Children and Adolescents’ Development: New Challenges and New Insights (Closed)
A topical collection in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (ISSN 1660-4601).
Viewed by 68868Editors
Interests: crime; adolescence; cyberbullying; victimization; school violence
Interests: social psychology; adolescents; violence; education
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
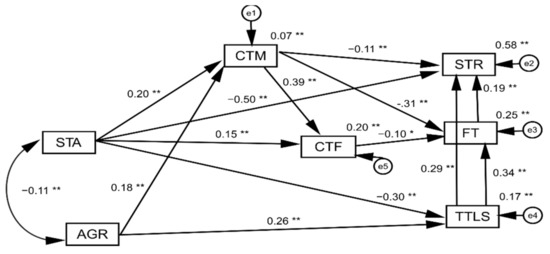
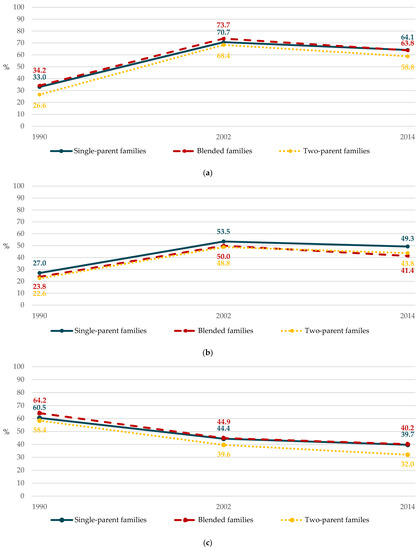
Social transformations have contributed to generating new transformations in children and adolescents’ development within the main socialization contexts: family, peers, school, and communities. For instance, the uses of the internet and social networking sites as communication tools have changed how they move quickly from the real world to the virtual world and vice versa. Consequently, maladjustment problems also show this continuity among online and offline scenarios. The growing complexity of our social reality is rapidly revealing new challenges in the lives of children, and all this challenges the influence of family, school, and community contexts.
On the other hand, these new challenges have become a subject of concern and interest from various fields, such as psychological, educational, social, health, and professional, in general, as well as from the research perspective in school and community contexts, especially during COVID-19, which has become one of the strongest stressors for children and adolescents. For this reason, a growing set of studies focused on children and adolescent new challenges are necessary for healthy development.
This Topical Collection, therefore, aims to provide ideas for psychologists and other professionals that will allow them to respond to the demands of social and educational institutions, in order to promote children and adolescents’ wellbeing.
This Topical Collection is open to high-quality contributions on the study of healthy development, especially those focused on children and adolescents and their socialization contexts. We invite authors to contribute research that addresses the influence of social determinants in adolescent adjustment and adaptation to this new environment.
Prof. Dr. Belén Martínez-Ferrer
Dr. Ana Romero-Abrio
Dr. Celeste León-Moreno
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Emotional adjustment
- Psychological adjustment
- Social networking sites
- Social media
- Adolescent health
- Children
- Adolescence
- High-Risk behavior
- Internet risks
- Adjustment