Renewable and Sustainable Energy Systems: Recent Developments, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
A topical collection in Applied Sciences (ISSN 2076-3417). This collection belongs to the section "Energy Science and Technology".
Viewed by 45338Editor
Interests: renewable and sustainable energy; energy sources; energy storage; energy conversion and management; geothermal energy; energy and environment; sustainable development
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Currently, a transition from non-renewable carbon-based fuels (mainly oil, coal, and natural gas) to renewable, eco-friendly, and sustainable energy sources (e.g., solar, wind, geothermal, hydro) is essential for a variety of reasons, the most important ones being the ongoing and emerging environmental problems and threats, the limited resources of fossil fuels, and fast-growing global demand for energy. Therefore, we need to pay more attention to and invest in clean, renewable, and sustainable energy technologies to overcome or minimize ongoing and emerging challenges facing the world today. Hence, submitting articles, including original research, reviews, case studies, and technical notes covering the following topics to this Special Issue is encouraged:
- Hybrid, integrated renewable energy systems
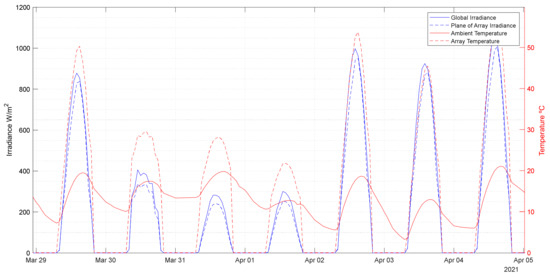
- Solar energy technology and uses
- Wind energy technology and applications
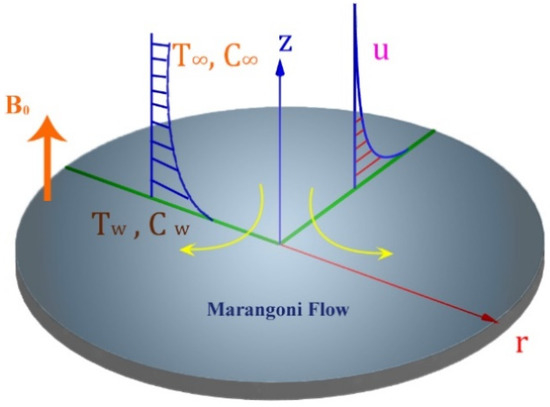
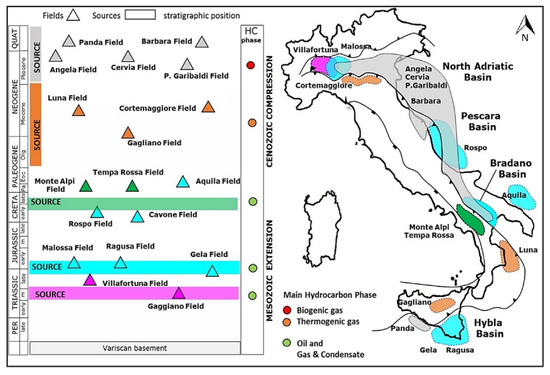
- Geothermal energy resources and applications
- Wave, tide, and ocean/marine thermal energies
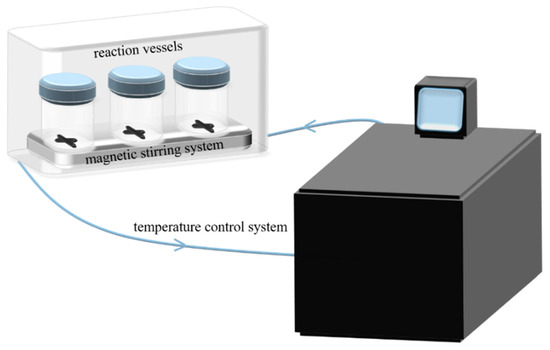
- Bio-energy technology and uses
- Hydrogen energy and fuel cells
- Socio-economic and policy issues related to renewable energy
- Energy conversion and storage technologies
- Energy and exergy analysis of renewable energy systems
- Life cycle assessment of renewable energy systems
- Application of renewable energy sources in buildings
- Renewable energy, sustainability, and climate change
The current Special Issue aims to fill knowledge gaps and address recent developments, challenges, and future outlooks associated with renewable and sustainable energy systems (both stand-alone and hybrid). Therefore, substantive and valuable articles addressing this Special Issue’s objectives will be selected and published after the peer-review process.
Dr. Alireza Dehghanisanij
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- renewable energy
- energy sources and production
- energy conversion and storage
- energy efficiency improvement
- energy conservation and management
- hybrid energy systems
- energy quality
- energy and buildings
- climate change
- sustainability