organizational actions.
Full article
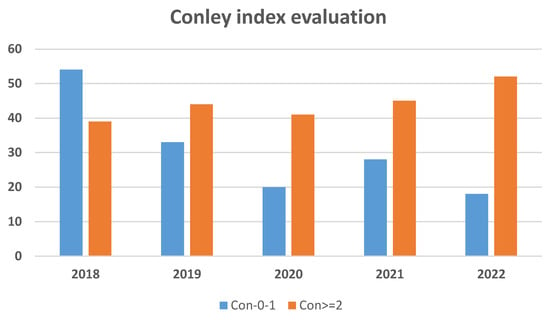
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Motivational Utility of Knowledge: Examining Fundamental Needs in the Context of Houselessness Knowledge
by
Micah Watanabe and Danielle S. McNamara
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 642-661; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040040 - 22 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Past research on knowledge has differentiated between dimensions (e.g., amount, accuracy, specificity, coherence) of knowledge. This paper introduces a novel dimension of knowledge, the Motivational Utility of Knowledge (MUK), that is based on fundamental human needs (e.g., physical safety, affiliation, actualization, reproduction). Adults
[...] Read more.
Past research on knowledge has differentiated between dimensions (e.g., amount, accuracy, specificity, coherence) of knowledge. This paper introduces a novel dimension of knowledge, the Motivational Utility of Knowledge (MUK), that is based on fundamental human needs (e.g., physical safety, affiliation, actualization, reproduction). Adults in the United States (N = 190) were recruited from an online survey platform and paid for participation. Participants read a set of four texts arguing different views of houselessness and were administered a comprehension test after each text. Participants were asked about their conceptions of houselessness before and after reading. Finally, they were given the MUK scale, a demographics questionnaire, including questions about their personal experience with houselessness, and were administered a general prior knowledge test and a vocabulary knowledge test. We examined MUK, the factor structure of the scale and the relationship between MUK and other measures of knowledge. The analyses showed that the subscales of MUK loaded onto a single factor—an overall value of houselessness knowledge. In addition, we found that MUK was correlated with conceptions of houselessness and comprehension of texts on houselessness, indicating that the scale was valid. Overall, the findings demonstrate that MUK is an important dimension of knowledge to consider in learning tasks.
Full article
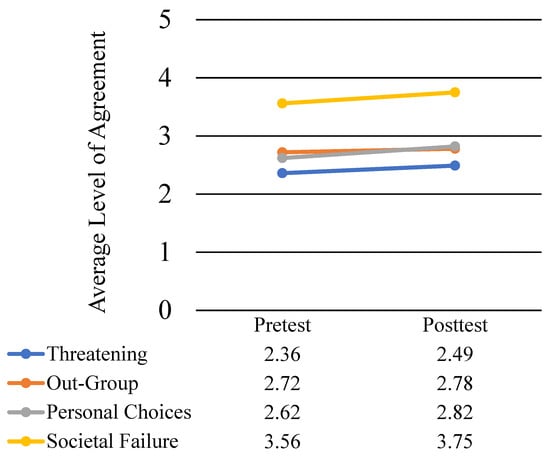
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cognitive Factors Affecting the Manufacturing Optimization Skills of Rural Indian BPO Workers
by
Gokula Vasantha, Jonathan Corney and Chandra Kant Upadhyay
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 626-641; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040039 - 09 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Crowdsourcing offers on-demand access to large numbers of human workers to implement new forms of human–computer collaborative functionalities that can be seamlessly integrated into advanced software and algorithms. However, crowdsourcing tasks are primarily undertaken by urban rather than rural workers. To enable the
[...] Read more.
Crowdsourcing offers on-demand access to large numbers of human workers to implement new forms of human–computer collaborative functionalities that can be seamlessly integrated into advanced software and algorithms. However, crowdsourcing tasks are primarily undertaken by urban rather than rural workers. To enable the development of skilled rural employment, this research aims to assess rural crowdsourcing workers’ spatial reasoning and creative abilities and their abilities to solve irregular strip packing problems associated with the manufacture of sheet materials. The study conducted experiments and data collection with 140 rural Business Processing Outsourcing (BPO) workers located in six states of India. The statistical analyses of the data collected from seven rural BPO firms (140 rural workers) reveal that rural workers can achieve a 2D packing efficiency that is up to 8% higher than that of commercial algorithm outcomes. The results suggest that rural crowdsourcing can lead to effective job creation, skill development, and, for a modest cost, it can support industries that employ CAD/CAM systems to generate geometric data for common manufacturing processes.
Full article
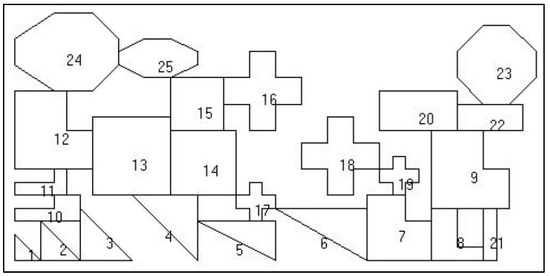
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Landfill Monitoring and Assessment: A Proposal Combining GIS-Based Analytic Hierarchy Processes and Fuzzy Artificial Intelligence
by
Anna Isabel Silva Loureiro, Adriano Bressane, Victor Fernandez Nascimento, José Victor Orlandi Simões and Rogério Galante Negri
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 610-625; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040038 - 20 Oct 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
The global surge in urbanization and population growth has led to a significant increase in municipal solid waste generation, posing a considerable challenge in identifying suitable landfill sites. This study proposes a novel framework that enhances landfill site monitoring and assessment by combining
[...] Read more.
The global surge in urbanization and population growth has led to a significant increase in municipal solid waste generation, posing a considerable challenge in identifying suitable landfill sites. This study proposes a novel framework that enhances landfill site monitoring and assessment by combining GIS-based hierarchical analytical processes with a fuzzy inference system (FIS). The study employs a systematic approach involving phases such as feature selection, spatial analysis, criteria weighting, FIS building, and a case study conducted in São Paulo State, Brazil. The proposed framework effectively assesses landfill suitability and offers practical recommendations for landfill management and future site selection. This framework provides actionable recommendations for landfill monitoring and assessment, supporting landfill management while minimizing environmental and social impacts. It offers a comprehensive approach to landfill assessment, enhancing the sustainability of waste management practices. Further research can improve the proposed framework by refining feature selection and incorporating real-time data for continuous monitoring. Additionally, exploring the integration of emerging technologies, such as remote sensing and artificial intelligence, can further enhance landfill site monitoring and assessment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Decision-Making: Processes and Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures
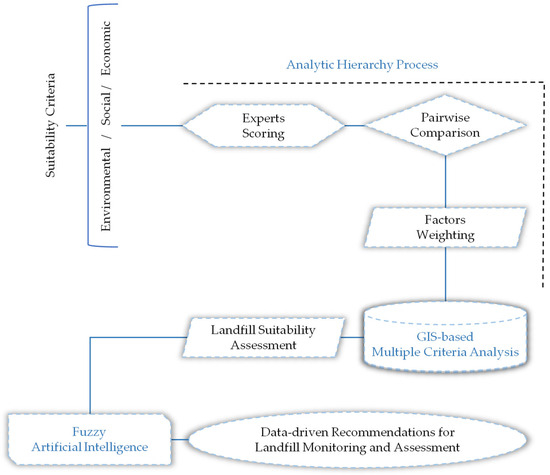
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Embedding Sustainability Justice in Greek Secondary Curricula through the DeCoRe Plus Methodology
by
Georgios Vouzaxakis, Vassilios Makrakis and Nelly Kostoulas-Makrakis
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 600-609; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040037 - 17 Oct 2023
Abstract
This paper describes the processes of embedding Sustainability Justice in secondary education curricula for economic courses in Greece applying the DeCoRe plus methodology and participatory action research. These processes resulted in a reconstructed curriculum that was implemented by nine teachers teaching courses in
[...] Read more.
This paper describes the processes of embedding Sustainability Justice in secondary education curricula for economic courses in Greece applying the DeCoRe plus methodology and participatory action research. These processes resulted in a reconstructed curriculum that was implemented by nine teachers teaching courses in economics. Sustainability justice emphasizes the ethics and praxis of education for sustainability and requires an understanding of the curriculum as a process and praxis and teaching as an ethical and political praxis. The implementation of the diagnostic evaluation of DeCoRe plus showed that economics teachers in Greece select more behavioral than constructive-emancipatory teaching approaches. On the other hand, the implementation of the reconstructed curriculum units in their courses using the DeCoRe plus methodology revealed a shift from instructive to constructivist and emancipatory teaching and learning approaches. Teachers by the great majority declared the political and ethical perspective of teaching and seeing curriculum as a living text that can always be under the process of deconstruction, construction, and reconstruction.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
SQMetrics: An Educational Software Quality Assessment Tool for Java
by
Dimitrios Sofronas, Dimitrios Margounakis, Maria Rigou, Efthimios Tambouris and Theodore Pachidis
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 557-599; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040036 - 29 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Over the years, various software quality measurement models have been proposed and used in academia and the software industry to assess the quality of produced code and to obtain guidelines for its improvement. In this article, we describe the design and functionality of
[...] Read more.
Over the years, various software quality measurement models have been proposed and used in academia and the software industry to assess the quality of produced code and to obtain guidelines for its improvement. In this article, we describe the design and functionality of SQMetrics, a tool for calculating object-oriented quality metrics for projects written in Java. SQMetrics provides the convenience of measuring small code, mainly covering academic or research needs. In this context, the application can be used by students of software engineering courses to make measurements and comparisons in their projects and gradually increase their quality by improving the calculated metrics. Teachers, on the other hand, can use SQMetrics to evaluate students’ Java projects and grade them in proportion to their quality. The contribution of the proposed tool is three-fold, as it has been: (a) tested for its completeness and functionality by comparing it with widely known similar tools, (b) evaluated for its usability and value as a learning aid by students, and (c) statistically tested for its value as a teachers’ aid assisting in the evaluation of student projects. Our findings verify SQMetrics’ effectiveness in helping software engineering students learn critical concepts and improve the quality of their code, as well as in helping teachers assess the quality of students’ Java projects and make more informed grading decisions.
Full article
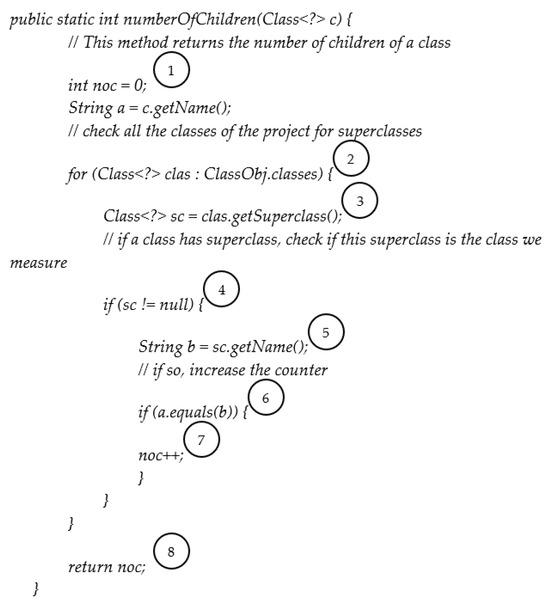
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
New Technology Deployment and Corporate Responsibilities in the Metaverse
by
Martin Wynn and Peter Jones
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 543-556; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040035 - 27 Sep 2023
Cited by 3
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The term “metaverse” came to the fore in 2021 when Facebook rebranded its corporate identity to Meta and signalled its intention to invest at least USD 10 billion in developing the concepts and related products that year. However, there is still little consensus
[...] Read more.
The term “metaverse” came to the fore in 2021 when Facebook rebranded its corporate identity to Meta and signalled its intention to invest at least USD 10 billion in developing the concepts and related products that year. However, there is still little consensus in defining what constitutes the metaverse, although there is a widespread, though not universal, agreement that it will bring a wide range of benefits across society. More specifically, the advent and continuing evolution of the metaverse has strategic and operational implications for, and impacts on, industry and business at large. Adopting an inductive, interpretivist approach, this exploratory research article presents case examples of the guidance on the responsible development of the metaverse provided by two IT business services companies. This article identifies the major risks and responsibilities associated with the metaverse and assesses how companies might address these responsibilities. Very little research has been published in this area, and this article attempts to make a small contribution to filling this gap in the literature. This article finds that these responsibilities are largely in line with those currently associated with corporate digital responsibility, and concludes that the strategic impact and extent of regulatory change will depend on the nature of the metaverse that materialises in the forthcoming decade.
Full article
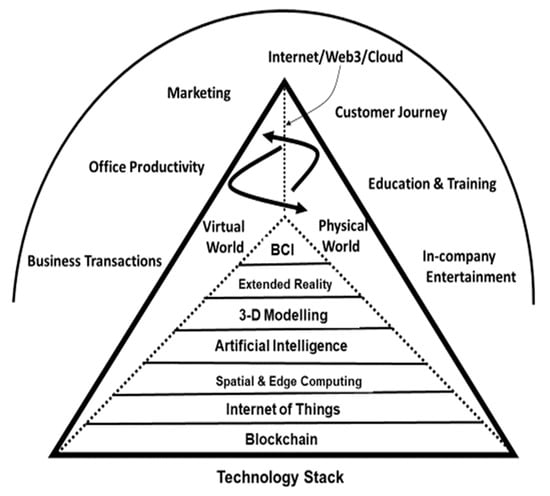
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dialogic and Dialectic Cooperation for Knowledge Creation in IS-Mediated Open Innovation
by
Emmanuel Adamides, Nikos Karacapilidis, Konstantinos Konstantinopoulos and Georgios Kournetas
Knowledge 2023, 3(4), 525-542; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/knowledge3040034 - 26 Sep 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cooperation is an important aspect of open innovation (OI) facilitated by information and communication technology (ICT). Cooperation may have two distinct forms, namely dialectic or dialogic, and it has already been argued that dialogic cooperation is more appropriate for knowledge creation and innovation.
[...] Read more.
Cooperation is an important aspect of open innovation (OI) facilitated by information and communication technology (ICT). Cooperation may have two distinct forms, namely dialectic or dialogic, and it has already been argued that dialogic cooperation is more appropriate for knowledge creation and innovation. In this paper, we test the hypothesis that the choice of the form of cooperation by an organisation, and its implementation in an OI-enabling Information System, are contingent to the organisation’s strategic orientation and competitive and innovation strategies, and it is mediated by the past experience of its OI initiative managers. We also examined, for the first time, which are the antecedents of the adoption of dialogic (and indirectly, dialectic) cooperation in OI initiatives. The empirical research carried out in a sample of senior managers of different sectors in Greece suggests that companies that have extrospective strategic orientations and that adopt differentiation/innovation strategies are more likely to implement dialogic cooperation in their OI endeavors, thus increasing their knowledge creation potential. This choice is further supported by managers who have participated in other organisations’ OI initiatives in the past.
Full article
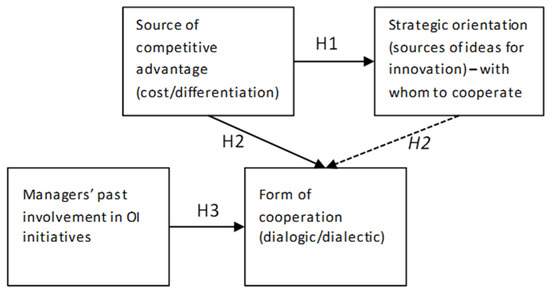
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Knowledge
New Trends in Knowledge Management
Guest Editor: Simon M. BurnettDeadline: 1 May 2024
Special Issue in
Knowledge
Decision-Making: Processes and Perspectives
Guest Editors: Francisco Banha, Adão Flores, Luís Serra CoelhoDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Knowledge
New Trends in Knowledge Creation and Retention
Guest Editor: Peter SharpDeadline: 31 July 2024
Special Issue in
Knowledge
Autonomous Human-Machine Teams: Knowledge, Information, and Information Gaps in Knowledge
Guest Editor: William LawlessDeadline: 15 February 2025



