Journal Description
Technologies
Technologies
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal singularly focusing on emerging scientific and technological trends and is published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, Inspec, INSPIRE, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Computer Science (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.1 (2022)
Latest Articles
Miniaturized Microstrip Dual-Channel Diplexer Based on Modified Meander Line Resonators for Wireless and Computer Communication Technologies
Technologies 2024, 12(5), 57; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12050057 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
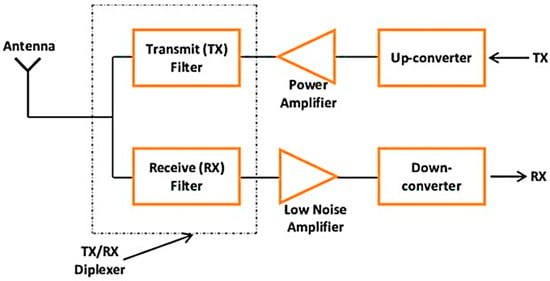
There has been a lot of interest in microstrip diplexers lately due to their potential use in numerous wireless and computer communication technologies, including radio broadcasts, mobile phones, broadband wireless, and satellite-based communication systems. It can do this because it has a communication
[...] Read more.
There has been a lot of interest in microstrip diplexers lately due to their potential use in numerous wireless and computer communication technologies, including radio broadcasts, mobile phones, broadband wireless, and satellite-based communication systems. It can do this because it has a communication channel that can combine two distinct filters into one. This article presents a narrow-band microstrip diplexer that uses a stepped impedance resonator, a uniform impedance resonator, tiny square patches, and a meander line resonator. The projected diplexer might be made smaller than its initial dimensions by utilizing the winding construction. To model the microstrip diplexer topology for WiMAX and WIFI/WLAN at 1.66 GHz and 2.52 GHz, the Advanced Wave Research (AWR) solver was employed. It exhibited an insertion loss of 3.2 dB and a return loss of 16 dB for the first channel, while the insertion loss and return loss were 2.88 dB and 21 dB, respectively, for the second channel. When both filters were simulated, the band isolation was 31 dB. The projected microstrip diplexer has been fabricated using an FR4 epoxy laminate with dimensions of 32 × 26 mm2. The simulated S-parameters phase and group delay closely matched the measurements.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
An End-to-End Lightweight Multi-Scale CNN for the Classification of Lung and Colon Cancer with XAI Integration
by
Mohammad Asif Hasan, Fariha Haque, Saifur Rahman Sabuj, Hasan Sarker, Md. Omaer Faruq Goni, Fahmida Rahman and Md Mamunur Rashid
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 56; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040056 - 21 Apr 2024
Abstract
To effectively treat lung and colon cancer and save lives, early and accurate identification is essential. Conventional diagnosis takes a long time and requires the manual expertise of radiologists. The rising number of new cancer cases makes it challenging to process massive volumes
[...] Read more.
To effectively treat lung and colon cancer and save lives, early and accurate identification is essential. Conventional diagnosis takes a long time and requires the manual expertise of radiologists. The rising number of new cancer cases makes it challenging to process massive volumes of data quickly. Different machine learning approaches to the classification and detection of lung and colon cancer have been proposed by multiple research studies. However, when it comes to self-learning classification and detection tasks, deep learning (DL) excels. This paper suggests a novel DL convolutional neural network (CNN) model for detecting lung and colon cancer. The proposed model is lightweight and multi-scale since it uses only 1.1 million parameters, making it appropriate for real-time applications as it provides an end-to-end solution. By incorporating features extracted at multiple scales, the model can effectively capture both local and global patterns within the input data. The explainability tools such as gradient-weighted class activation mapping and Shapley additive explanation can identify potential problems by highlighting the specific input data areas that have an impact on the model’s choice. The experimental findings demonstrate that for lung and colon cancer detection, the proposed model was outperformed by the competition and accuracy rates of 99.20% have been achieved for multi-class (containing five classes) predictions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Future of Healthcare: Biomedical Technology and Integrated Artificial Intelligence)
►▼
Show Figures
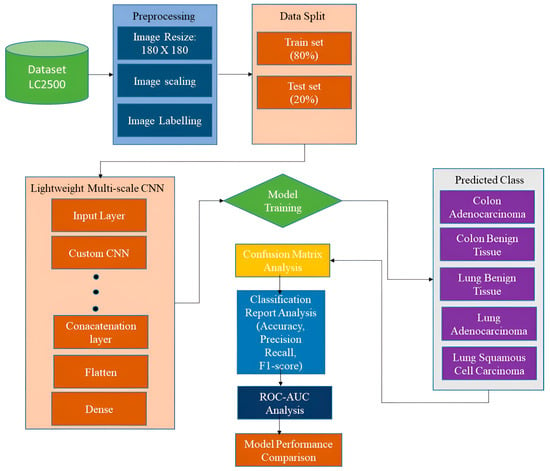
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Digital Twin Models for Personalised and Predictive Medicine in Ophthalmology
by
Miruna-Elena Iliuţă, Mihnea-Alexandru Moisescu, Simona-Iuliana Caramihai, Alexandra Cernian, Eugen Pop, Daniel-Ioan Chiş and Traian-Costin Mitulescu
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 55; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040055 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article explores the integration of Digital Twins in Systems and Predictive Medicine, focusing on eye diagnosis. By utilizing the Digital Twin models, the proposed framework can support early diagnosis and predict evolution after treatment by providing customized simulation scenarios. Furthermore, a structured
[...] Read more.
This article explores the integration of Digital Twins in Systems and Predictive Medicine, focusing on eye diagnosis. By utilizing the Digital Twin models, the proposed framework can support early diagnosis and predict evolution after treatment by providing customized simulation scenarios. Furthermore, a structured architectural framework comprising five levels has been proposed, integrating Digital Twin, Systems Medicine, and Predictive Medicine for managing eye diseases. Based on demographic parameters, statistics were performed to identify potential correlations that may contribute to predispositions to glaucoma. With the aid of a dataset, a neural network was trained with the goal of identifying glaucoma. This comprehensive approach, based on statistical analysis and Machine Learning, is a promising method to enhance diagnostic accuracy and provide personalized treatment approaches.
Full article
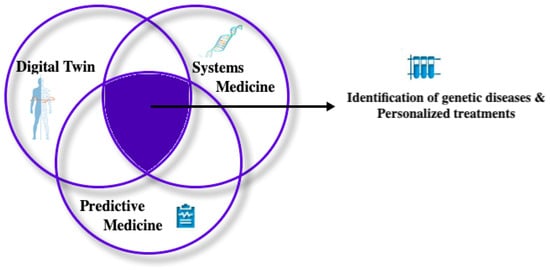
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Novel Cycloid-Type Rotor versus S-Type Rotor for Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine
by
José Eli Eduardo González-Durán, Juan Manuel Olivares-Ramírez, María Angélica Luján-Vega, Juan Emigdio Soto-Osornio, Juan Manuel García-Guendulain and Juvenal Rodriguez-Resendiz
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 54; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040054 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
The performance of a new vertical-axis wind turbine rotor based on the mathematical equation of the cycloid is analyzed and compared through simulation and experimental testing against a semicircular or S-type rotor, which is widely used. The study examines three cases: equalizing the
[...] Read more.
The performance of a new vertical-axis wind turbine rotor based on the mathematical equation of the cycloid is analyzed and compared through simulation and experimental testing against a semicircular or S-type rotor, which is widely used. The study examines three cases: equalizing the diameter, chord length and the area under the curve. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) was used to simulate these cases and evaluate moment, angular velocity and power. Experimental validation was carried out in a wind tunnel that was designed and optimized with the support of CFD. The rotors for all three cases were 3D printed in resin to analyze their experimental performance as a function of wind speed. The moment and Maximum Power Point (MPP) were determined in each case. The simulation results indicate that the cycloid-type rotor outperforms the semicircular or S-type rotor by 15%. Additionally, experimental evidence confirms that the cycloid-type rotor performs better in all three cases. In the MPP analysis, the cycloid-type rotor achieved an efficiency of 10.8% which was 38% better than the S-type rotor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Environmental Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
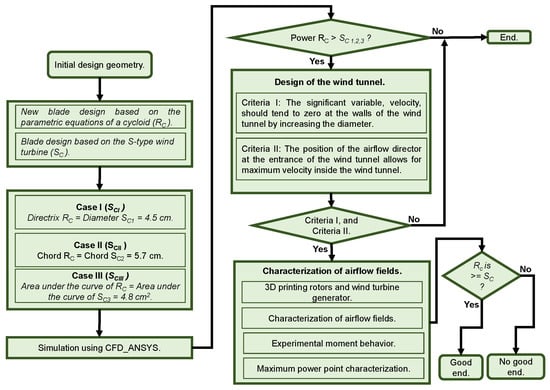
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Developing a Performance Evaluation Framework Structural Model for Educational Metaverse
by
Elena Tsappi, Ioannis Deliyannis and George Nathaniel Papageorgiou
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 53; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040053 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
In response to the transformative impact of digital technology on education, this study introduces a novel performance management framework for virtual learning environments suitable for the metaverse era. Based on the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) approach, this paper proposes a comprehensive evaluative model,
[...] Read more.
In response to the transformative impact of digital technology on education, this study introduces a novel performance management framework for virtual learning environments suitable for the metaverse era. Based on the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) approach, this paper proposes a comprehensive evaluative model, anchored on the integration of the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), and the Community of Inquiry Framework (CoI). The model synthesizes five Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)—content delivery, student engagement, metaverse tool utilization, student performance, and adaptability—to intricately assess academic avatar performances in virtual educational settings. This theoretical approach marks a significant stride in understanding and enhancing avatar efficacy in the metaverse environment. It enriches the discourse on performance management in digital education and sets a foundation for future empirical studies. As virtual online environments gain prominence in education and training, this research study establishes the basic principles and highlights the key points for further empirical research in the new era of the metaverse educational environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Theoretical and Applied Problems in Human-Computer Intelligent Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
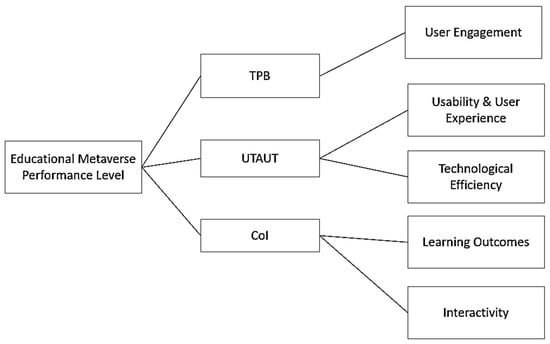
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comparison of Machine Learning-Based and Conventional Technologies for Video Compression
by
Lesia Mochurad
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 52; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040052 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The growing demand for high-quality video transmission over bandwidth-constrained networks and the increasing availability of video content have led to the need for efficient storage and distribution of large video files. To improve the latter, this article offers a comparison of six video
[...] Read more.
The growing demand for high-quality video transmission over bandwidth-constrained networks and the increasing availability of video content have led to the need for efficient storage and distribution of large video files. To improve the latter, this article offers a comparison of six video compression methods without loss of quality. Particularly, H.255, VP9, AV1, convolutional neural network (CNN), recurrent neural network (RNN), and deep autoencoder (DAE). The proposed decision is to use a dataset of high-quality videos to implement and compare the performance of classical compression algorithms and algorithms based on machine learning. Evaluations of the compression efficiency and the quality of the received images were made on the basis of two metrics: PSNR and SSIM. This comparison revealed the strengths and weaknesses of each approach and provided insights into how machine learning algorithms can be optimized in future research. In general, it contributed to the development of more efficient and effective video compression algorithms that can be useful for a wide range of applications.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Monitoring of Hip Joint Forces and Physical Activity after Total Hip Replacement by an Integrated Piezoelectric Element
by
Franziska Geiger, Henning Bathel, Sascha Spors, Rainer Bader and Daniel Kluess
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 51; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040051 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Resultant hip joint forces can currently only be recorded in situ in a laboratory setting using instrumented total hip replacements (THRs) equipped with strain gauges. However, permanent recording is important for monitoring the structural condition of the implant, for therapeutic purposes, for self-reflection,
[...] Read more.
Resultant hip joint forces can currently only be recorded in situ in a laboratory setting using instrumented total hip replacements (THRs) equipped with strain gauges. However, permanent recording is important for monitoring the structural condition of the implant, for therapeutic purposes, for self-reflection, and for research into managing the predicted increasing number of THRs worldwide. Therefore, this study aims to investigate whether a recently proposed THR with an integrated piezoelectric element represents a new possibility for the permanent recording of hip joint forces and the physical activities of the patient. Hip joint forces from nine different daily activities were obtained from the OrthoLoad database and applied to a total hip stem equipped with a piezoelectric element using a uniaxial testing machine. The forces acting on the piezoelectric element were calculated from the generated voltages. The correlation between the calculated forces on the piezoelectric element and the applied forces was investigated, and the regression equations were determined. In addition, the voltage outputs were used to predict the activity with a random forest classifier. The coefficient of determination between the applied maximum forces on the implant and the calculated maximum forces on the piezoelectric element was R2 = 0.97 (p < 0.01). The maximum forces on the THR could be determined via activity-independent determinations with a deviation of 2.49 ± 13.16% and activity-dependent calculation with 0.87 ± 7.28% deviation. The activities could be correctly predicted using the classification model with 95% accuracy. Hence, piezoelectric elements integrated into a total hip stem represent a promising sensor option for the energy-autonomous detection of joint forces and physical activities.
Full article
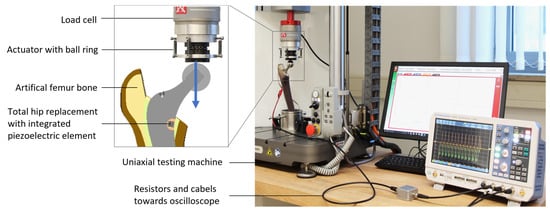
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Past, Present, and Future of New Applications in Utilization of Eddy Currents
by
Nestor O. Romero-Arismendi, Juan C. Olivares-Galvan, Jose L. Hernandez-Avila, Rafael Escarela-Perez, Victor M. Jimenez-Mondragon and Felipe Gonzalez-Montañez
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 50; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040050 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
Eddy currents are an electromagnetic phenomenon that represent an inexhaustible source of inspiration for technological innovations in the 21st century. Throughout history, these currents have been a subject of research and technological development in multiple fields. This article delves into the fascinating world
[...] Read more.
Eddy currents are an electromagnetic phenomenon that represent an inexhaustible source of inspiration for technological innovations in the 21st century. Throughout history, these currents have been a subject of research and technological development in multiple fields. This article delves into the fascinating world of eddy currents, revealing their physical foundations and highlighting their impact on a wide range of applications, ranging from non-destructive evaluation of materials to levitation phenomena, as well as their influence on fields as diverse as medicine, the automotive industry, and aerospace. The nature of eddy currents has stimulated the imaginations of scientists and engineers, driving the creation of revolutionary technologies that are transforming our society. As we progress through this article, we will cover the main aspects of eddy currents, their practical applications, and challenges for future works.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Electrical Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
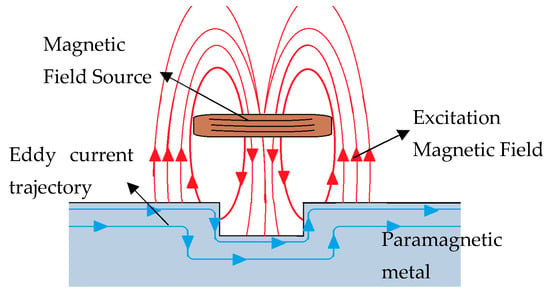
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Study of the Influence of the Structural Parameters on the Stress Dissipation of 3D Orthogonal Woven Composites under Low-Velocity Impact
by
Wang Xu, Mohammed Zikry and Abdel-Fattah M. Seyam
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 49; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040049 - 05 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study investigates the effects of the number of layers, x-yarn (weft) density, and z-yarn (binder) path on the mechanical behavior of E-glass 3D orthogonal woven (3DOW) composites during low-velocity impacts. Meso-level finite element (FE) models were developed and validated for 3DOW composites
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the effects of the number of layers, x-yarn (weft) density, and z-yarn (binder) path on the mechanical behavior of E-glass 3D orthogonal woven (3DOW) composites during low-velocity impacts. Meso-level finite element (FE) models were developed and validated for 3DOW composites with different yarn densities and z-yarn paths, providing analyses of stress distribution within reinforcement fibers and matrix, energy absorption, and failure time. Our findings revealed that lower x-yarn densities led to accumulations of stress concentrations. Furthermore, changing the z-yarn path, such as transitioning from plain weaves to twill or basket weaves had a noticeable impact on stress distributions. The research highlights the significance of designing more resilient 3DOW composites for impact applications by choosing appropriate parameters in weaving composite designs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Innovations in Materials Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
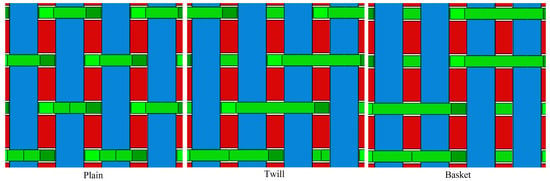
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Carbon Fiber Polymer Reinforced 3D Printed Composites for Centrifugal Pump Impeller Manufacturing
by
Gabriel Mansour, Vasileios Papageorgiou and Dimitrios Tzetzis
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 48; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040048 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
Centrifugal pumps are used extensively in various everyday applications. The occurrence of corrosion phenomena during operation often leads to the failure of a pump’s operating components, such as the impeller. The present research study examines the utilization of composite materials for fabricating centrifugal
[...] Read more.
Centrifugal pumps are used extensively in various everyday applications. The occurrence of corrosion phenomena during operation often leads to the failure of a pump’s operating components, such as the impeller. The present research study examines the utilization of composite materials for fabricating centrifugal pump components using additive manufacturing as an effort to fabricate corrosion resistant parts. To achieve the latter two nanocomposite materials, carbon fiber reinforced polyamide and carbon fiber reinforced polyphenylene sulfide were compared with two metal alloys, cast iron and brass, which are currently used in pump impeller manufacturing. The mechanical properties of the materials are extracted by performing a series of experiments, such as uniaxial tensile tests, nanoindentation and scanning electron microscope (SEM) examination of the specimen’s fracture area. Then, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis is performed using various impeller designs to determine the fluid pressure exerted on the impeller’s geometry during its operation. Finally, the maximum power rating of an impeller that can be made from such composites will be determined using a static finite element model (FEM). The FEM static model is developed by integrating the data collected from the experiments with the results obtained from the CFD analysis. The current research work shows that nanocomposites can potentially be used for developing impellers with rated power of up to 9.41 kW.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Manufacturing Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
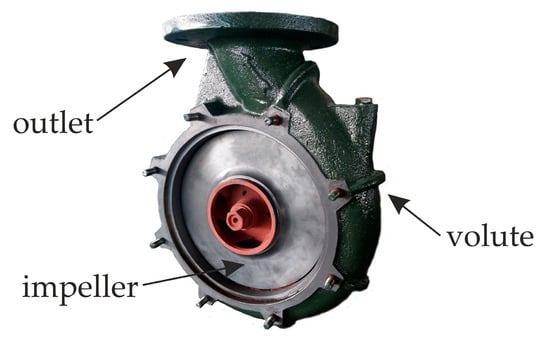
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact Localization for Haptic Input Devices Using Hybrid Laminates with Sensoric Function
by
René Schmidt, Alexander Graf, Ricardo Decker, Stephan Lede, Verena Kräusel, Lothar Kroll and Wolfram Hardt
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 47; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040047 - 01 Apr 2024
Abstract
The required energy savings can be achieved in all automotive domains through weight savings and the merging of manufacturing processes in production. This fact is taken into account through functional integration in lightweight materials and manufacturing in a process close to large-scale production.
[...] Read more.
The required energy savings can be achieved in all automotive domains through weight savings and the merging of manufacturing processes in production. This fact is taken into account through functional integration in lightweight materials and manufacturing in a process close to large-scale production. In previous work, separate steps of a process chain for manufacturing a center console cover utilizing a sensoric hybrid laminate have been developed and evaluated. This includes the process steps of joining, forming and inline polarization as well as connecting to an embedded system. This work continues the research process by evaluating impact localization methods to use the center console as a haptic input device. For this purpose, different deep learning methods are derived from the state of the art and analyzed for their applicability in two consecutive studies. The results show that MLPs, LSTMs, GRUs and CNNs are suitable to localize impacts on the novel laminate with high localization rates of up to 99%, and thus the usability of the developed laminate as a haptic input device has been proven.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Innovations in Materials Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
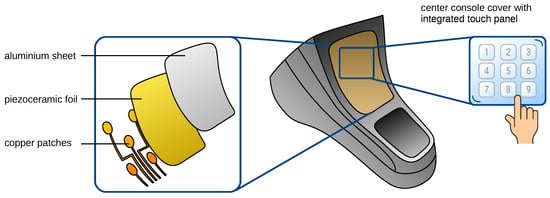
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Patient Care in Radiotherapy: Proof-of-Concept of a Monitoring Tool
by
Guillaume Beldjoudi, Rémi Eugène, Vincent Grégoire and Ronan Tanguy
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 46; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040046 - 29 Mar 2024
Abstract
Introduction: A monitoring tool, named Oncology Data Management (ODM), was developed in radiotherapy to generate structured information based on data contained in an Oncology Information System (OIS). This study presents the proof-of-concept of the ODM tool and highlights its applications to enhance patient
[...] Read more.
Introduction: A monitoring tool, named Oncology Data Management (ODM), was developed in radiotherapy to generate structured information based on data contained in an Oncology Information System (OIS). This study presents the proof-of-concept of the ODM tool and highlights its applications to enhance patient care in radiotherapy. Material & Methods: ODM is a sophisticated SQL query which extracts specific features from the Mosaiq OIS (Elekta, UK) database into an independent structured database. Data from 2016 to 2022 was extracted to enable monitoring of treatment units and evaluation of the quality of patient care. Results: A total of 25,259 treatments were extracted. Treatment machine monitoring revealed a daily 11-treatement difference between two units. ODM showed that the unit with fewer daily treatments performed more complex treatments on diverse locations. In 2019, the implementation of ODM led to the definition of quality indicators and in organizational changes that improved the quality of care. As consequences, for palliative treatments, there was an improvement in the proportion of treatments prepared within 7 calendar days between the scanner and the first treatment session (29.1% before 2020, 40.4% in 2020 and 46.4% after 2020). The study of fractionation in breast treatments exhibited decreased prescription variability after 2019, with distinct patient age categories. Bi-fractionation once a week for larynx prescriptions of 35 × 2.0 Gy achieved an overall treatment duration of 47.0 ± 3.0 calendar days in 2022. Conclusions: ODM enables data extraction from the OIS and provides quantitative tools for improving organization of a department and the quality of patient care in radiotherapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Smart Healthcare: Technologies and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
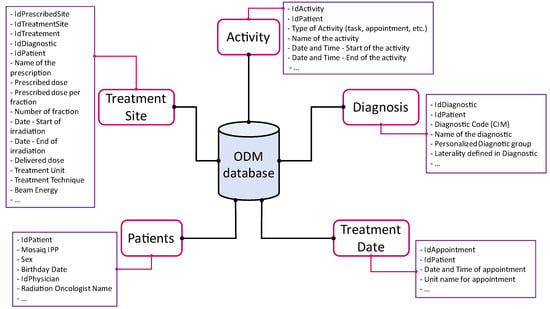
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm for Coordinated Scheduling of Production Jobs and Flexible Maintenance in Permutation Flowshops
by
Asma Ladj, Fatima Benbouzid-Si Tayeb, Alaeddine Dahamni and Mohamed Benbouzid
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 45; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040045 - 25 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This research work addresses the integrated scheduling of jobs and flexible (non-systematic) maintenance interventions in permutation flowshop production systems. We propose a coordinated model in which the time intervals between successive maintenance tasks as well as their number are assumed to be non-fixed
[...] Read more.
This research work addresses the integrated scheduling of jobs and flexible (non-systematic) maintenance interventions in permutation flowshop production systems. We propose a coordinated model in which the time intervals between successive maintenance tasks as well as their number are assumed to be non-fixed for each machine on the shopfloor. With such a flexible nature of maintenance activities, the resulting joint schedule is more practical and representative of real-world scenarios. Our goal is to determine the best job permutation in which flexible maintenance activities are properly incorporated. To tackle the NP-hard nature of this problem, an artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm is developed to minimize the total production time (Makespan). Experiments are conducted utilizing well-known Taillard’s benchmarks, enriched with maintenance data, to compare the proposed algorithm performance against the variable neighbourhood search (VNS) method from the literature. Computational results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in terms of both solution quality and computational times.
Full article
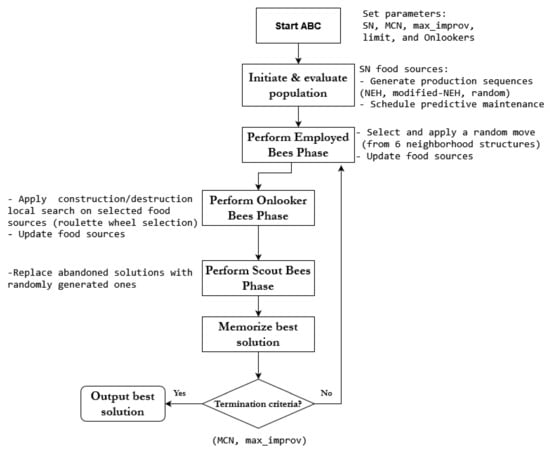
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Blood Pressure Measurement Device Accuracy Evaluation: Statistical Considerations with an Implementation in R
by
Tanvi Chandel, Victor Miranda, Andrew Lowe and Tet Chuan Lee
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 44; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040044 - 25 Mar 2024
Abstract
Inaccuracies from devices for non-invasive blood pressure measurements have been well reported with clinical consequences. International standards, such as ISO 81060-2 and the seminal AAMI/ANSI SP10, define protocols and acceptance criteria for these devices. Prior to applying these standards, a sample size of
[...] Read more.
Inaccuracies from devices for non-invasive blood pressure measurements have been well reported with clinical consequences. International standards, such as ISO 81060-2 and the seminal AAMI/ANSI SP10, define protocols and acceptance criteria for these devices. Prior to applying these standards, a sample size of N >= 85 is mandatory, that is, the number of distinct subcjects used to calculate device inaccuracies. Often, it is not possible to gather such a large sample. Many studies apply these standards with a smaller sample. The objective of the paper is to introduce a methodology that broadens the method first developed by the AAMI Sphygmomanometer Committee for accepting a blood pressure measurement device. We study changes in the acceptance region for various sample sizes using the sampling distribution for proportions and introduce a methodology for estimating the exact probability of the acceptance of a device. This enables the comparison of the accuracies of existing device development techniques even if they were studied with a smaller sample size. The study is useful in assisting BP measurement device manufacturers. To assist clinicians, we present a newly developed “bpAcc” package in R to evaluate acceptance statistics for various sample sizes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Future of Healthcare: Biomedical Technology and Integrated Artificial Intelligence)
►▼
Show Figures
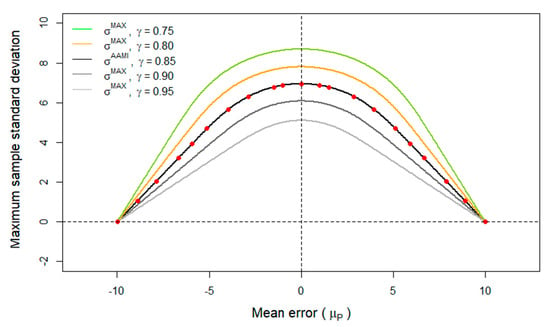
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Applied Deep Learning-Based Crop Yield Prediction: A Systematic Analysis of Current Developments and Potential Challenges
by
Khadija Meghraoui, Imane Sebari, Juergen Pilz, Kenza Ait El Kadi and Saloua Bensiali
Technologies 2024, 12(4), 43; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12040043 - 24 Mar 2024
Abstract
Agriculture is essential for global income, poverty reduction, and food security, with crop yield being a crucial measure in this field. Traditional crop yield prediction methods, reliant on subjective assessments such as farmers’ experiences, tend to be error-prone and lack precision across vast
[...] Read more.
Agriculture is essential for global income, poverty reduction, and food security, with crop yield being a crucial measure in this field. Traditional crop yield prediction methods, reliant on subjective assessments such as farmers’ experiences, tend to be error-prone and lack precision across vast farming areas, especially in data-scarce regions. Recent advancements in data collection, notably through high-resolution sensors and the use of deep learning (DL), have significantly increased the accuracy and breadth of agricultural data, providing better support for policymakers and administrators. In our study, we conduct a systematic literature review to explore the application of DL in crop yield forecasting, underscoring its growing significance in enhancing yield predictions. Our approach enabled us to identify 92 relevant studies across four major scientific databases: the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI), and ScienceDirect. These studies, all empirical research published in the last eight years, met stringent selection criteria, including empirical validity, methodological clarity, and a minimum quality score, ensuring their rigorous research standards and relevance. Our in-depth analysis of these papers aimed to synthesize insights on the crops studied, DL models utilized, key input data types, and the specific challenges and prerequisites for accurate DL-based yield forecasting. Our findings reveal that convolutional neural networks and Long Short-Term Memory are the dominant deep learning architectures in crop yield prediction, with a focus on cereals like wheat (Triticum aestivum) and corn (Zea mays). Many studies leverage satellite imagery, but there is a growing trend towards using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for data collection. Our review synthesizes global research, suggests future directions, and highlights key studies, acknowledging that results may vary across different databases and emphasizing the need for continual updates due to the evolving nature of the field.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Information and Communication Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
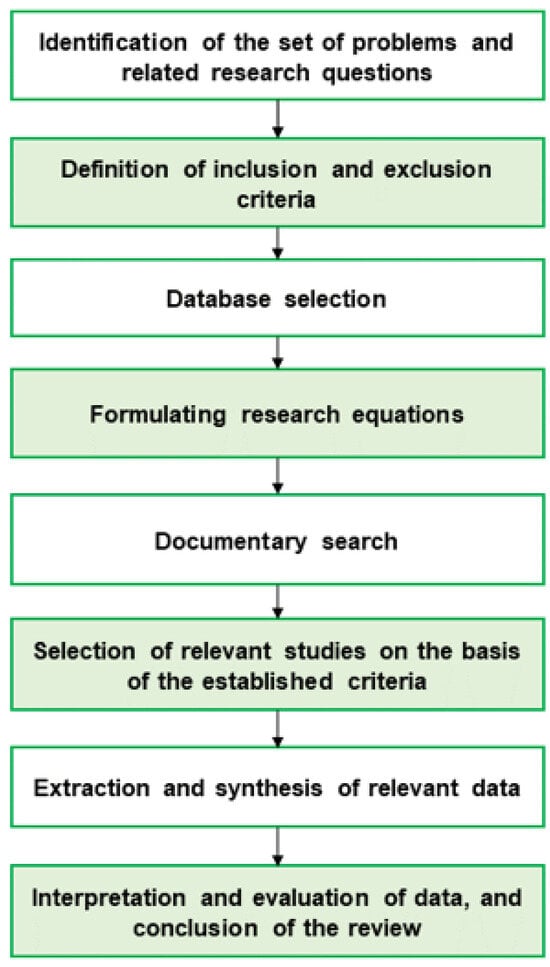
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Performance Assessment of Different Sustainable Energy Systems Using Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making Model and Self-Organizing Maps
by
Satyabrata Dash, Sujata Chakravarty, Nimay Chandra Giri, Umashankar Ghugar and Georgios Fotis
Technologies 2024, 12(3), 42; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12030042 - 19 Mar 2024
Abstract
The surging demand for electricity, propelled by the widespread adoption of intelligent grids and heightened consumer interaction with electricity demand and pricing, underscores the imperative for precise prognostication of optimal power plant utilization. To confront this challenge, a dataset centered on issue-centric power
[...] Read more.
The surging demand for electricity, propelled by the widespread adoption of intelligent grids and heightened consumer interaction with electricity demand and pricing, underscores the imperative for precise prognostication of optimal power plant utilization. To confront this challenge, a dataset centered on issue-centric power plans is meticulously crafted. This dataset encapsulates pivotal facets indispensable for attaining sustainable power generation, including meager gas emissions, installation cost, low maintenance cost, elevated power generation, and copious resource availability. The selection of an optimal power plant entails a multifaceted decision-making process, demanding a systematic approach. Our research advocates the amalgamation of multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) models with self-organizing maps to gauge the efficacy of diverse sustainable energy systems. The examination discerns solar energy as the preeminent MCDM criterion, securing the apex position with a score of 83.4%, attributable to its ample resource availability, considerable energy generation, nil greenhouse gas emissions, and commendable efficiency. Wind and hydroelectric power closely trail, registering scores of 75.3% and 74.5%, respectively, along with other energy sources. The analysis underscores the supremacy of the renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind, in fulfilling sustainability objectives and scrutinizing factors such as cost, resource availability, and the environmental impact. The proposed methodology empowers stakeholders to make judicious decisions, accentuating facets that are required for more sustainable and resilient power infrastructure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Electrical Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
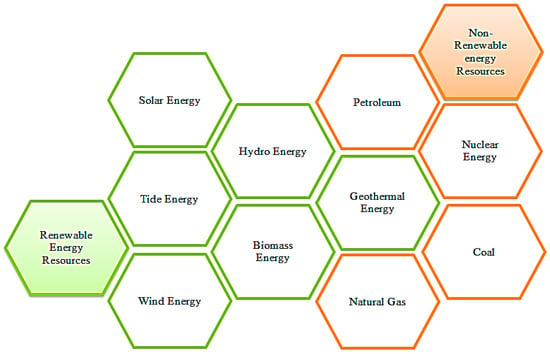
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Implementation of a Wireless Sensor Network for Environmental Measurements
by
Rosa M. Woo-García, José M. Pérez-Vista, Adrián Sánchez-Vidal, Agustín L. Herrera-May, Edith Osorio-de-la-Rosa, Felipe Caballero-Briones and Francisco López-Huerta
Technologies 2024, 12(3), 41; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12030041 - 16 Mar 2024
Abstract
Nowadays, the need to monitor different physical variables is constantly increasing and can be used in different applications, from humidity monitoring to disease detection in living beings, using a local or wireless sensor network (WSN). The Internet of Things has become a valuable
[...] Read more.
Nowadays, the need to monitor different physical variables is constantly increasing and can be used in different applications, from humidity monitoring to disease detection in living beings, using a local or wireless sensor network (WSN). The Internet of Things has become a valuable approach to climate monitoring, daily parcel monitoring, early disease detection, crop plant counting, and risk assessment. Herein, an autonomous energy wireless sensor network for monitoring environmental variables is proposed. The network’s tree topology configuration, which involves master and slave modules, is managed by microcontrollers embedded with sensors, constituting a key part of the WSN architecture. The system’s slave modules are equipped with sensors for temperature, humidity, gas, and light detection, along with a photovoltaic cell to energize the system, and a WiFi module for data transmission. The receiver incorporates a user interface and the necessary computing components for efficient data handling. In an open-field configuration, the transceiver range of the proposed system reaches up to 750 m per module. The advantages of this approach are its scalability, energy efficiency, and the system’s ability to provide real-time environmental monitoring over a large area, which is particularly beneficial for applications in precision agriculture and environmental management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Perpetual Sensor Nodes for Sustainable Wireless Network Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Applications of 3D Reconstruction in Virtual Reality-Based Teleoperation: A Review in the Mining Industry
by
Alireza Kamran-Pishhesari, Amin Moniri-Morad and Javad Sattarvand
Technologies 2024, 12(3), 40; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12030040 - 15 Mar 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Although multiview platforms have enhanced work efficiency in mining teleoperation systems, they also induce “cognitive tunneling” and depth-detection issues for operators. These issues inadvertently focus their attention on a restricted central view. Fully immersive virtual reality (VR) has recently attracted the attention of
[...] Read more.
Although multiview platforms have enhanced work efficiency in mining teleoperation systems, they also induce “cognitive tunneling” and depth-detection issues for operators. These issues inadvertently focus their attention on a restricted central view. Fully immersive virtual reality (VR) has recently attracted the attention of specialists in the mining industry to address these issues. Nevertheless, developing VR teleoperation systems remains a formidable challenge, particularly in achieving a realistic 3D model of the environment. This study investigates the existing gap in fully immersive teleoperation systems within the mining industry, aiming to identify the most optimal methods for their development and ensure operator’s safety. To achieve this purpose, a literature search is employed to identify and extract information from the most relevant sources. The most advanced teleoperation systems are examined by focusing on their visualization types. Then, various 3D reconstruction techniques applicable to mining VR teleoperation are investigated, and their data acquisition methods, sensor technologies, and algorithms are analyzed. Ultimately, the study discusses challenges associated with 3D reconstruction techniques for mining teleoperation. The findings demonstrated that the real-time 3D reconstruction of underground mining environments primarily involves depth-based techniques. In contrast, point cloud generation techniques can mostly be employed for 3D reconstruction in open-pit mining operations.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reinforcement-Learning-Based Virtual Inertia Controller for Frequency Support in Islanded Microgrids
by
Mohamed A. Afifi, Mostafa I. Marei and Ahmed M. I. Mohamad
Technologies 2024, 12(3), 39; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12030039 - 15 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As the world grapples with the energy crisis, integrating renewable energy sources into the power grid has become increasingly crucial. Microgrids have emerged as a vital solution to this challenge. However, the reliance on renewable energy sources in microgrids often leads to low
[...] Read more.
As the world grapples with the energy crisis, integrating renewable energy sources into the power grid has become increasingly crucial. Microgrids have emerged as a vital solution to this challenge. However, the reliance on renewable energy sources in microgrids often leads to low inertia. Renewable energy sources interfaced with the network through interlinking converters lack the inertia of conventional synchronous generators, and hence, need to provide frequency support through virtual inertia techniques. This paper presents a new control algorithm that utilizes the reinforcement learning agents Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3) and Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) to support the frequency in low-inertia microgrids. The RL agents are trained using the system-linearized model and then extended to the nonlinear model to reduce the computational burden. The proposed system consists of an AC–DC microgrid comprising a renewable energy source on the DC microgrid, along with constant and resistive loads. On the AC microgrid side, a synchronous generator is utilized to represent the low inertia of the grid, which is accompanied by dynamic and static loads. The model of the system is developed and verified using Matlab/Simulink and the reinforcement learning toolbox. The system performance with the proposed AI-based methods is compared to conventional low-pass and high-pass filter (LPF and HPF) controllers.
Full article
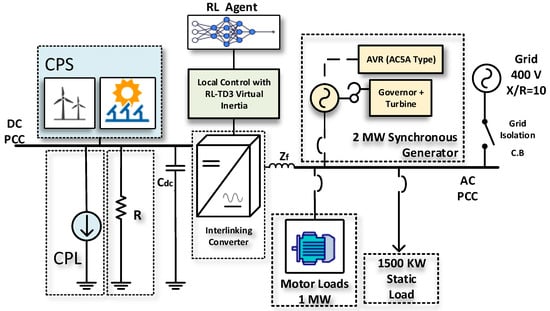
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Examining the Landscape of Cognitive Fatigue Detection: A Comprehensive Survey
by
Enamul Karim, Hamza Reza Pavel, Sama Nikanfar, Aref Hebri, Ayon Roy, Harish Ram Nambiappan, Ashish Jaiswal, Glenn R. Wylie and Fillia Makedon
Technologies 2024, 12(3), 38; https://0-doi-org.brum.beds.ac.uk/10.3390/technologies12030038 - 11 Mar 2024
Abstract
Cognitive fatigue, a state of reduced mental capacity arising from prolonged cognitive activity, poses significant challenges in various domains, from road safety to workplace productivity. Accurately detecting and mitigating cognitive fatigue is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and minimizing potential risks. This paper
[...] Read more.
Cognitive fatigue, a state of reduced mental capacity arising from prolonged cognitive activity, poses significant challenges in various domains, from road safety to workplace productivity. Accurately detecting and mitigating cognitive fatigue is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and minimizing potential risks. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the current landscape in cognitive fatigue detection. We systematically review various approaches, encompassing physiological, behavioral, and performance-based measures, for robust and objective fatigue detection. The paper further analyzes different challenges, including the lack of standardized ground truth and the need for context-aware fatigue assessment. This survey aims to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners seeking to understand and address the multifaceted challenge of cognitive fatigue detection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Selected Papers from the PETRA Conference Series)
►▼
Show Figures
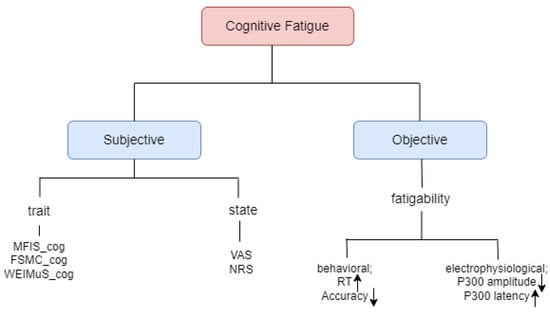
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Technologies Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
12 April 2024
Meet Us at the ISPRS TC I Mid-term Symposium on Intelligent Sensing and Remote Sensing Application (ISPRS 2024 TC I), 13–17 May 2024, Changsha, China
Meet Us at the ISPRS TC I Mid-term Symposium on Intelligent Sensing and Remote Sensing Application (ISPRS 2024 TC I), 13–17 May 2024, Changsha, China

7 April 2024
Meet Us at the 28th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences—Micro-Total Analysis Systems (µTAS 2024), 13–17 October 2024, Montréal, Canada
Meet Us at the 28th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences—Micro-Total Analysis Systems (µTAS 2024), 13–17 October 2024, Montréal, Canada

Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Future Internet, JCP, Sensors, Technologies
Cyber-Physical Security for IoT Systems
Topic Editors: Keping Yu, Chinmay ChakrabortyDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Photonics, Remote Sensing, Technologies
Emerging Terahertz Technologies for Integrated Sensing and Communication
Topic Editors: Jianjun Ma, Xiue Bao, Bin Li, Suman MukherjeeDeadline: 31 July 2024
Topic in
Electronics, Geomatics, Remote Sensing, Sensors, Smart Cities, Technologies
Smartphone Positioning, Navigation and Timing: Advances and Challenges
Topic Editors: Vincenzo Capuano, Alex Minetto, Fabio DovisDeadline: 31 August 2024
Topic in
Algorithms, Behavioral Sciences, Societies, Technologies
Getting Insight into How Different Chatbots Answer the Same Questions and How Reliable They Are
Topic Editors: Eugène Loos, Loredana IvanDeadline: 1 September 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Technologies
Smart Systems (SmaSys2023)
Guest Editors: Tomoya Higashihara, Sathish K. Sukumaran, Bungo Ochiai, Go MatsubaDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Technologies
3D Printing Technologies II
Guest Editor: Roberto BernasconiDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Technologies
IoT-Enabling Technologies and Applications
Guest Editor: Xavier FernandoDeadline: 20 July 2024
Special Issue in
Technologies
Perpetual Sensor Nodes for Sustainable Wireless Network Applications
Guest Editors: Johan Jair Estrada-López, Alejandro A. Castillo Atoche, Javier Vázquez-CastilloDeadline: 30 September 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Technologies
Selected Papers from the PETRA Conference Series
Collection Editor: Fillia Makedon
Topical Collection in
Technologies
Technology Advances on IoT Learning and Teaching
Collection Editors: Sergio Martin Gutiérrez, George F. Fragulis
Topical Collection in
Technologies
Review Papers Collection for Advanced Technologies
Collection Editor: Manoj Gupta
Topical Collection in
Technologies
Electrical Technologies
Collection Editors: Valeri Mladenov, Vasiliki Vita